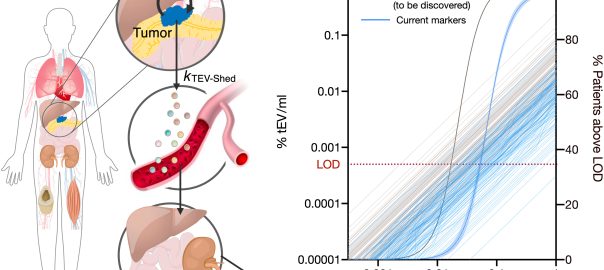
Tumor cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) are being explored as circulating biomarkers for cancer detection. However, the effectiveness of bulk measurement in enabling early cancer detection remains uncertain. Professor Ralph Weissleder’s team fromRead More…
Brown Adipose Tissue Excretes Damaged Mitochondria via EVs and is Cleared by Macrophages
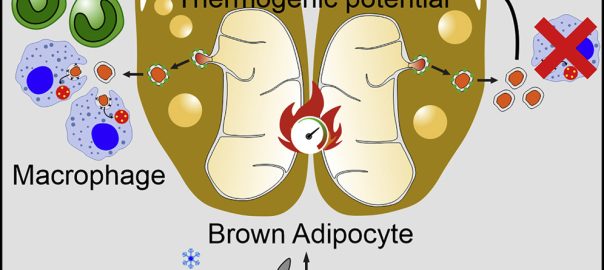
Recent findings has uncovered that mitochondria can be transferred between cells to control metabolic homeostasis. Although the mitochondria in brown adipocytes occupy a significant portion of the cell’s volume and undergo reorganizationRead More…
Multifunctional Magnetic Nanomaterials Facilitate Biomedical Applications of Extracellular Vesicles
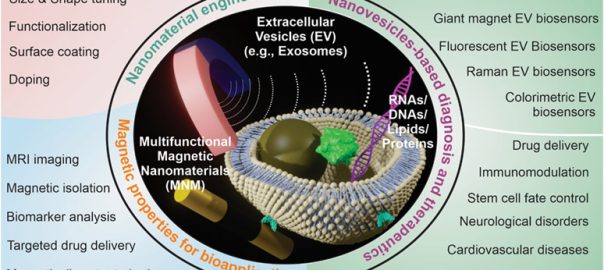
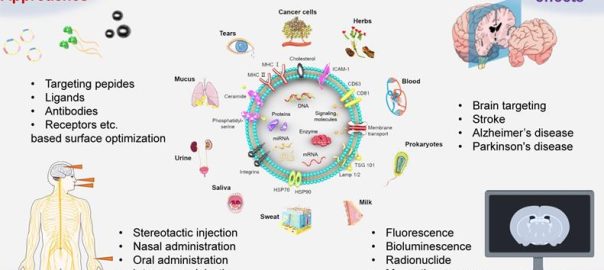
Extracellular vesicles(EVs), which carry various biomolecules such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids have rapidly become a promising platform for many biomedical applications. Despite their great potential, the heterogeneity in their surfaceRead More…
Emerging Prospects of Extracellular Vesicles for Brain Disease Theranostics
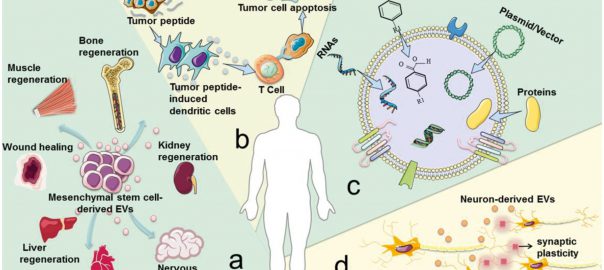
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanoscale, naturally derived vesicles that contain a variety of bioactive molecules reflecting their origin. These nanovesicles have a natural ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and exhibit excellentRead More…
Promoting or Inhibiting the Release of Extracellular Vesicles brings New Therapeutic Opportunities
Extracellular vesicles (EVs), released from various cell types under physiological and pathological conditions, are carriers of cell-to-cell communication. Recently, the Journal of Controlled Release published a review paper entitled ” Promotion orRead More…
