Functional Analysis of Neoantigen-Specific TCR
With our Professional competence in functional analysis of neoantigen-specific TCR, Creative Biolabs has developed a comprehensive platform for neoantigen-based cancer immunotherapy development.
Introduction of Neoantigen-specific TCR
In contrast with conventional TCRs, as shown in Fig.1, TCR-like CARs or TCR-CARs based on neoantigens have the advantages of both TCRs and CARs.TCR-like CARs and TCR-CARs with a scFv targeting neoantigens could specifically target the tumor site and could be rapidly activated to offer robust and long-term protection. Creative Biolabs has established a comprehensive platform for the functional analysis of neoantigen-specific TCR.
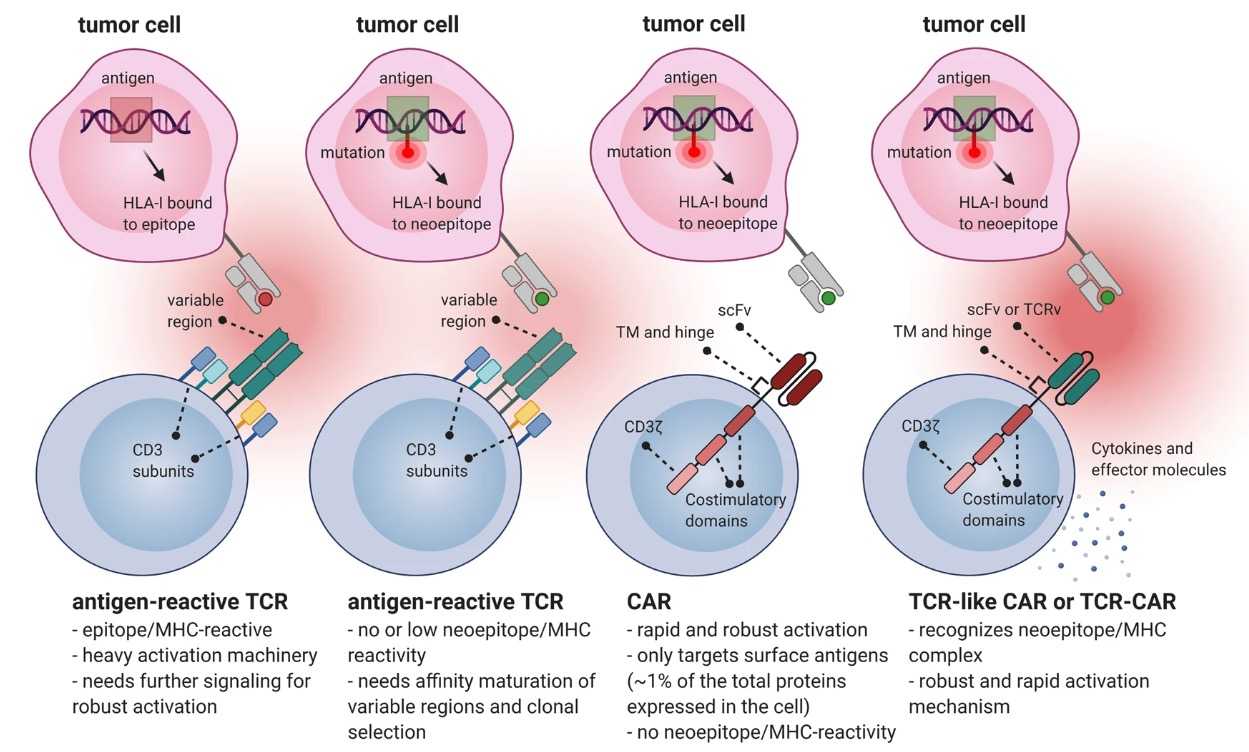 Fig.1 Advantages of Neoantigen-based TCR-like CAR or TCR-CAR.1
Fig.1 Advantages of Neoantigen-based TCR-like CAR or TCR-CAR.1
One-Stop Workflow for Functional Analysis of Neoantigen-specific TCR
Functional analysis of neoantigen-specific TCR is a routine program operated by a team of experts. With accumulated successful experiences, we could fulfill specific project requirements with quick responses. The typical workflow for our neoantigen-specific TCR analysis is shown in Fig.2.
