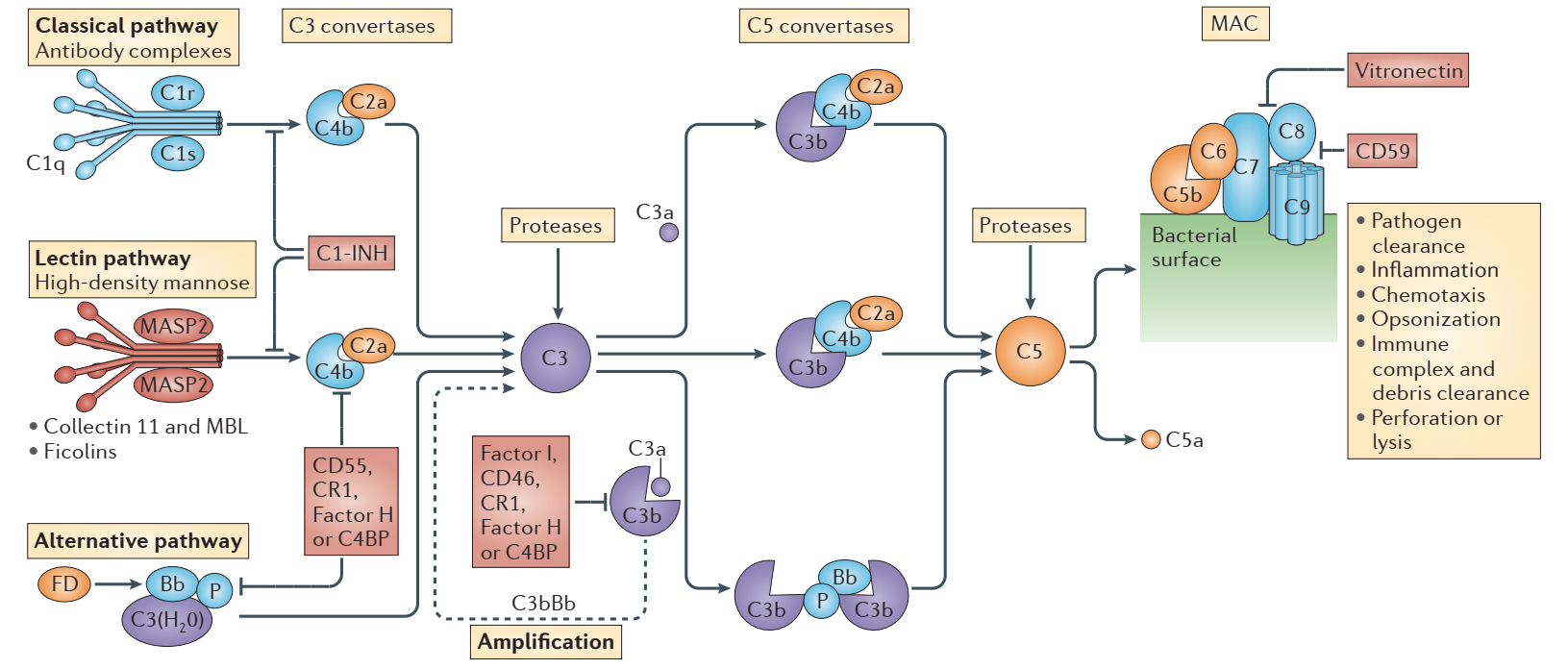
There are three complement activation pathways in the complement system, that is, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway. The three pathways have different origins, but they cross each other and share a common terminal pathway.
(Martin Kolev et al., Nature Reviews Immunology, 2014)
- The main features of the classical pathway
- The activator is mainly an immune complex formed by IgG or IgM combined with a membrane-type antigen or free antigen, and C1q recognizes the antigen-antibody complex as the initial step of this pathway.
- The C3 convertase and C5 convertase are C4b2a and C4b2a3b, respectively.
- Its initiation depends on the production of specific antibodies, so it can play a role in the late infection (or recovery period) and contribute to the body’s defense against re-infection by the same pathogen. It has been discovered that some microorganisms can activate C1q directly or indirectly by combining C-reactive protein and other factors, thereby initiating the classical activation pathway.
- The main features of the alternative pathway
- Its activator is a bacterial, fungal or virus-infected cell that provides a reaction surface for spontaneously generated C3b.
- The C3 convertase and C5 convertase are C3bBb and C3bBb3b, respectively.
- There is a positive feedback amplification loop.
- Complement can be activated without the presence of the antibodies, so it can contribute to the early infection or primary infection before the production of antibodies.
- The main features of the lectin pathway
- The activating substances of the lectin pathway are extensive, mainly N-galactosamine or mannose on the surface of various pathogenic microorganisms recognized by MBL and FCN.
- Its subsequent process is the same as the classical pathway except for the recognition mechanism.
- It has a cross-promoting effect on both the classical and the alternative pathways.
- Complement can be activated without the involvement of antibodies, which can play a role in early infection or primary infection.
The three activation pathways share the same goal, and the common pathway is C3, C5–C9.
