Creative Biolabs is a well-known expert in the field of antibody discovery and development. To support the development of in vitro diagnostic (IVD) tools, we offer high-quality IVD antibody development services to global clients based on our advanced technology platforms. Our services target many potential or validated diagnostic markers of a variety of diseases. Here, we focus on the Fli-1 marker of renal cancer.
Fli-1 Introduction
Fli-1 (Friend leukemia virus integration 1 or Friend leukemia virus-induced erythroleukemia-1 also known as ERGB) was first found in 1990 and initially identified as a proto-oncogene due to its presence near a common site for retroviral integration in Friend virus-induced erythroleukemias. Both the mouse and human Fli-1 genes are approximately 120 kb that contain nine exons and encode two protein isoforms of p51 (452 aa) and p48 (419 aa). This gene is located on mouse chromosome 9 and in humans mapped to the chromosome 11q24.3, a region of several abnormalities in human disease, with a processed mRNA transcript length of 1359 bp. The transcription factor Fli-1 belongs to a member of the ETS transcription factor family and defined by a highly conserved DNA-binding domain. And the EST family shares the ETS domain which is a DNA binding domain and responsible for sequence-specific DNA recognition on target promoters. In adults, Fli-1 is highly expressed in hematopoietic tissues and vascular endothelial cells, with lower levels detected in heart, lung, and ovary.
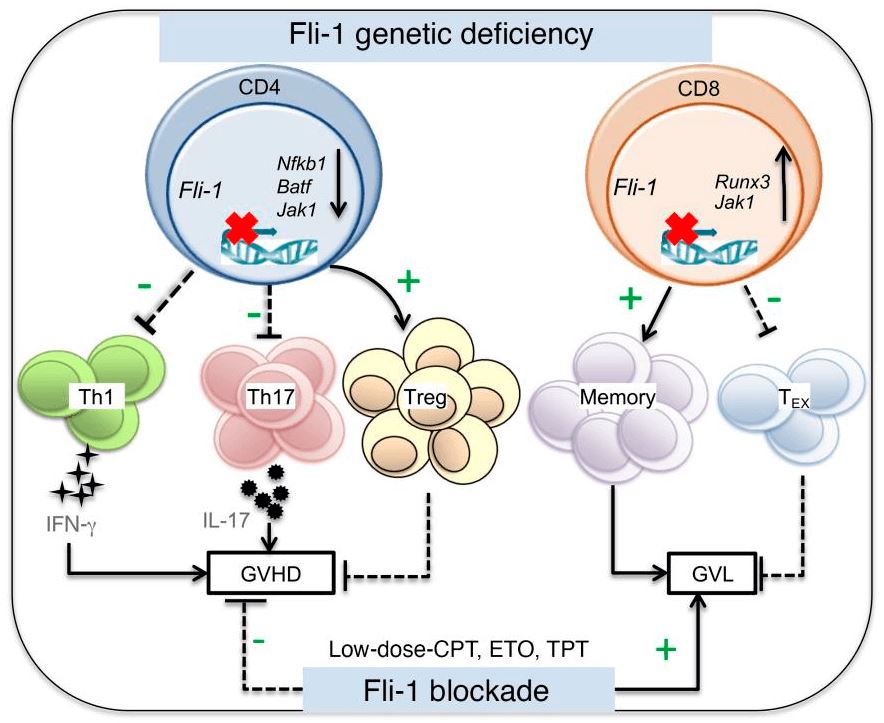 Fig.1 Fli-1 regulates T cell immunity and tolerance in graft-versus-host disease.1
Fig.1 Fli-1 regulates T cell immunity and tolerance in graft-versus-host disease.1
Fli-1 has since been recognized to play an important part in normal development, homeostasis as well as tumorigenesis, functioning as a transcriptional activator and repressor. For instance, it transcriptionally regulates genes that drive body's hematopoiesis and vasculogenesis. Meanwhile, Fli-1 is indeed one of the key regulators of hematopoietic stem cell maintenance and differentiation. The clinical role of Fli-1 is most apparent in the human Ewing sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor (ES/PNET) category, wherein Fli-1 undergoes a t(11;22)(q24;q12) translocation with the Ewing sarcoma gene on chromosome 22 which results in the production of EWS/FLI-1 fusion genes. Fli-1 has also been identified as a target of the characteristic balanced chromosomal translocation associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemias on t(4;11)(q21;q23) translocation.
Fli-1 and Diseases
Fli-1 is both disease-related gene and cancer-related gene. The disease associated with Fli-1 includes Ewing sarcoma, bleeding disorder, platelet-type and so on. Among their related pathways are transcriptional misregulation in cancer and NF-kappaB signaling. Specifically, abnormal expression of Fli-1 underlies some virally induced leukemias, such as Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia and various types of human cancers. The aberrant Fli-1 level is essential in the etiology of autoimmunity diseases including systemic sclerosis (SSc) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Furthermore, Fli-1 is linked to the acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) by chromosomal events at the Fli locus, but its biologic impact is not clear. There is evidence showing that abnormal expression of the Fli-1 protein is an adverse prognostic factor in AML. Such studies establish Fli-1 as a strong and promising candidate for drug development.
Deregulated expression of ETS proteins is connected with aberrant development and malignant transformation. Aberrant expression of Fli-1strongly relates to the progression of malignant melanoma. Limited attention has been devoted to elucidating the effect of Fli-1 on epithelial-derived cancers. Fli-1 mRNA and protein levels are decreased in human breast cancer, and Fli-1 mRNA expression is declined in the small sample of primary breast tumors. The oncogenic functions of Fli-1 over-expression in erythrocytes are considered to arise from the downstream effects of altered gene transcription. Fli-1 is also testified to activate or inactivate a wide range of genes that may facilitate oncogenesis, such as GADD153, BCL-2, Tenascin-C, MDM2, GATA-1, and RB.
Fli-1 and Renal Cancer
Fli-1 generally participates in the regulation of cell growth and differentiation. The report appears that scientists generated a number of transgenic mice that over-express Fli-1 in varieties of mouse tissues. And there are the highest expressions of Fli-1 protein in the thymus and spleen of these animals. The transgenic mice gradually developed a high incidence of a progressive immunological renal disease and finally died of renal failure. Cumulative research shows the incidence of renal disease correlates with the level of Fli-1 protein in lymphoid tissues of transgenic lines. Additionally, the detection of autoantibodies in the serum of Fli-1 transgenic mice suggests the involvement of an immune dysfunction in the pathogenesis of the renal disease.
IVD Antibody Development Service for Fli-1 Marker
Renal cancer is a disease in which kidney cells grow out of control and then become malignant, forming a carcinoma. Tumor cells are positive for Fli-1, hence confirming the diagnosis of the primary renal primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Since Fli-1 is a potential marker for renal cancer diagnosis, Creative Biolabs offers customized antibody development services targeting this marker. Further, we offer IVD immunoassay development services by providing feasibility analysis, assay design, assay protocol establishment, parameter optimization, validation, and production services. We can start from scratch if you do not have available antibodies or antibody pairs.
If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details.
Reference
- Schutt, Steven D., et al. "The druggable transcription factor Fli-1 regulates T cell immunity and tolerance in graft-versus-host disease." The Journal of Clinical Investigation 132.21 (2022). Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.

