ATP, NADH, and Other Associated Molecules Assay Service
Cofactors and Coenzymes Linked to Tumor Metabolism
Metabolic disorders are important in the onset and progression of malignancies. Numerous molecular markers and their related regulatory mechanisms are impacted as a consequence of metabolic disorders. Cofactors and coenzymes serve as prerequisites for catalysis in cellular metabolic activities. They help proteins or enzymes work properly in a different manner. Thus, a thorough examination of the functions of coenzymes and cofactor systems will assist in the development of effective therapeutics for metabolic disorders such as cancer, as well as the enhancement of quality of life.
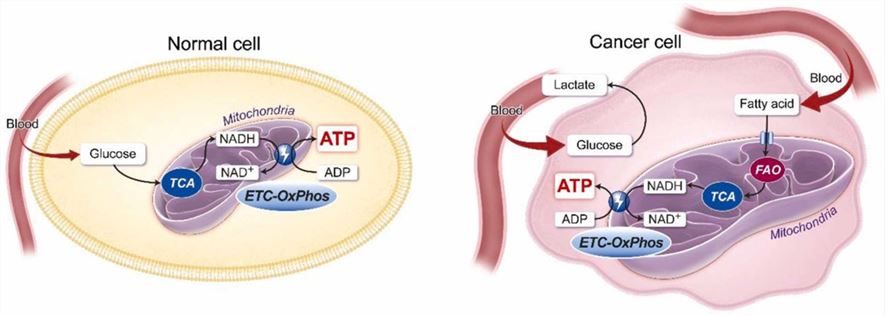 Fig.1 Cancer requires fatty acids to generate ATP.1
Fig.1 Cancer requires fatty acids to generate ATP.1
Our ATP, NADH, and Other Associated Molecules Assay Service
To aid in the development of cancer therapy, Creative Biolabs developed a sensitive and stable ATP, NADH, and other associated molecules assay service. In this assay, we utilize an enzymatic reaction that is coupled to the oxidative phosphorylation reaction of co-molecules like ATP and NADH, which induce bioluminescence. We measure the intensity of the bioluminescence as an indicator to characterize the corresponding molecules. At Creative Biolabs, we provide our global customers with innovative tools and comprehensive services to accelerate drug discovery and biological research.
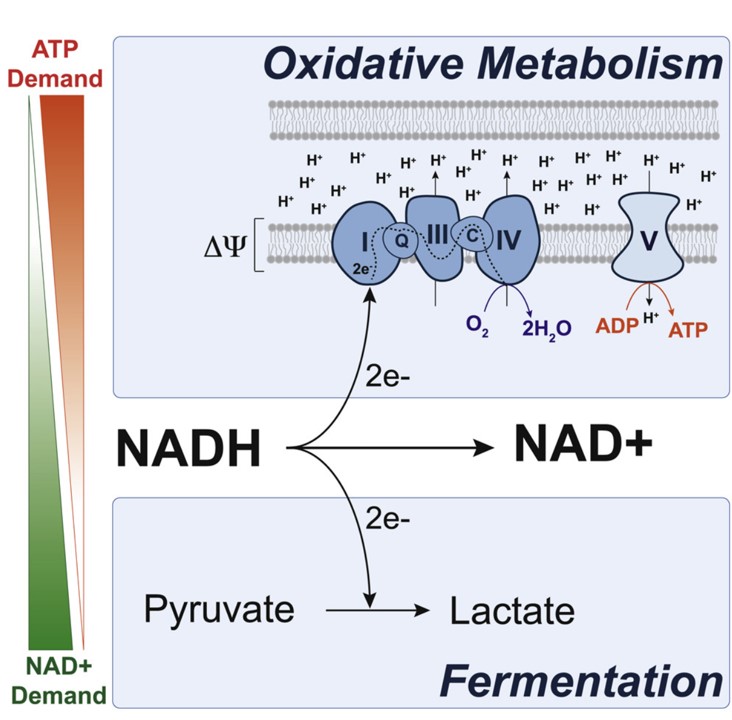 Fig.2 NAD+ is required for aerobic glycolysis.2
Fig.2 NAD+ is required for aerobic glycolysis.2
Why Choose Us?