The Link between Autophagy Inhibitors and Extracellular Vesicle Secretion and Its Challenges in Cancer Therapy
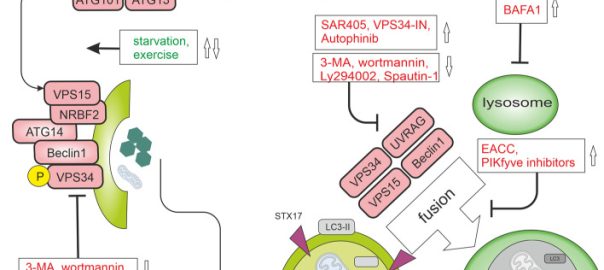
Autophagy mediates organelle and protein transport, cell quality control, and metabolism. However, this mechanism also controls the secretion of extracellular vesicles (EVs) through unconventional pathways, such as endosome-related secretory routes. Tumor cellsRead More…
Non-coding RNA and Extracellular Vesicles Help CAR-T Enhance the Efficacy of Solid Tumors
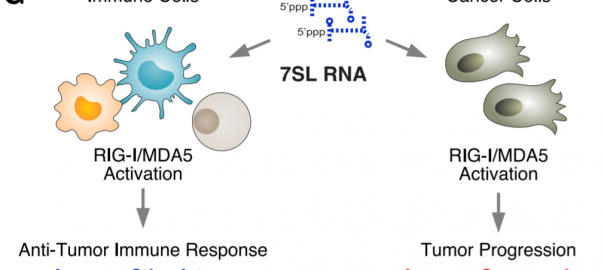
Poor tumor invasion, progression of exhaustion, and antigen insufficiency are common mechanisms that limit the efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells. Delivery of pattern recognition receptor agonists is a strategy toRead More…
Engineered Exosomes for the Treatment of Cerebrovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Exosomes have great therapeutic potential in cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases; however, their poor natural targeting ability significantly reduces their efficacy. In contrast, engineered exosomes possess active targeting capabilities for specific cell typesRead More…
Exosomes Deliver Gene Vectors for Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is a therapy that treats genetic diseases by introducing genetic material (such as the expression system of therapeutic proteins or editing tools to correct wrong genes in diseased cells). TheRead More…
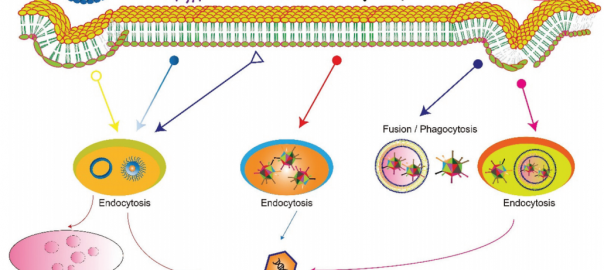
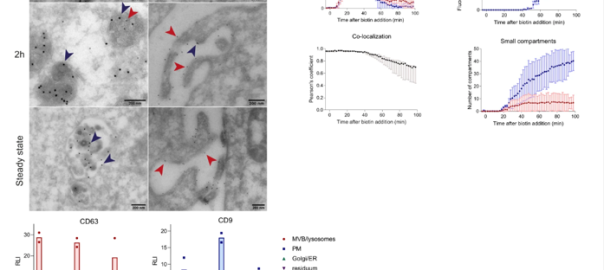
CD63: the Specific Marker Protein of Exosomes
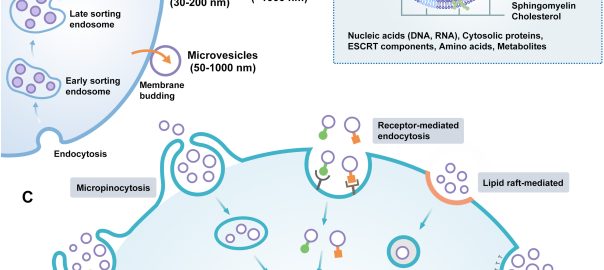
Although extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a role in intercellular communication, their various populations and secretion mechanisms have not been fully characterized. It remains unclear how and to what extent EVs form asRead More…