Creative Biolabs is a leading CRO in the development of high-quality antibodies against different antigens and serological biomarkers that are used for in vitro diagnosis of parainfluenza infections of the respiratory system. Especially, we offer customized in vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibody development services targeting Parainfluenza. Our combined knowledge and expertise guarantee that premium solutions will be provided to our customers.
Introduction of Parainfluenza
Parainfluenza refers to a group of viruses called human parainfluenza viruses (HPIVs). There are four distinct single-stranded RNA viruses in this group: HPIV-1, HPIV-2, HPIV-3, and HPIV-4. The HPIV genome contains approximately 15,000 nucleotides. These are organized to encode at least six common structural proteins (3’-N-P-C-M-F-HN-L-5’). All forms of HPIV cause an infection in either the upper or lower respiratory area of a person’s body. The diagnosis of HPIVs utilizes a range of techniques including isolation and detection of the virus in culture, detection of viral antigens directly within bodily respiratory tract secretions, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), serological testing, etc.
 Fig.1 Activation of NK, dendritic cells and soluble molecules during virus infection. (Manjarrezzavala, M. E., 2013)
Fig.1 Activation of NK, dendritic cells and soluble molecules during virus infection. (Manjarrezzavala, M. E., 2013)
HPIV Antigen Detection Assay
This assay directly detects viral antigens through the binding of specific antibodies. As many useful antigens can be produced with the whole virus and chemically or physically disrupted HPIV, polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies can be generated accordingly. For instance, the intranasal inoculation of the whole virus into guinea pigs produces hyperimmune serum that works well in standard serologic tests. Besides, monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) have been produced to all four major serotypes of HPIV and are commercially available. These serologic reagents can be used for virus detection in ELISA, immunofluorescence (IF) assays, hemagglutinin inhibition (HI), hemadsorption inhibition (HAdI), complement fixation, Western blotting, radioimmunoprecipitation, and neutralization assays. HPIV antigen detection using a modification of the ELISA technique (time-resolved fluorometry) is reported to be more sensitive than standard ELISA. However, the fact is that HPIV antigenic variation is occurring steadily and many MAbs no longer bind and/or function in HI or neutralization assays. As a result, assays utilizing MAbs in the future need to routinely contain multiple different antibodies for maximum sensitivity.
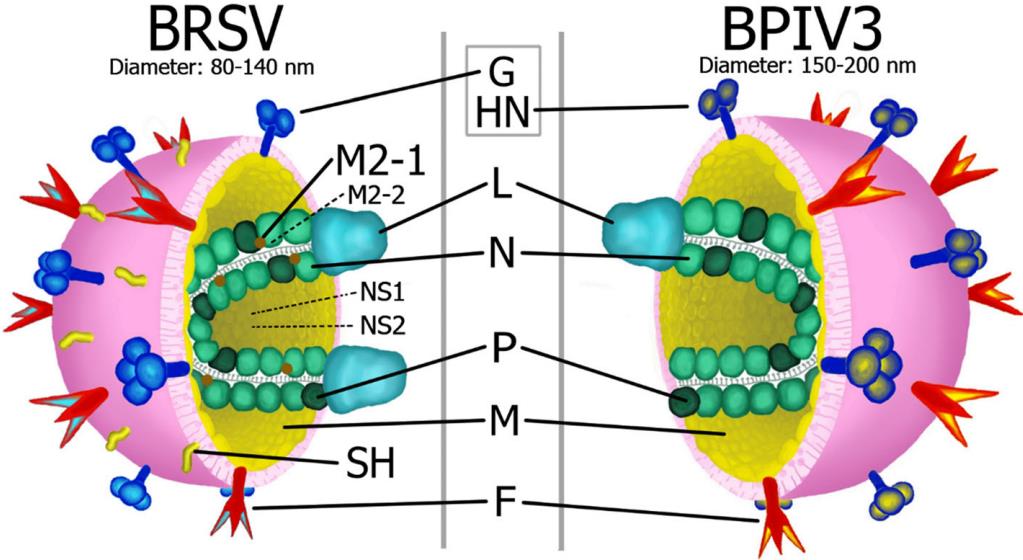 Fig.2 Morphology of bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV) and bovine parainfluenza 3 virus (BPIV3).2
Fig.2 Morphology of bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV) and bovine parainfluenza 3 virus (BPIV3).2
Serological Testing
Antibodies to HPIV can be detected by many antibody-based assays, including ELISA, radioimmunoassays (RIA), HI, complement fixation, western blotting, and neutralization assays. However, the problem is that it is difficult to develop heterologous antibodies against closely related HPIV serogroups. This problem is greatest when trying to separate HPIV-1 infection from HPIV-3 infection. As a result, the future goals are to develop antibodies with lower serologic cross-reactivity and to develop more sensitive serologic assays.
Creative Biolabs is specialized in the development of antibodies that are suitable for different antibody-based diagnostic assays (e.g., immunohistochemistry, ELISA, IF) for different viral and bacterial infections. Moreover, we offer diagnostic immunoassay development services, including feasibility analysis, assay design, assay protocol establishment, assay optimization, and kit production. If you are interested in our services, contact us to discuss your specific requirements.
References
For Research Use Only.
