As a first-class antibody service provider, Creative Biolabs has been devoted to the development of high-quality in vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibodies for the diagnosis of many different diseases, especially cancers. We offer customized antibody development services targeting specific biomarkers of gastrointestinal cancers to aid in their prognosis, diagnosis, and therapeutic monitoring. Remarkably, the granulin precursor (GRN) is a promising marker for gastrointestinal (GI) cancer diagnosis.
GRN, also known as the granulin-epithelin precursor, is a secreted glycoprotein conserved in most eukaryotes. As a soluble factor, it has been reported to regulate cell proliferation, cycle progression, motility, and inflammatory processes. Structurally, it belongs to no well-established growth factor families and could inhibit known growth factor receptors (e.g. IGF, EGF receptors) failing to prevent the actions of GRN. The full-length protein of GRN is approximately 68.5 kDa. After secretion, the protein can be cleaved between the granulin-like domains by metalloproteinases such as matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), MMP-14, and ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 7 (ADAMTS-7).
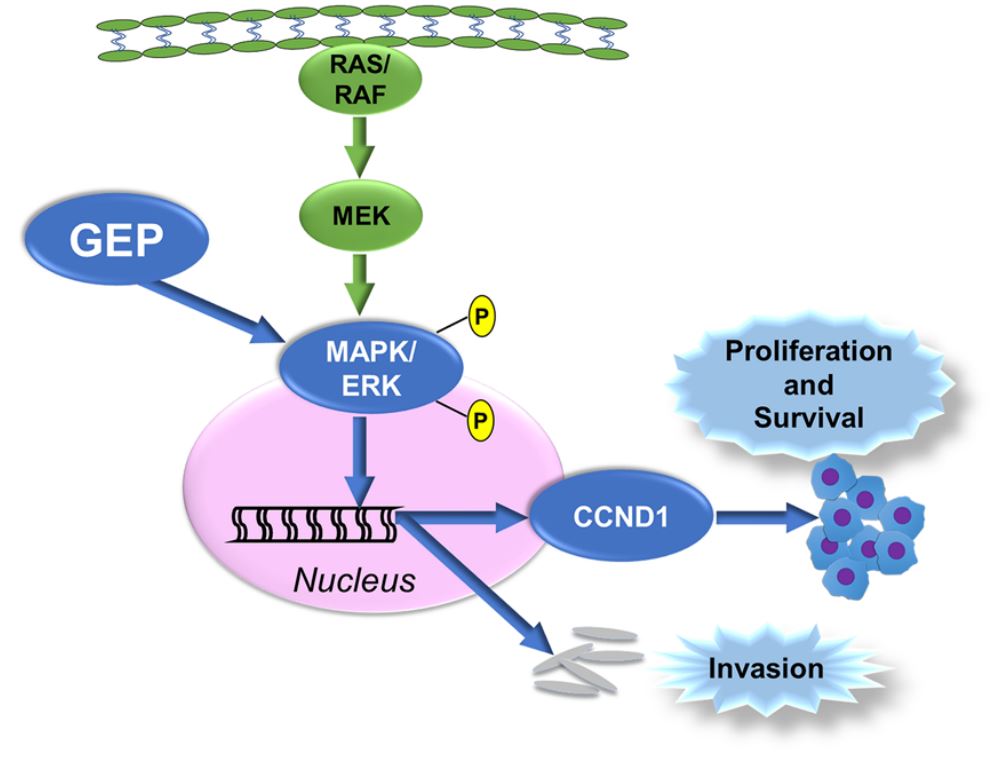 Fig.1 GEP (GRN) upregulates the phosphorylation of MAPK/ERK, regulating CRC.1
Fig.1 GEP (GRN) upregulates the phosphorylation of MAPK/ERK, regulating CRC.1
GRN has been implicated in a number of disease states. For instance, a loss-of-function mutation in this factor is associated with the onset of frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Conversely, GRN over-activity occurs in various types of cancers and is thought to confer a greater aggressive phenotype on the tumor cells.
Elevated GRN expression has been shown in many tumor types, such as ovarian, breast, prostate, liver, renal, and esophageal cancers. In experimental systems, the malignancy of highly tumorigenic GRN-expressing cell lines relies on the expression level, since reduced GRN mRNA levels significantly inhibit the tumor progression.
GI cancer refers to a group of cancers that influence the digestive system and cause the malignant conditions, including esophagus, gallbladder & biliary tract, stomach, liver, pancreas, bowel (large intestine or colon and rectum), small intestine, and anus. Gastric cancer (GC) is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the world. Currently, there’s no clinically relevant biomarker for GC diagnosis or prognosis.
Regardless of the tumor type, it is evident that GRN is upregulated within cancer cells and allows growth-promoting and chemoresistant effects. Also, the role of GRN in migration, invasion, and angiogenesis is obvious. Specific targeting of GRN factor represents an alternative target for the development of therapeutic strategies to fight with GI cancers. At Creative Biolabs, we offer IVD antibody development services against GRN marker to help the diagnosis of GI cancers and to improve patient selection. With our versatile IVD platform, Creative Biolabs is proud to develop novel GRN-specific (paired) antibodies from scratch to commercial IVD kit (we can also start with provided antibody candidates).
As a professional service provider in the field of antibodies, Creative Biolabs has gained a great reputation for having successfully accomplished numerous projects. If you’re interested in our services, please contact us for more information or directly send us an inquiry.
Reference
For Research Use Only.
