Creative Biolabs has extensive experience of conducting preclinical urological studies in a variety of different rodent models of acute kidney injury (AKI), chronic kidney disease, cystitis, and so on. We offer several AKI models in rats and mice for screening, testing, and evaluation of new drugs and formulations, among which renal ischemia-reperfusion model is one of the most commonly used.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) and IRI Models
A wide range of in vivo experimental models of AKI has been developed to mirror the complexity and diversity of the human condition. Different models mimic different aspects of the pathophysiology, exhibiting both strengths and weaknesses. The most widely used model is the renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) model that can be induced in both rats and mice, as well as large animals such as pigs. AKI as a result of IRI has a complicated pathogenesis involving both the innate and adaptive immune response, and currently, no specific treatment is available.
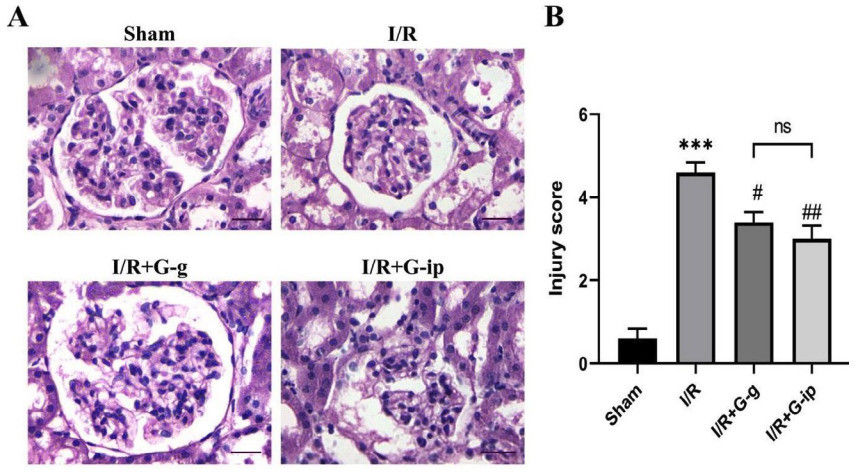 Fig. 1 Histopathological examination of I/R-induced renal injury.1
Fig. 1 Histopathological examination of I/R-induced renal injury.1
Induction of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion (IR) Model
Currently, two kinds of warm renal IR models are mainly used: bilateral renal IR and unilateral renal IR. The bilateral ischemic AKI model is commonly used because it is considered more relevant to human pathological conditions where blood supply is normally affected by both kidneys and it is the most frequent clinical situation. Depending on whether the contralateral kidney is removed, the unilateral model can be further divided into two subtypes: unilateral IR with contralateral nephrectomy or without contralateral nephrectomy. The former one has proved to be useful for studying the molecular and cellular pathophysiology of AKI as well as analysis of the subsequent renal regeneration.
IR surgery requires familiarity with the animal kidney anatomy to perform well. Typically, models can be established by renal artery clamping using a small non-traumatic vascular clamp followed by reperfusion. Technically, this surgery can be performed via ventral (laparotomy) or dorsal (retroperitoneal) approaches. Besides, an important advantage of renal artery clamping is that it is an easily reproducible procedure. Clamping time (30-45 min), maintenance of body temperature and the type of anesthesia are key parameters to be standardized for reproducibility. Despite the limitations, this model is extensively used by investigators and is expected to provide more important insights into the underlying mechanisms of AKI and therapy, largely because of its reproducibility.
Creative Biolabs provides measurements of renal functions mainly including but not limited to:
-
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
-
Serum Creatinine
-
Proinflammatory Cytokines
-
Histological Examination
-
Immunohistochemistry
Meanwhile, Creative Biolabs also offers other types of rodent urological disease models that you may be interested in:
Creative Biolabs offers urological study services with extensive expertise in conducting preclinical efficacy, proof-of-concept and mechanism of action studies in various rodent models. Our team has the skills and experience required to evaluate your preclinical drug candidates such as small molecules, biologics and RNA therapeutics for efficacy studies. Moreover, professional interpretation of the preclinical data is also offered to facilitate your drug development.
Reference
-
Bagheri, Yasin, et al. "Comparative study of gavage and intraperitoneal administration of gamma-oryzanol in alleviation/attenuation in a rat animal model of renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury." Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences 24.2 (2021): 175. Doi:10.22038/IJBMS.2020.51276.11642
For Research Use Only.


 Fig. 1 Histopathological examination of I/R-induced renal injury.1
Fig. 1 Histopathological examination of I/R-induced renal injury.1