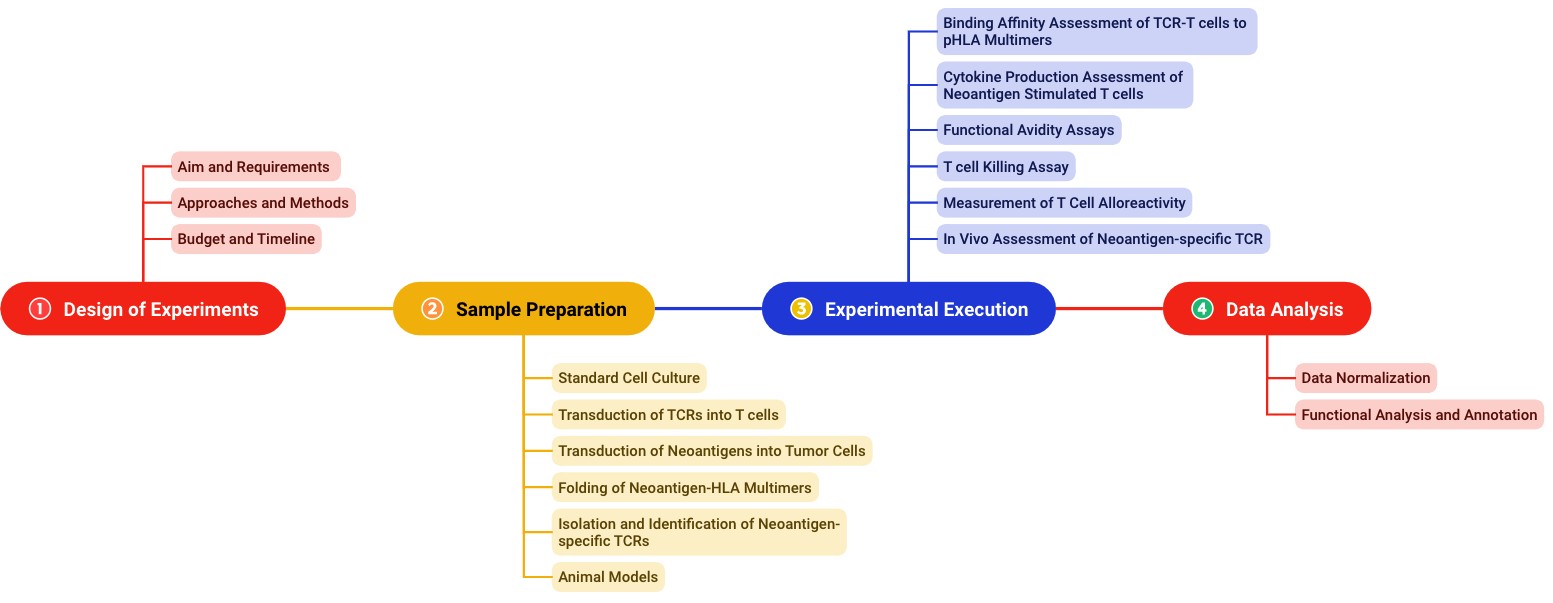 Fig.2 Experimental workflow for functional analysis of neoantigen-specific TCR.
Fig.2 Experimental workflow for functional analysis of neoantigen-specific TCR.
Key Features
-
Quick responses with a short timeline
-
High transduction efficiency to ensure cellular functional analysis
-
Comprehensive assessment routinely executed with a team of experts
-
Multi-dimensional analysis of the specificity, avidity, and longevity of neoantigen-specific TCRs
-
Professional data analysis with visual interpretation
Results Display
Aim: To decipher the cytokine production differences between TCRs.
Method: TCR-transduced T cells were co-cultured with LCL-1 cells pulsed with mutated peptides. Cytokines measured in the multiplex analysis included GM-CSF, IL-2, IL-12, and TNF-α.
Result: The highest cytokine levels were found to be secreted by T cells expressing TCR SYTL4-TIL1 and SYTL4-PBC1. 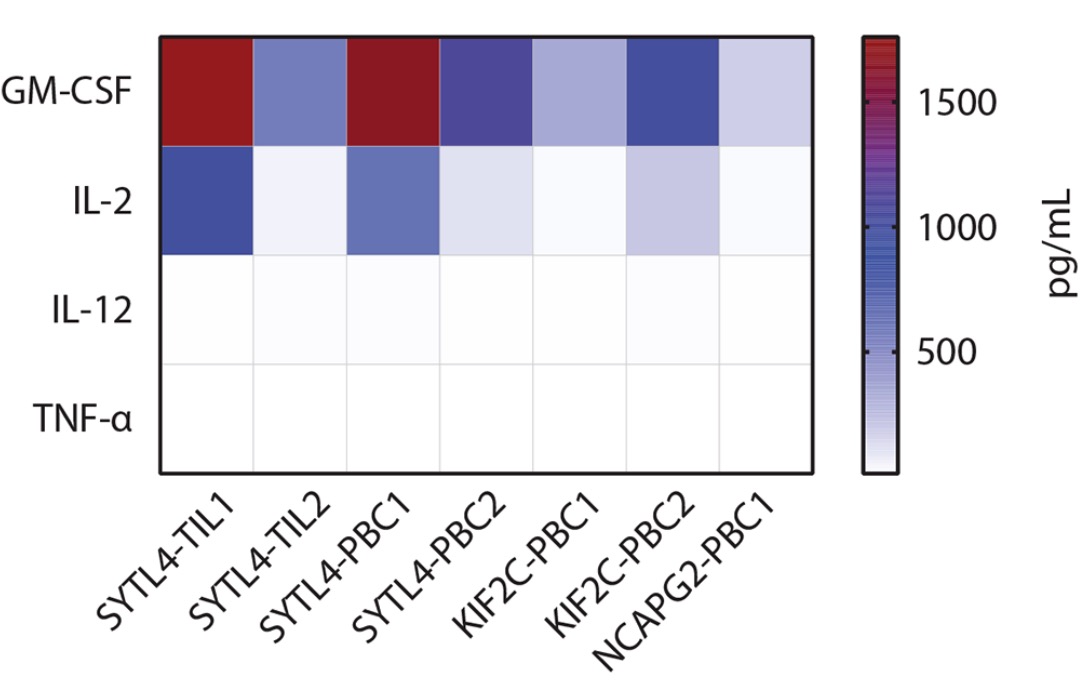 Fig.3 Assessment of multi-cytokine secretion of TCR-T cells.2 Fig.3 Assessment of multi-cytokine secretion of TCR-T cells.2
|
Aim: To measure the cross-reactivity of neoantigen-specific TCRs.
Method: The IFN-γ secretion levels of TCR-T cells separately elicited by a collection of peptides with a single position difference from the neoantigen were investigated.
Result: The IFN-γ secretion levels with peptides replaced NCAPG2ᵖ³³³ᴸ at different positions were shown in Fig.4. 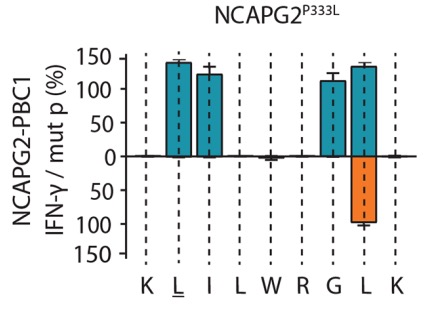 Fig.4 IFN-γ secretion of a defined neoantigen.2 Fig.4 IFN-γ secretion of a defined neoantigen.2
|
Aim: To compare the functional avidity of different neoantigen-specific TCRs.
Method: TCR-transduced T cells were co-cultured with mutated peptide-pulsed T2-A3 or T2-B27 cells in the IFN-γ assay.
Result: The EC50 values indicated that the functional avidity of NCAPG2ᵖ³³³ᴸ-specific TCRs was higher than that of KIF2Cᵖ¹³ᴸ. 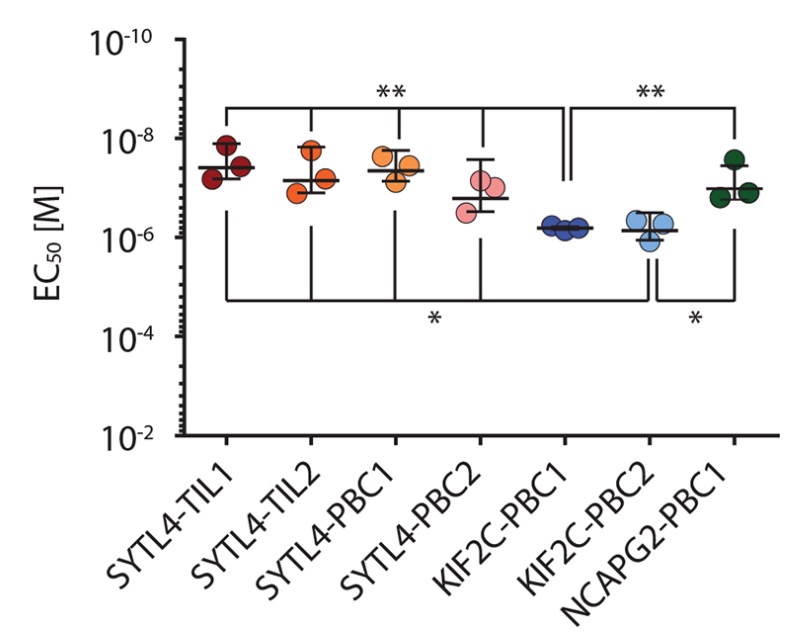 Fig.5 Functional avidity analysis of neoantigen-specific TCRs.2 Fig.5 Functional avidity analysis of neoantigen-specific TCRs.2
|
Aim: To assess the in vivo antitumor possibilities of neoantigen-specific TCRs.
