Creative Biolabs, who always focuses on the research highlight of antibody discovery, provides the best guarantee in the industry of in vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibody development and has launched a series of biomarker-specific antibody development services. A team of senior scientists focused on IVD antibody development can support you to explore novel IVD antibodies in a timely and cost-effective method. Here, we focus on IVD antibody development for Campylobacter.
Campylobacter
Campylobacter, which means "curved bacteria", is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. Campylobacter characteristically appears comma or S-shaped and can move by unipolar or bipolar flagella. Currently, there are 17 species and 6 subspecies designated to the genus Campylobacter. They commonly survive under hypoxic condition. Campylobacter is nonfermentative and positive by the catalase test and oxidase test. Campylobacter can be best cultured at 42°C and have poor survival at room temperature. However, they can survive for a short time at refrigerated temperatures. The bacteria would perish slowly at freezing temperatures and is heat-sensitive, and the cells are destroyed at high temperatures above 48°C. Campylobacter gain energy from amino acids or tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediaries and do not use sugars or produce indole. Several species of Campylobacter can grow anaerobically with certain electron acceptors, such as fumarate, aspartate or nitrate.
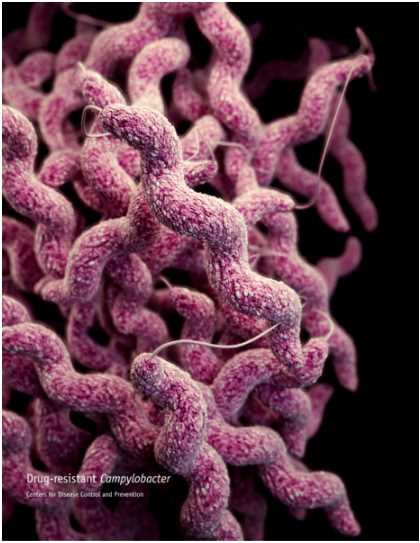 Fig.1 The morphology of Campylobacter.1
Fig.1 The morphology of Campylobacter.1
Campylobacter Gastroenteritis
Campylobacter infection (also called campylobacteriosis) is a digestive tract infection caused by Campylobacter, which can lead to gastroenteritis. Most of the Campylobacter species are able to cause illness and can infect humans as well as other animals. Poultry is the main reservoir of the bacterium. Humans can be infected by ingesting food contaminated with Campylobacter species. Another way of infection is exposure to infected animals, which usually carry Campylobacter asymptomatically. At least a dozen of Campylobacter have been involved in human disease, wherein C. jejuni, and C. coli are the most common ones. C. jejuni can change into a coccal form when exposed to atmospheric oxygen. The typical symptoms of campylobacteriosis are nausea, diarrhoea (sometimes bloody diarrhoea), and vomiting, even though vomiting does not always occur. Other symptoms occur uncommonly, which including fever and crampy stomach pains. Symptoms tend to occur within 2-5 days of ingesting contaminated food or of exposure the contaminated animal. C. jejuni is now regarded as one of the primary causes of bacterial foodborne disease in many developed countries.
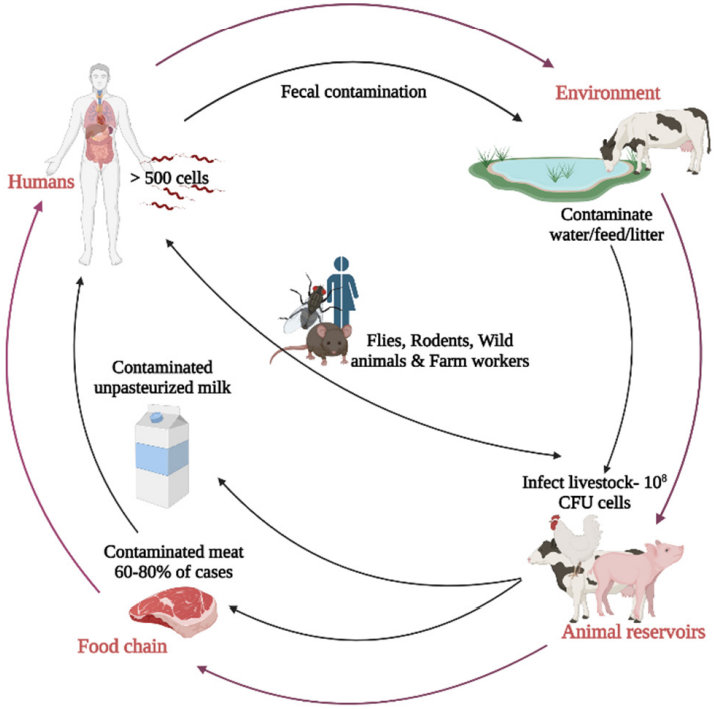 Fig.2 Reservoirs and routes of transmission of Campylobacter jejuni.2
Fig.2 Reservoirs and routes of transmission of Campylobacter jejuni.2
Complications of Campylobacter
As Campylobacter directly spreads from the gastrointestinal tract, the possible following local complications include pancreatitis, cholecystitis, peritonitis, and massive gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Moreover, the extraintestinal manifestations of Campylobacter infection are really rare and may include endocarditis, meningitis, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, and neonatal sepsis. Serious systemic illness caused by Campylobacter infection rarely occurs, but can lead to sepsis and death. The most important postinfectious complication of Campylobacter jejuni infection is the Guillain-Barre´ syndrome (GBS) which is an acute demyelinating disease of the peripheral nervous system.
Treatment of Campylobacter
For most patients with campylobacteriosis, the principal therapies include particularly fluid, supportive measures, and electrolyte replacement. In general, intravenous fluids are necessary for dehydrated patients while oral rehydration is indicated for most other patients. For the patients with symptoms of high fever and bloody diarrhea, the antibiotic therapy may be prudent even Campylobacter infections are almost self-limiting. By the way, the ideal way to prevent Campylobacter infections is to limit contamination of poultry flocks and have a careful food-preparation habit in the kitchen.
IVD antibodies have been commonly used in immunodiagnostic kits for the disease diagnosis and prognosis. Creative Biolabs has built a versatile IVD platform to provide custom biomarker-specific IVD antibody development services to global clients. Along with over a decade of rich experience in providing excellent custom services for IVD antibody discovery, our services can totally meet your special requirements.
In addition, Creative Biolabs provides one-stop diagnostic immunoassay development services, including feasibility analysis, assay design, assay protocol establishment, validation, and production. If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
References
For Research Use Only.
