1.Rh Factor Discovery and Blood Compatibility: Why Monkey Blood Mimics Humans The Rh blood group system, a cornerstone of transfusion safety, was uncovered through experiments with rhesus monkey blood in the 1940s.Read More…
Monkey Body Fluids: Why They’re Still the Gold Standard in Medical Research
When it comes to understanding human diseases, scientists often turn to an unlikely hero: the body fluids of monkeys. Body fluids such as blood and cerebrospinal fluid as well as synovial fluid serveRead More…
Advancing Hepatology Research with Non-Human Primate Models
Introduction For many years, non-human primates (NHPs) have served as a key biological test bed because they are genetically and physiologically comparable to humans. At Creative Biolabs, we know how important NHP modelsRead More…
Immortalized Non-Human Primate (NHP) Cells: Applications in Modern Biomedical Research
Immortalized non-human primate (NHP) cell lines can be a goldmine in biomedical research, providing an affordable, predictable source of primate cells for a range of experiments. These cell lines come from NHPRead More…
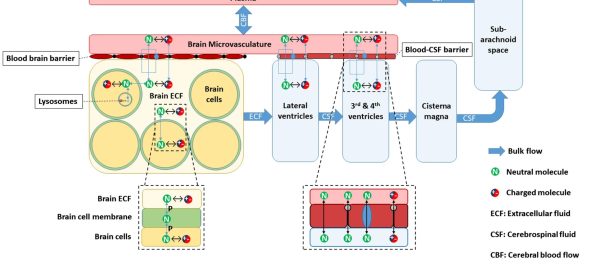
Non-Human Primate (NHP) Biologicals and Their Applications to CSF Research
The non-human primates (NHPs)—macaques, baboons, and chimpanzees—have always been biomedical subjects, with the same genes and bodies as us. Probably the most interesting NHP biology study in neuroscience concerns the chemistry of CSF. CSFRead More…
Non-Human Primate (NHP) Plasma: A Critical Tool in Biomedical Research
Non-human primate (NHP) plasma has become a cornerstone in biomedical research, driving breakthroughs across various fields. Species like macaques, baboons, and marmosets are crucial for research due to their close physiological similaritiesRead More…
Non-Human Primate Serum: A Crucial Resource for Biomedical Research
Non-human primate (NHP) serum is an indispensable tool for biomedical research, used extensively in various scientific applications, including immunology, virology, neuroscience, and metabolic studies. Obtained from the blood of primates such asRead More…
Exploring the Role of Cynomolgus Monkey PBMCs in Scientific Research
Introduction One of the most commonly-used nonhuman primate species, not only in toxicology but also other biomedical research fields, particularly neuroscience and infectious disease studies is Cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis), known as crab-eatingRead More…
The Latest Advances in Non-Human Primate Research: Insights and Implications
The field of non-human primate (NHP) research has seen remarkable advancements, particularly in genetics, neuroscience, and evolutionary biology. These developments not only enhance our understanding of primate biology but also provide valuableRead More…
Cynomolgus Monkey Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): A Key Biomaterial in Neuroscience and Drug Delivery Research
Cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis) are among the most widely used non-human primates in biomedical research, especially in experiments focused on cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This fluid is crucial for maintaining central nervous systemRead More…