-
Step-by-step procedures, simple and rapid, high throughput.
-
Suitable for multiple cell types.
-
Strict control of quality to ensure reproducible results.
-
Affordable price for high-quality results.
-
One-stop customized service to meet global customers’ diverse needs.
Case Display
Case 1: N-terminal acetyltransferase D (NatD) is known for its high selectivity, specifically recognizing histone H4 and H2A proteins as its substrates. There is evidence that connects the dysregulation of NatD to the development of colorectal and lung cancer, indicating that it could potentially be targeted for therapeutic purposes in treating these diseases. To monitor NatD activity in real-time, this study developed and downsized a continuous fluorescence-based assay to work in a 384-well format. The results confirmed that the continuous fluorescence-based assay for high-throughput screening (HTS) is effective in identifying small molecule inhibitors of NatD, which has the potential to assist in the future identification of NatD inhibitors and further enable the study of NatD's biological functions.
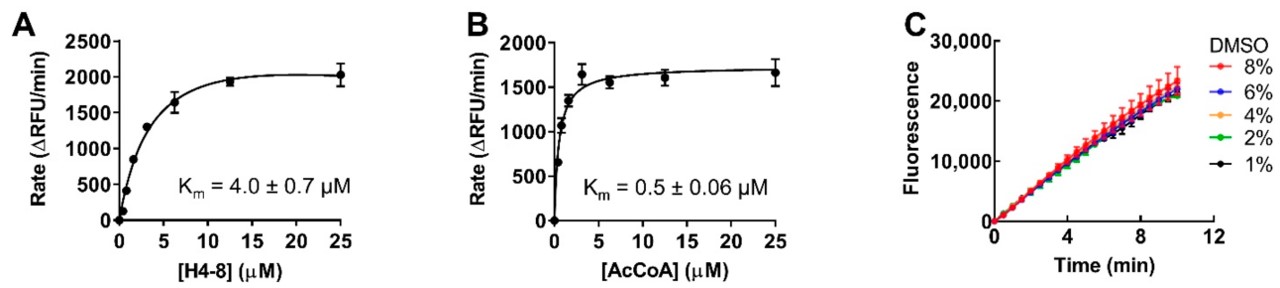 Fig.3 NatD activity steady-state kinetics.3
Fig.3 NatD activity steady-state kinetics.3
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What should we do for tissues?
A1: As an example, consider ATP measurement in heart tissue. The heart tissue must be flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen before being ground into powder in a mortar. Centrifuge tissue powder at appropriate centrifugal force after suspending it in lysis buffer (According to the ratio of 1mg tissue powder:10μL lysis buffer) at room temperature for 5 minutes to pellet insoluble particles. We used 50μL of supernatant for every test and built a standard curve of ATP dilutions to convert luciferase units to picomoles of ATP levels. To normalize the results to the amount of protein in the supernatant, the Bradford test was utilized.
Work with Creative Biolabs
Here is a simple inquiry mode for your convenience. If you are interested in our ATP, NADH, and other associated molecules assay service, please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Lee, Ho, et al. "Cancer depends on fatty acids for ATP production: A possible link between cancer and obesity." Seminars in Cancer Biology. Academic Press, 2022.
-
Luengo, Alba, et al. "Increased demand for NAD+ relative to ATP drives aerobic glycolysis." Molecular cell 81.4 (2021): 691-707.
-
Ho, Yi-Hsun, et al. "Development of a continuous fluorescence-based assay for N-terminal acetyltransferase D." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22.2 (2021): 594.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Cancer requires fatty acids to generate ATP.1
Fig.1 Cancer requires fatty acids to generate ATP.1
 Fig.2 NAD+ is required for aerobic glycolysis.2
Fig.2 NAD+ is required for aerobic glycolysis.2
 Fig.3 NatD activity steady-state kinetics.3
Fig.3 NatD activity steady-state kinetics.3

 Download our brochure
Download our brochure