NASH Target Development Service for Serine Palmitoyltransferase (SPT) Inhibitors
Serine palmitoyltransferase is an important enzyme catalyzing the first step of ceramide synthesis in the de novo pathway. Creative Biolabs offers our clients high-quality services of serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) inhibitors development for the NASH treatment.
What is Serine Palmitoyltransferase?
Serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT), also known as 3-oxosphinganine synthetase, is a key enzyme in sphingolipid biosynthesis, which is responsible for the catalysis of the first reaction of sphingolipid synthesis in eukaryote cells. SPT essentially catalyzes the initial step of the de novo pathway in ceramide production by converting L-serine and palmitoyl-CoA to 3-keto-dihydrosphingosine (KDS), which is a precursor of sphingolipids. This SPT catalyzed reaction is the rate-limiting step of the de novo pathway. Actually, SPT is a kind of pyridoxal 5’-phosphate-dependent enzyme belonging to α-oxoamine synthases (AOS) family with the catalytic activity of condensation of acyl-CoA thioester substrates and amino acids. Human SPT is a membrane-bound heterodimer that consists of long-chain base 1 (LCB1) and LCB2 subunits. In addition, other forms, including SPT LCB3, SPT small subunit A (SPTSSA) and SPT small subunit A (SPTSSB), are also critical forms of SPT activity. As a critical enzyme, SPT shows important actions on a variety of bioactive processes and activities by affecting the formation of sphingolipids, which are essential substrates of cellular membranes and cellular activities.
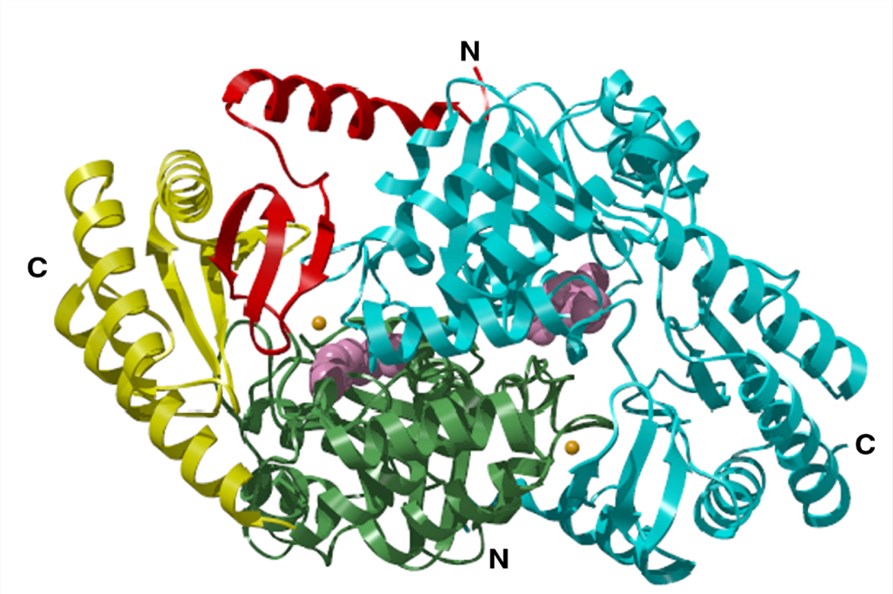 Fig.1 Overall structure of the holo serine palmitoyltransferase homodimer. (Yard, 2007)
Fig.1 Overall structure of the holo serine palmitoyltransferase homodimer. (Yard, 2007)
Serine Palmitoyltransferase (SPT) Inhibitors for NASH Treatment
As mentioned before, SPT is an important and rate-limiting enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of ceramides, which are sphingolipids participating in many cellular signaling. Excessive ceramides accumulation in the liver leads to fatty liver disease and hepatitis. Therefore, SPT up-regulation or over-activation may also result in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) by promoting ceramides production. And SPT can serve as one of the potential biomarkers in the NASH target treatment.
In vitro researches have been performed to ameliorate NASH by reducing production or increasing depletion of ceramides or a combination of these. Hepatic-specific SPT inhibitors can be a promising therapeutic strategy of NASH by inhibiting ceramide accumulation. Currently, discovered natural SPT inhibitors are lipoxamycin, sphingofungins, fungal metabolite myriocin, and its derivative fingolimod. However, the therapeutic effects of SPT inhibitors on NASH starve for further exploration both in laboratory and clinical trials.
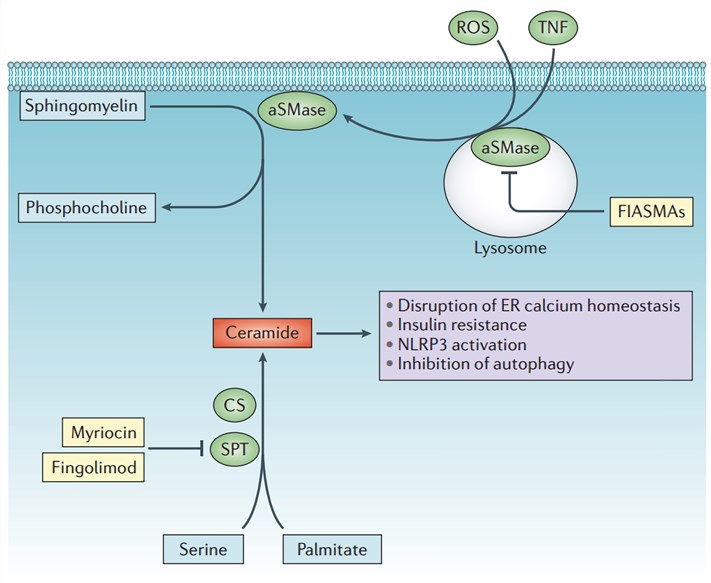 Fig.2 Ceramide synthesis and the pathogenesis of NASH. (Musso, 2016)
Fig.2 Ceramide synthesis and the pathogenesis of NASH. (Musso, 2016)
Creative Biolabs has engaged in NASH research for over a decade, and we have developed therapeutic strategies based on a series of potential targets for NASH treatment. Based on our advanced platforms (e.g. Hit to Lead, Lead Optimization, IND-Enabling, Target Identification, and Validation, Hit identification) and abundant background in target identification for drug discovery, we can provide a full range of NASH services ranging from biomarkers development, target discovery and therapeutic strategies, to preclinical models of NASH. You can directly contact us or communicate with us about your questions or interests.
References
- Yard, B.A.; et al. The structure of serine palmitoyltransferase; gateway to sphingolipid biosynthesis. Journal of molecular biology. 2007, 370(5): 870-886.
- Musso, G.; et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: emerging molecular targets and therapeutic strategies. Nature reviews. Drug discovery. 2016, 15(4): 249-274.
 For Research Use Only.
For Research Use Only.