Cell-based Phospholipidosis Analysis Service
Precision in Phospholipidosis Analysis
A key issue facing the development of any pharmaceutical compound is the definition and understanding of drug-induced phospholipidosis. Creative Biolabs provides custom cell-based phosphor analysis to meet the unique demands of your study by employing state-of-the-art techniques combined with our specialized experience in cellular toxicity. Here, to evaluate drug-induced phospholipidosis in HepG2 cells, Creative Biolabs has introduced a fast and advanced high-content analysis (HCA) assay based on imaging technologies. We go above and beyond to ensure that the data we give you is precise, and reliable, and provides you with intelligent information for your decision-making in drug research and safety evaluation.
Creative Biolabs offers a functional, cell-based phospholipidosis analysis service utilizing advanced Imaging and HCA methods. We recommend performing a dose-response study with 6-8 concentrations and 2-3 replicates per concentration. Leveraging our advanced platform, our assay measures fluorescence responses to provide precise and reliable data. This sophisticated approach ensures comprehensive insights into drug-induced phospholipidosis, supporting your research with high-quality and actionable results.
Techniques for the Analysis of Phospholipidosis
Traditionally, the detection of drug-induced phospholipidosis has relied on techniques such as electron microscopy, which is known for its high resolution but is also time-consuming and labor-intensive. Another approach involves quantitative PCR to measure the expression levels of genes associated with phospholipid metabolism. While effective, these methods may not be suitable for high-throughput screening or rapid analysis of large compound libraries.
To overcome these limitations, Creative Biolabs has adapted a new high-content image-based HCA assay. HepG2 has been extensively used for toxicological studies and has the major advantage of being metabolically competent and thus more relevant for drug-induced liver injury studies. This assay takes advantage of high-throughput imaging technology to allow for rapid evaluation of drug-induced phospholipidosis.
Keys:
HepG2 cells are exposed to test compounds, including cationic amphiphilic drugs (CADs) and other potential inducers of phospholipidosis, at various concentrations and time points. Following exposure, cells are stained with fluorescent dyes that specifically label phospholipids, allowing for visualization and quantification of intracellular lipid accumulation. This imaging-based approach provides detailed insights into the extent and localization of phospholipidosis within the cells.
The use of HCA allows for the simultaneous evaluation of multiple cellular parameters, including cell morphology, viability, and organelle integrity, in addition to phospholipid accumulation.
Overall, our rapid image-based HCA assay offers a reliable and efficient solution for assessing drug-induced phospholipidosis, providing valuable data to support drug development and safety evaluation efforts.
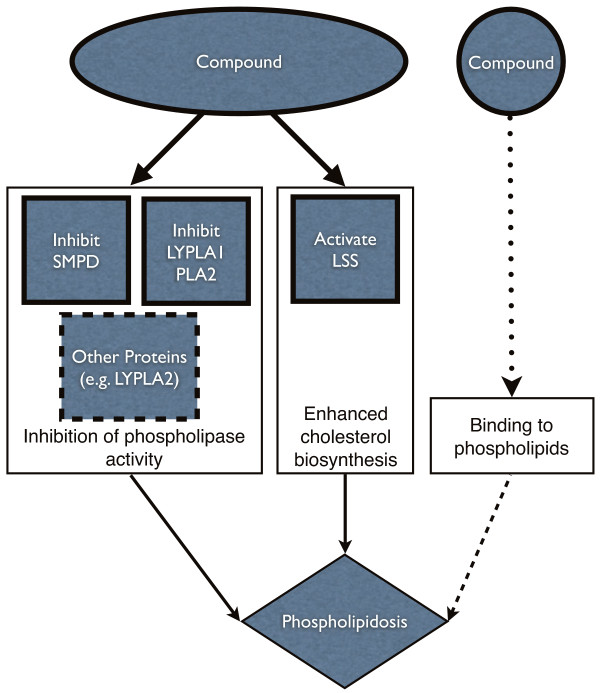 Fig.1 Overview of the predicted mechanisms for phospholipidosis.1
Fig.1 Overview of the predicted mechanisms for phospholipidosis.1
Applications
-
Drug Safety Assessment: Evaluate the phospholipidosis-inducing potential of new pharmaceutical compounds to ensure their safety before clinical trials.
-
Mechanistic Studies: Investigate the underlying mechanisms of drug-induced phospholipidosis, contributing to a deeper understanding of cellular responses to drug exposure.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Generate comprehensive data required for regulatory submissions, supporting the safety profiles of drug candidates.
Advantages
-
Our advanced detection and quantification techniques
-
Multiple analytical approaches
-
Tailored assay designs
Equipped with advanced technologies and a team of experienced scientists in phospholipidosis analysis, Creative Biolabs ensures that our data is both precise and reliable. Contact us today to learn how our phospholipidosis analysis services can help drive your projects to success.
Reference
-
Lowe, Robert, et al. "Predicting the mechanism of phospholipidosis." Journal of cheminformatics 4 (2012): 1-9.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Overview of the predicted mechanisms for phospholipidosis.1
Fig.1 Overview of the predicted mechanisms for phospholipidosis.1
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure