The field of accurate medicine is being revolutionized not by what we see in the bulk cells of a tumor, but by the subtle messages exchanged at the cellular frontier. Among theRead More…
Exosome Manufacturing: Scaling the Future of Advanced Therapies and Cosmeceuticals
The dawn of exosome-based medicine and next-generation cosmeceuticals has placed a monumental challenge before the biomanufacturing industry: scalability. Exosomes—those nanosized lipid-bilayer vesicles carrying potent biological cargo—are no longer just a research curiosity;Read More…
Exosomes: The Next Generation of Skincare—Research, Application, and Cosmeceutical Potential
As a PhD biologist with extensive experience navigating the intersection of cellular science and commercial development, I can confidently state that the cosmetic industry stands at the precipice of a paradigm shift.Read More…
LipidSync Exosomes: The Next Generation of Targeted Drug Delivery The Exosome Revolution: A New Frontier in Therapeutics
For decades, the pharmaceutical industry has been in pursuit of the perfect drug delivery system. One that is safe, efficient, and, most importantly, can precisely target a specific site in the body.Read More…
Exosome Cargo Loading: Strategies, Mechanisms, and Research Advances
Introduction Exosomes—nano-sized extracellular vesicles secreted by nearly all cell types—have emerged as promising delivery vehicles for therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Their inherent biocompatibility, stability in circulation, and ability to cross biological barriersRead More…
Exosomal Proteomic Detection: Advancing Biomarker Discovery and Molecular Diagnostics
Exosomes, the small extracellular vesicles secreted by various cell types, have emerged as critical players in intercellular communication and disease pathogenesis. Measuring 30–150 nm in diameter, these vesicles carry diverse molecular cargo,Read More…
Exosome Characterization: Unlocking the Potential of Nanoscale Messengers
Exosomes are small, membrane-bound vesicles ranging from 30 to 150 nanometers in diameter, secreted by nearly all living cells. These nanoscale structures carry a diverse array of biomolecules, including proteins, lipids, andRead More…
Scalable Exosome Manufacturing: Powering the Next Generation of Biomedical Innovations
Introduction: The Growing Need for Scalable Exosome Manufacturing Exosomes, small extracellular vesicles ranging from 30 to 150 nanometers, have gained significant traction in biomedical research and clinical development due to their remarkableRead More…
Exosome Isolation: Essential Techniques for Advancing Biomedical Research
Introduction: The Growing Importance of Exosome Research Almost every cell type secretes exosomes which are extracellular vesicles measuring between 30 and 150 nanometers in diameter. Exosomes perform essential roles in cellular interactionRead More…
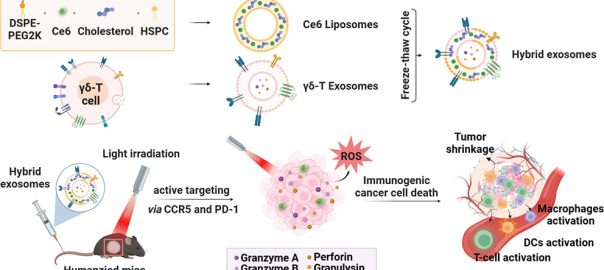
Photosensitive Hybrid γδ-T Exosomes for Targeted Cancer Photoimmunotherapy
Melanoma is one of the most aggressive types of skin cancer, characterized by rapid progression and a high metastasis rate, with a median survival of only 3 to 11 months. Current melanomaRead More…