Agonist Development Service for Cancer Immunotherapy
Why Develop Immune Agonists
Under normal circumstances, the human immune system can recognize and eliminate tumor cells, but tumor cells have an "immune escape" mechanism, that is, they evade the recognition and attack of the immune system through a variety of mechanisms, so that they cannot be eliminated normally, so as to survive at all stages of the anti-tumor immune response.
Tumor immunotherapy can be divided into two ways: the first is to use drugs to allow the immune cells that fight tumors to reach smoothly, so as to kill cancer cells. Drugs such as CTLA-4 antibodies, PD-1 antibodies, and PD-L1 antibodies all fall into this category. Another way is to recharge the immune cells that fight cancer through drugs, so that the anti-cancer power is more durable and effective. Immune agonists are such drugs, which are currently a new hot topic in the global research and development of tumor immunity.
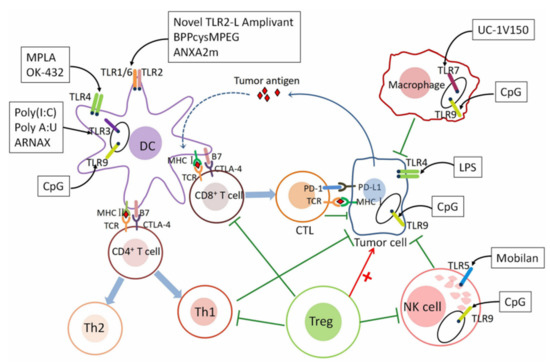 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of TLR agonist-mediated tumor immunity.1
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of TLR agonist-mediated tumor immunity.1
Our Service
Creative Biolabs is committed to better cancer immunotherapy, providing appropriate in vitro/in vivo testing services for a variety of agonist targets. We assist you throughout the process of developing agonists and collating experimental procedures and parameters into complete protocols for customer use, which can help you save development cycles. Our cancer immunotherapy agonist development service platform includes the development of co-stimulatory agonists and the development of Glucopyranosyl Lipid A (GLA) system TRL4 agonists.
-
Agonist Development Service Platform
-
Design and synthesis of agonists
-
In vitro evaluation of agonists
-
In vivo evaluation of agonists
Creative Biolabs provides one-stop immune agonist development services, including pre-agonist design and synthesis, biomarker prediction, in vitro cell culture and functional identification, in vitro efficacy and safety evaluation, and animal models, etc., to provide systematic and comprehensive high-quality services and reliable data results for your cancer immunotherapy.
-
Co-stimulatory Agonist Development Platform
In the process of immune cell activation, co-stimulatory molecules are often the key to forming an effective immune response. Immune cell activation requires costimulatory molecules in addition to antigen-specific signals from their antigen receptors. Creative Biolabs provides development services for co-stimulatory molecular targets for activating the immune system.
-
Co-stimulatory signaling targets
|
Target
|
Family
|
|
GITR
|
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily
|
|
OX40
|
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily
|
|
4-1BB
|
Co-stimulatory molecules
|
|
ICOS
|
CD28 cell surface receptor superfamily
|
|
CD40
|
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily
|
-
Mechanism of action of the costimulatory signaling pathway
-
In immune cells: regulating activation and proliferation of immune cells.
-
In tumor immunity: promoting immune escape of tumor cells.
-
Research and development of co-stimulatory signaling pathway-targeting agonists: drug therapy strategies for non-costimulatory signaling pathways.
-
Application of co-stimulatory signaling pathway-targeting agonists: improving the efficacy of tumor immunotherapy and reducing side effects.
-
Development service of co-stimulatory signal agonists
 Fig.2 Development service of co-stimulatory signal agonists.
Fig.2 Development service of co-stimulatory signal agonists.
-
Glucopyranosyl Lipid A (GLA) System TRL4 Agonist Development Platform
TLR4 is the most studied member of the TLR family, and it recognizes lipopolysaccharide (LPS). TLR4 is located on the plasma membrane and is mainly expressed on myeloid cells, while pDCs and naïve B cells are not. TLR4 recognizes LPS through its co-receptors bone marrow differentiation factor-2 (MD-2) and CD14. Creative Biolabs offers TLR4 agonist development services to increase its immune activity by modifying products such as glucopyranosyl A (GLA), which are structurally associated with LPS but do not have high pyrogenicity and maintain strong immune-boosting properties.
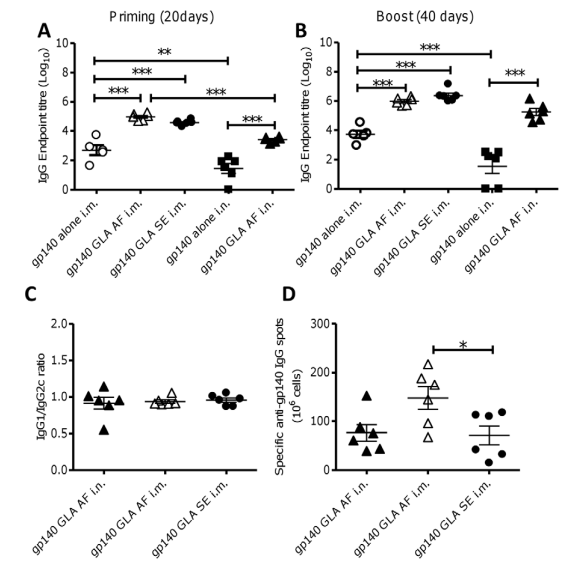 Fig.3 Modification of GLA enhances the humoral immune response to gp140.2
Fig.3 Modification of GLA enhances the humoral immune response to gp140.2
If you are interested in antagonist development service for cancer immunotherapy, you can click here for more information!
References
-
Jeong, Sehwan.; et al. "Engineering therapeutic strategies in cancer immunotherapy via exogenous delivery of toll-like receptor agonists" Pharmaceutics. (2021) 13, no. 9: 1374.
-
Arias, M.A.; et al. "Glucopyranosyl lipid adjuvant (GLA), a synthetic TLR4 agonist, promotes potent systemic and mucosal responses to intranasal immunization with HIVgp140." PLoS One. (2012) 7(7): e41144.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of TLR agonist-mediated tumor immunity.1
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of TLR agonist-mediated tumor immunity.1
 Fig.2 Development service of co-stimulatory signal agonists.
Fig.2 Development service of co-stimulatory signal agonists.
 Fig.3 Modification of GLA enhances the humoral immune response to gp140.2
Fig.3 Modification of GLA enhances the humoral immune response to gp140.2
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure