All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
The Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) consists of several integral parts that bridge antigen recognition to T cell signaling, driving T cell activation following ligation of the CAR. The structure of a second-generation CAR includes an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain. The T cell activation domain and co-stimulatory domain are located within the intracellular domain. The co-stimulatory domain is crucial for T cell expansion, IL-2 production, evasion of T cell anergy, and apoptosis. The choice of co-stimulatory domain in CAR design can impact T cell differentiation, persistence, anti-tumor response kinetics, and toxicity profiles. Different co-stimulatory molecules may result in varying therapeutic outcomes. Ongoing research focuses on exploring novel co-stimulatory molecules, combinations of multiple co-stimulatory domains, and understanding the crosstalk between CAR-driven and endogenous co-stimulatory pathways to enhance CAR-T cell therapy efficacy.
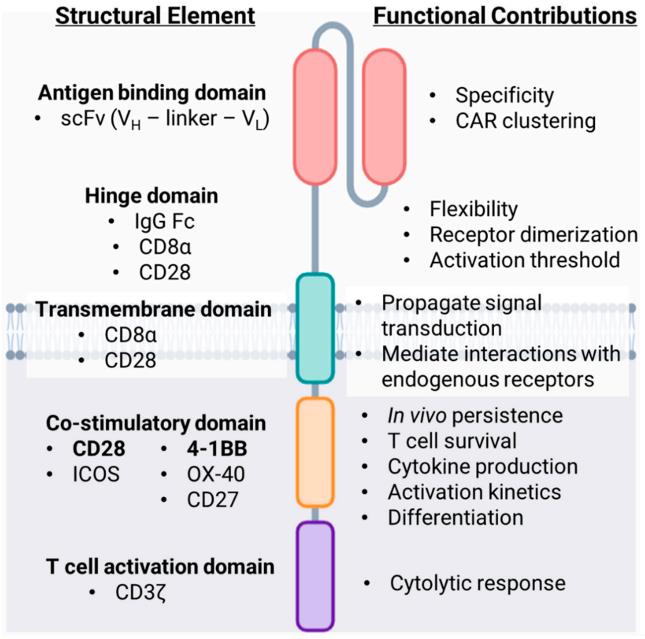 Fig 1. The structure of a second-generation CAR.1
Fig 1. The structure of a second-generation CAR.1
In traditional CAR-T cells, the intracellular domain contains signaling 1 and signaling 2 domains, which activate the T cell receptor (TCR) and co-stimulatory pathways of the T cell, respectively. Signal 1 is delivered primarily by the intracellular domain of the CAR and activates the proliferation and killing of T cells. Traditional CAR-T cells contain only one CAR structure, which is responsible for recognizing tumor cells and delivering signal 1.
In co-stim CAR-T cells, the natural TCR (T-cell receptor) is retained. In addition to the CAR structure, the natural TCR recognizes and transmits Signal 1, while the co-stimulatory CAR structure is introduced, which transmits Signal 2. Signal 1 is mainly transmitted by the intracellular domain of the TCR, while signal 2 is mainly transmitted by the intracellular domain of the co-stimulatory CAR. Co-stimulation of CAR-T cells can activate the proliferation and killing functions of T cells at the same time, as well as enhance the anti-tumor effect.
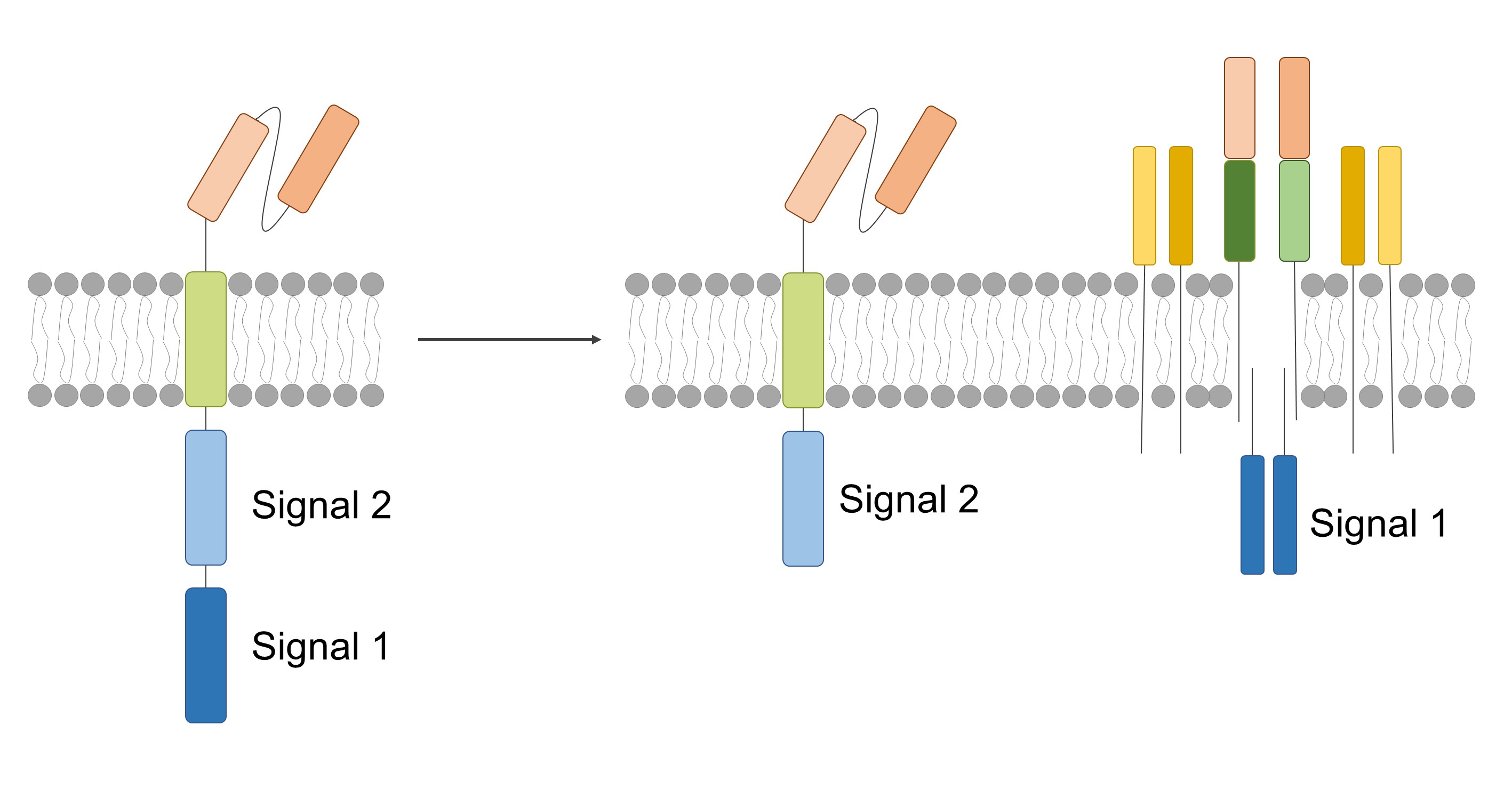
By preserving the natural TCR and introducing a co-stimulatory CAR, co-stim CAR-T cells can recognize and kill tumor cells more efficiently with fewer side effects.
Co-stim CAR has broad application prospects and is expected to become an important weapon in the field of cancer treatment in the future. Creative Biolabs is dedicated to helping researchers design more effective CAR-T cells. Please feel free to contact us.
Reference
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION