The lectin complement pathway is an essential part of the complement system, which provides an effective defense against invading pathogens and apoptotic cells in an organism. Similar to classical pathway, the lectin pathway is also a proteolytic cascade that elicits various effector functions including phagocytosis, cell lysis, inflammation, and guidance of the adaptative immune response.
Lectin Complement Pathway
The lectin pathway is initiated when one of the pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) binds to pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) (D-mannose, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, or acetyl groups), on the surface of invading microorganisms or apoptotic/necrotic cells. The well-characterized PRRs include mannose-binding lectin (MBL), ficolins and collagen-containing soluble C-type lectins (collectins), such as kidney collectin-11 (CL-K1). These circulated lectins are complexed with serine proteases named MBL-associated serine proteases (MASPs), comprising MASP-1, -2, and -3. The enzymatic cascade is really started after the binding of MBL/MASPs, CL-K1/MASPs, or ficolin/MASPs complexes to their targets.
-
MBL and MBL Deficiency
The mature MBL in serum is characterized by a mixture of different forms, in which dimers and trimers are not biologically active. The tetramer form has the capacity to active lectin pathway. A variant of the MBL2 gene causes the deficiency of functional MBL in serum, giving rise to a phagocytic defect associated with increased risk of recurrent childhood infections such as pneumonia and meningitis.
-
Ficolins
Ficolin family comprises ficolin-1, ficolin-2, and ficolin-3, and all of these are capable of forming complexes with MASPs, subsequently activating complement through the lectin pathway. Abnormal function or expression of ficolins is associated with infectious diseases and inflammation, e.g. the deficiency of ficolin-3 is associated with chronic and/or recurrent infections and lung damage. Whereas, autoimmune disorders are related to the abundance of ficolin.

Fig.1 The Structural subunits of MBL and ficolins.1, 4
-
Collectins
There are a series of collectins involved in the complement cascade. Collectin-10 (CL-10) was found in MASP1 complex, suggesting a potential role in the complement system. Collectin-11 (CL-11 or CL-K1) is now accepted as an activator of the lectin pathway. The heteromeric CL-10/11 seems to be pattern recognition and complement activation.
The Activation Steps of Lectin Complement Pathway
The domain structures of MASPs resemble C1r and C1s in the classical pathway, so their activation steps are very similar. Like C1s, MASP-2 contributes to the generation of C3 convertase via subsequent cleavage of C4 (C4a+C4b) and C2 (C2a+C2b). The cleaved product C4b and C2a is membrane- associated, and they can combine to form C4bC2a (C3 convertase) to trigger the downstream integrated enzyme reaction. The activation of MASP-2 is dependent on MASP-1. C3 convertase can cleave C3 to C3b, which unites C4bC2a to form C5 convertase (C4bC2aC3b). C5 convertase dissociates C5 to C5a and C5b, initiating the assembly of the membrane-attack complex (MAC). C5b recruits C6, C7, C8, C9 to form a fully functional MAC, resulting in cell lysis and death.

Fig.2 The activation of lectin pathway.2, 4
Creative Biolabs provides customized services based on the lectin pathway targets, including:
-
MASP-1
-
MASP-2
Our comprehensive complement platform offers a great number of complement-related products in a rapid and cost-effective manner. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Published Data
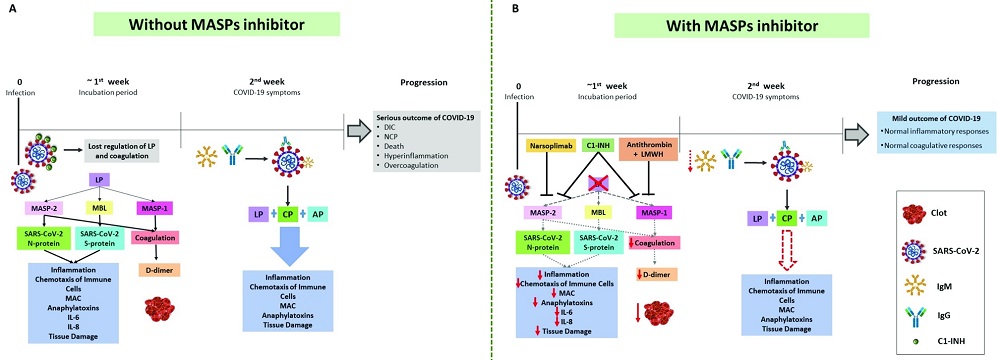 Fig.3 Therapeutic potential of MASPs.3, 4
Fig.3 Therapeutic potential of MASPs.3, 4
In COVID-19 patients, irregularities in both complement and coagulation systems, alongside heightened inflammation and clotting activity, have been observed. MASPs are crucial for detecting viruses, activating the lectin complement pathway, and triggering coagulation, thereby linking both processes. Variants in MASP1 and MASP2 genes influence the levels and activity of these proteins, affecting disease outcomes. In COVID-19, inhibiting the lectin pathway with a MASP inhibitor may impede excessive inflammation and coagulation, as this pathway is initially activated by the virus, MASPs initiate coagulation pathways, and MASP2 identifies the SARS-CoV-2 N protein. Positive outcomes using anti-MASP-2 antibodies suggest exploring MASPs as biomarkers and targeting MASP inhibitors in new treatment approaches for COVID-19, owing to their dual functionality in managing inflammation, coagulation, and viral interaction.
References
-
Beltrame, Marcia Holsbach, et al. "The lectin pathway of complement and rheumatic heart disease." Frontiers in pediatrics 2 (2015): 148.
-
Mason, Christopher P., and Alexander W. Tarr. "Human lectins and their roles in viral infections." Molecules 20.2 (2015): 2229-2271.
-
Bumiller-Bini, Valeria, et al. "MASPs at the crossroad between the complement and the coagulation cascades-the case for COVID-19." Genetics and molecular biology 44.1 Suppl 1 (2021): e20200199.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: Researchers often employ techniques like ELISA, flow cytometry, and immunoprecipitation to assess lectin pathway activity. Our lectin complement pathway functional kit is also helpful. In vivo models using knockout mice or gene silencing techniques are also utilized.
A: Targeting molecules like MBL-associated serine proteases (MASPs) or ficolins within the lectin pathway has been investigated using techniques such as RNA interference (RNAi) or small molecule inhibitors.
A: Commonly used experimental models include animal models like mice, rabbits, and zebrafish, as well as cell lines such as HEK293T cells and human primary cells. These models offer advantages in terms of tractability and relevance to human physiology.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:



 Fig.3 Therapeutic potential of MASPs.3, 4
Fig.3 Therapeutic potential of MASPs.3, 4