Method: The U-698-M tumor model was established and animals were treated with different TCR-transduced T cells.
Result: The lifetime of animals that received neoantigen-specific TCRs was significantly prolonged. 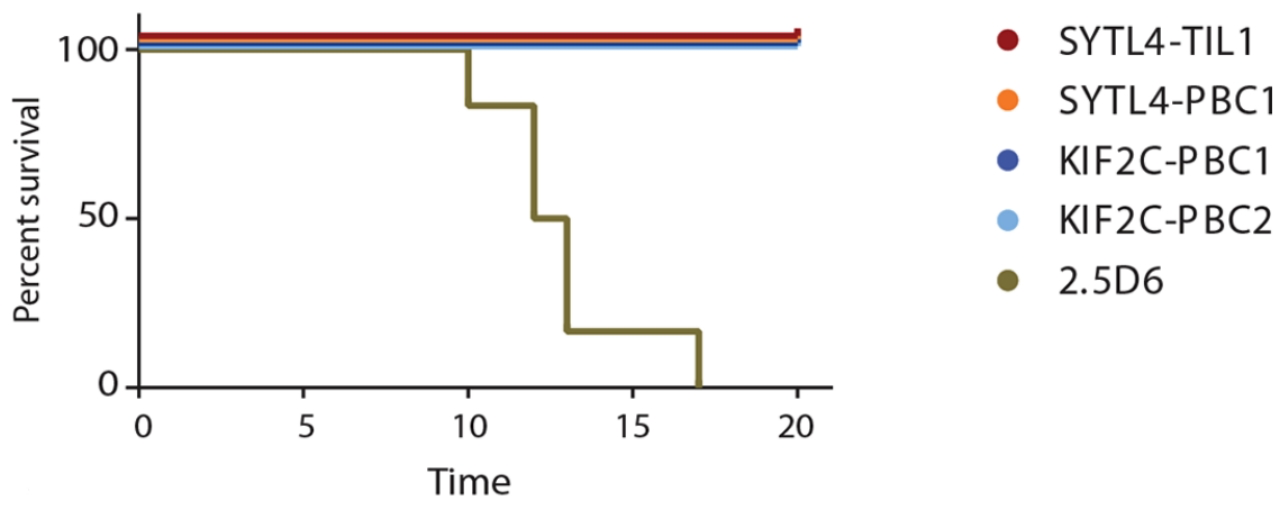 Fig.6 Survival curve of tumor-bearing mice injected with neoantigen-specific TCR-T cells.2 Fig.6 Survival curve of tumor-bearing mice injected with neoantigen-specific TCR-T cells.2
|
Neoantigen-based immunotherapy has become a novel and ideal strategy for cancer treatment. For the advantages of neoantigen-specific TCR-like CARs and TCR-CARs, Creative Biolabs already has a professional and well-established platform to help our clients with the functional assessment of neoantigen-specific TCRs.
References
-
Poorebrahim, Mansour, et al. "TCR-like CARs and TCR-CARs targeting neoepitopes: An emerging potential." Cancer gene therapy 28.6 (2021): 581-589.
-
Bräunlein, Eva, et al. "Functional analysis of peripheral and intratumoral neoantigen-specific TCRs identified in a patient with melanoma." Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer 9.9 (2021).
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Advantages of Neoantigen-based TCR-like CAR or TCR-CAR.1
Fig.1 Advantages of Neoantigen-based TCR-like CAR or TCR-CAR.1
 Fig.2 Experimental workflow for functional analysis of neoantigen-specific TCR.
Fig.2 Experimental workflow for functional analysis of neoantigen-specific TCR.
 Fig.3 Assessment of multi-cytokine secretion of TCR-T cells.2
Fig.3 Assessment of multi-cytokine secretion of TCR-T cells.2 Fig.4 IFN-γ secretion of a defined neoantigen.2
Fig.4 IFN-γ secretion of a defined neoantigen.2  Fig.5 Functional avidity analysis of neoantigen-specific TCRs.2
Fig.5 Functional avidity analysis of neoantigen-specific TCRs.2  Fig.6 Survival curve of tumor-bearing mice injected with neoantigen-specific TCR-T cells.2
Fig.6 Survival curve of tumor-bearing mice injected with neoantigen-specific TCR-T cells.2  Download our brochure
Download our brochure