Introduction
Vaccines have transformed public health, limiting infectious disease spread and saving millions of lives worldwide. mRNA vaccines, by which medical science developed a method of vaccination without losing effectiveness, have made it possible. We look at one scientific paper in this blog that provides a new approach to enhance COVID-19 vaccine performance against the new SARS-CoV-2 strains. Let’s delve into the study’s findings and discuss how Creative Biolabs is contributing to the future of vaccine development.
The mRNA Vaccine Revolution
mRNA vaccines changed immunology. Unlike traditional vaccines that rely on weakened or inactivated viruses, mRNA vaccines instruct cells to generate a particular viral protein, which initiates an immune reaction but does not spread the disease. This technology has been at the forefront of accelerated COVID-19 vaccine development and delivery, with Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna at the forefront. Yet the rise of variants of SARS-CoV-2 has made it urgent to have vaccines that can manage these genetic shifts and offer wider protection.
The Breakthrough: T-Cell-Activating Antigens from mRNA
A new report in Nature Communications proposes a new method for building COVID-19 vaccines. They derived an mRNA-derived T-cell activating antigen, bound to lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), that targets pockets of the SARS-CoV-2 proteome enriched in human HLA-I epitopes (HLA-EPs). These areas are highly conserved between SARS-CoV-2 strains and so perfect targets for a broad-spectrum protection vaccine.
Methodology and Key Findings
They used the latest bioinformatics methods to calculate epitopes for 78 common HLA-I alleles from the SARS-CoV-2 proteome. They found four fragments that had the most number of effective epitopes and chose three HLA-I epitope-rich peptides from nonstructural proteins to investigate further. These peptides were immunogenic and stimulated human cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs).
In animal models, double immunization with LNP-formulated mRNAs encoding HLA-EPs and the receptor-binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.351 variant (RBDβ) outperformed single immunization with LNP-RBDβ. This dual strategy not only enhanced the humoral immune response but also significantly improved the cellular immune response, including elevated interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) production and CD8+ T-cell activation.
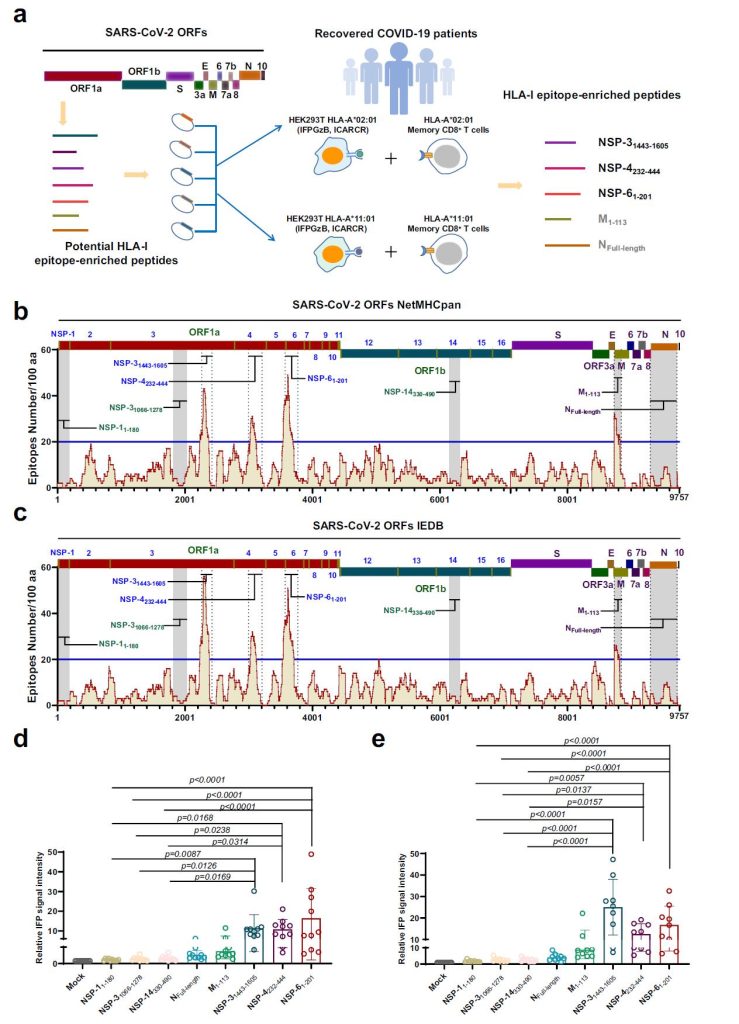
Fig. 1 Identification of HLA-I epitope-enriched peptides that activate CD8+ T lymphocytes from convalescent COVID-19 patients.1
Implications for Vaccine Design
This study highlights a promising approach for next-generation COVID-19 vaccines. The combination of HLA-EPs and RBD antigens as the two immunization protocols is an idea for next-generation COVID-19 vaccines. That might even be extended to cover more vulnerable variants against new ones, circumventing the immune escape problem that plagues vaccines today. By inducing humoral and cellular immunity, this approach is designed to build a stronger and more durable defense against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants.
Vaccine Development at Creative Biolabs.
Creative Biolabs is a leader in the innovation of vaccine technologies with a range of vaccine design and manufacturing services. We combine old methods with the most advanced genetic engineering technologies to create highly immunogenic vaccines for life-saving medical applications. Our services include:
- Vaccine Development: With our knowledge of immunology and molecular biology, we develop vaccines that pinpoint pathogens. Our scientists consult with clients directly on their specific needs and build bespoke vaccine solutions.
- Manufacturing Services: Our manufacturing services ensure that the vaccines are manufactured in state-of-the-art factories that are 100% safe and effective. Our manufacturing facilities comply with the requirements of regulatory bodies, so our clients can have full confidence in the products we produce.
- Preclinical and Clinical Care: We are there throughout the vaccine development process, from preclinical to clinical. We advise and support clients through the regulatory process from the lab to the market.
The Science Behind mRNA Vaccines
mRNA vaccines cause the immune system to respond by commanding cells to secrete a specific viral protein. This is a radical change from older vaccines that tend to induce immunity using killed or weakened viruses. The benefit of mRNA vaccines is that they can be made faster and targeted at particular viral proteins, which means they’re highly tolerant of novel viral strains.
It’s the lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) that transmit the mRNA that are crucial to the vaccine. They keep the mRNA intact from degradation and get it into cells. The mRNA gets translated inside the cell and then arranged onto the cell’s surface to activate the immune system.
T-Cells and Their Role in Immunity
T-cells are vital for combating viral infections, and identifying and eliminating infected cells to prevent viral replication and spread. T-cell activation is a central part of the immune response, and having a strong T-cell response is a characteristic of a vaccine.
Its treatment of T-cell-induced antigens is important because it fills a void in the existing vaccine pipeline. If most vaccines target the generation of neutralizing antibodies, T-cell-inducing antigens could amplify the immune response. This is especially true for SARS-CoV-2 strains, which can even partially avoid antibody protection.
The Path Forward: Combating Variants
The spread of SARS-CoV-2 strains has been a big threat in the COVID-19 fight. Such mutants can bypass immunity generated by current vaccines and trigger breakthrough infections. This is a problem the dual immunization strategy proposed in the study would solve with broad protection against multiple variants.
Since the vaccine can hit protected areas of the virus, the vaccine remains potent even when the virus changes. This is essential for vaccines to evolve with the ever-evolving viral landscape. Any vaccine program needs to be able to adjust to the new variants, and long-term success requires this.
Conclusion
Vaccines of the future must combine new technologies with knowledge of immune responses. The mRNA T-cell-inducer antigen discovery opens up new avenues for vaccine design, and Creative Biolabs is on track to take the science to the clinic. As we fight the epidemics and threats, we’re committed to making vaccine technology even better.
The Importance of Continued Research
In the near future, research and development of vaccine technology will be a key step. The work on mRNA-based T-cell-provocative antigens is not the only promising frontier being pursued. By investing in research, we can be ready to deal with the next affliction and come up with vaccines that work on a diverse range of germs.
The Power of Collaboration
It is only by working together between scientists, clinicians, and industry that a vaccine can become effective. Creative Biolabs knows the value of teamwork and works hard with partners to create cutting-edge solutions. If we do, we can both survive the new diseases and have a healthier world for the next generation. Here’s an overview of our core service offerings:
- Vaccine Design: We offer pathogen-based and target-based vaccine design, utilizing database and in silico models for epitope identification and immunogenicity prediction, along with data analysis and consulting services.
- Adjuvant Selection: Our services include adjuvant candidate identification by PRR ligands scanning, coupled with custom adjuvant synthesis.
- Analytical Development & Qualification: We conduct a variety of tests, including identity, purity, microbial, and potency testing, using chromatographic, electrophoresis, and immunological testing methods.
- Vaccine Preclinical Assessment: Our comprehensive assessment includes immunization-challenge tests, serological analyses, and T cell response assays.
- Vaccine Formulation Development: We specialize in formulation optimization, adjuvant development, and delivery system selection.
The Promise of mRNA Technology
mRNA is also a great option for future vaccines. Because it is so quickly adaptable to new viruses and it can activate both humoral and cellular immune systems, it becomes an effective weapon against infectious diseases. In the coming years, as we perfect and develop this technology, we will have vaccines that are even more efficient, easier to obtain, and more individualized.
The Role of Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs aims to break the limits of vaccine development. Our scientists are always trying new technologies and approaches to enhance the effectiveness and safety of vaccines. Our focus is on working with our partners to produce vaccines of the highest quality and innovation.
The Impact on Global Health
Effective vaccines change the health of the world. Vaccines prevent the transmission of infectious diseases, which saves lives and saves healthcare resources. It is the work of Creative Biolabs and international researchers like them that will make it possible for us to continue defending global health against a changing landscape.
The Journey Ahead
The search for good vaccines for SARS-CoV-2 and variants isn’t done. There has been great progress but much more remains. mRNA-based T-cell-inducing antigens are a promising direction and we can’t wait to see what this work will lead to in practice.
Our advocates ask the scientific community, industry, and policymakers to continue to support vaccine technology research and development. Collectively, we can be well prepared for emerging diseases, and we can make vaccines that offer general and long-term protection.
The Healthier Future on a Clearer Screen
Creative Biolabs wants to end infectious diseases from being a problem for world health. We will dedicate our knowledge and resources to creating vaccines that enable this dream to become a reality. Let’s go on this journey with us and make the world a better place.
Reference:
- Tai, W., Feng, S., Chai, B. et al.An mRNA-based T-cell-inducing antigen strengthens COVID-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat Commun 14, 2962 (2023).
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
