On February 4, 2022, Sanofi announced that its complement C1s antibody Sutimlimab was approved by the FDA for the treatment of cold agglutinin disease (CAD) under the trade name Enjaymo. Sutimlimab is the second antibody drug approved by the FDA this year, following Roche’s VEGF/Ang2 bispecific antibody Faricimab approved just a few days ago.
On November 14, 2020, the marketing application of Sanofi’s C1s antibody Sutimlimab for the treatment of CAD received a complete response letter (CRL) from the FDA, which mainly focuses on the production defects in third-party manufacturers, without concerns for clinical or safety issues. After more than a year, Sutimlimab was finally approved by the FDA.
C1s is a component of the complement C1 complex and the starting molecule of the classical complement pathway. Usually, the immune complex binds to C1q, thereby activating C1r.
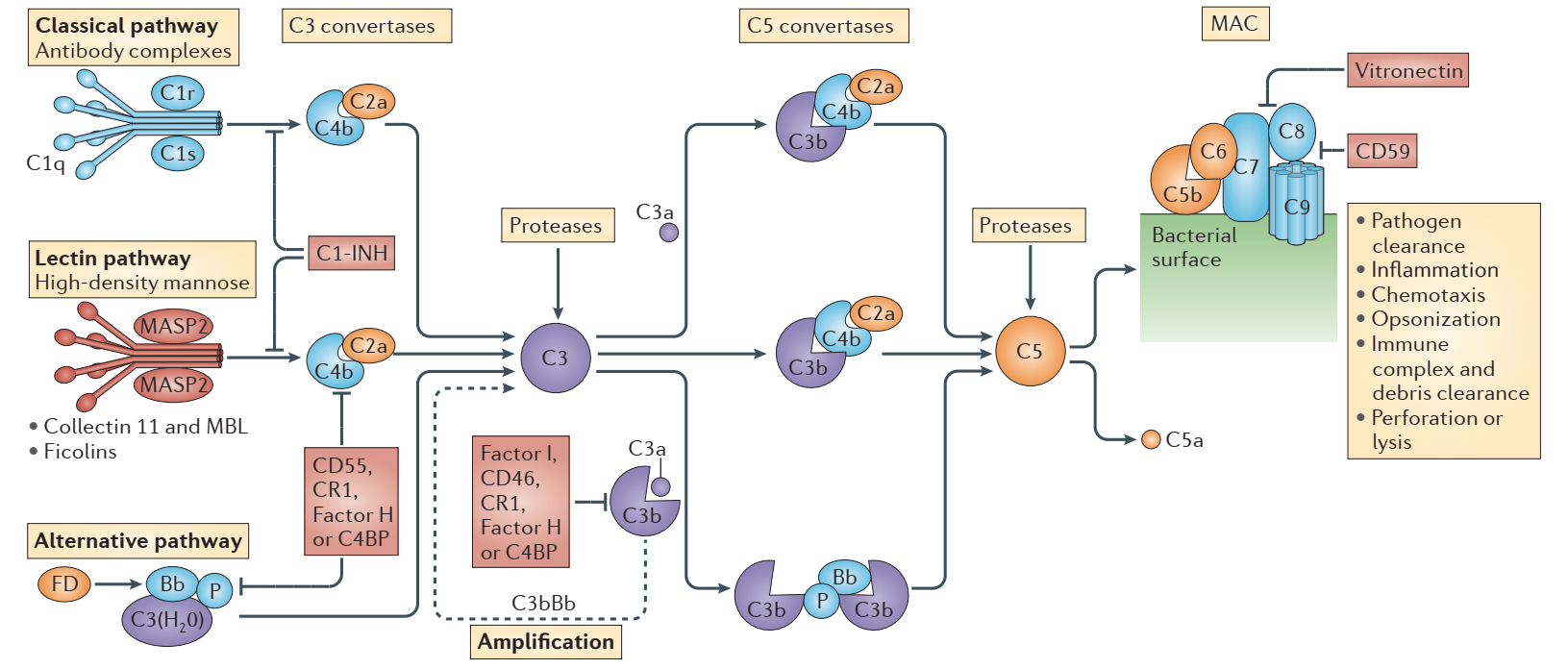
(Martin Kolev et al., Nature Reviews Immunology, 2014)
CAD is a rare disease with a total of about 10,000 patients in the United States, Europe, and Japan. In terms of pathogenesis, immunoglobulins (more than 90% of which are IgM) will be abnormally deposited on red blood cells in patients in an environment below 31 °C. IgM immune complexes can strongly activate complement to attack red blood cells, thereby leading to anemia. The mechanism of action of Sutimlimab is to block the activation of the classical pathway of complement to avoid damage to red blood cells.
A total of 24 patients were enrolled in the Phase III CARDINAL clinical trial of Sutimlimab, of which 2 patients withdrew for reasons unrelated to treatment. The primary endpoint was a 2 g/dL increase in hemoglobin or a response rate with a hemoglobin ≥12 g/dL after 26 weeks of treatment. The study showed that 54% (n=13) of patients met the composite endpoint, and 62.5% (n=15) had a hemoglobin higher than 12 g/dL.
Summary
Complement-targeting drugs have achieved significant progresses in recent years. In addition to Alexion’s C5 antibodies Soliris and Ultomiris, Apellis’ C3 inhibitor APL-2 and Chemocentryx’s C5aR inhibitor Avacopan have successively been approved by the FDA. In December 2020, AstraZeneca acquired Alexion for $39 billion. Complement-targeting drugs are gaining traction globally.
