Immunogenicity Assessment of Candidate Neoantigens
With our industry-leading technology and first-class research capability, Creative Biolabs has developed a comprehensive platform for neoantigen-based cancer immunotherapy development.
Introduction of Immunogenicity Assessment of Neoantigens
Neoantigens derived from genomic alterations of tumor cells could elicit a series of antitumor immune responses, as shown in Fig.1b. The immunogenicity assessment of candidate neoantigens is of great importance to guarantee good therapeutic outcomes. Creative Biolabs has been focused on this area with continuous efforts to provide a full-service neoantigen immunogenicity assessment.
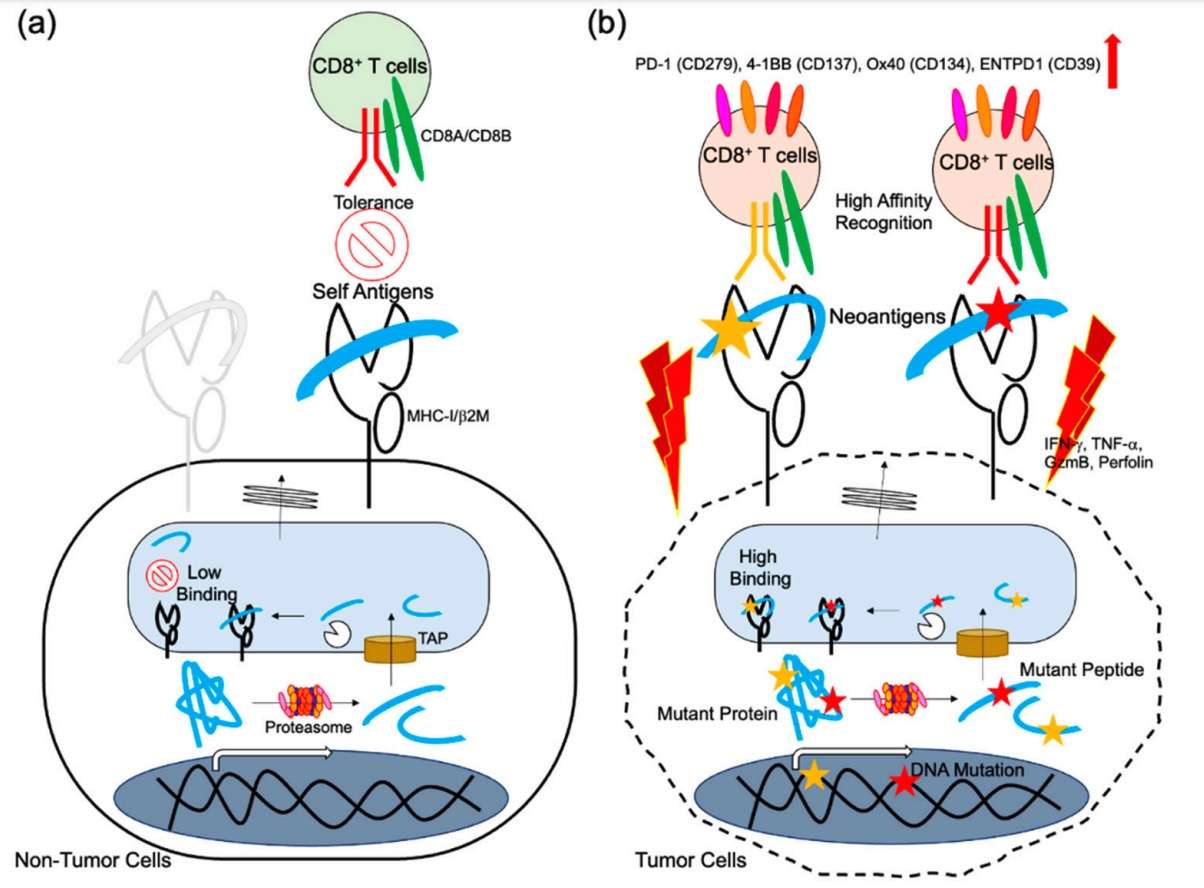 Fig.1 Neoantigen presentation and immune responses.1
Fig.1 Neoantigen presentation and immune responses.1
One-Stop Workflow for Immunogenicity Assessment of Neoantigens
With our team of experts, we accumulated a series of key technological breakthroughs. Now we have solid foundations to offer a scientific and whole-process service for the immunogenicity assessment (as shown in Fig.2). We operate procedures with strict quality standards to obtain accurate results.
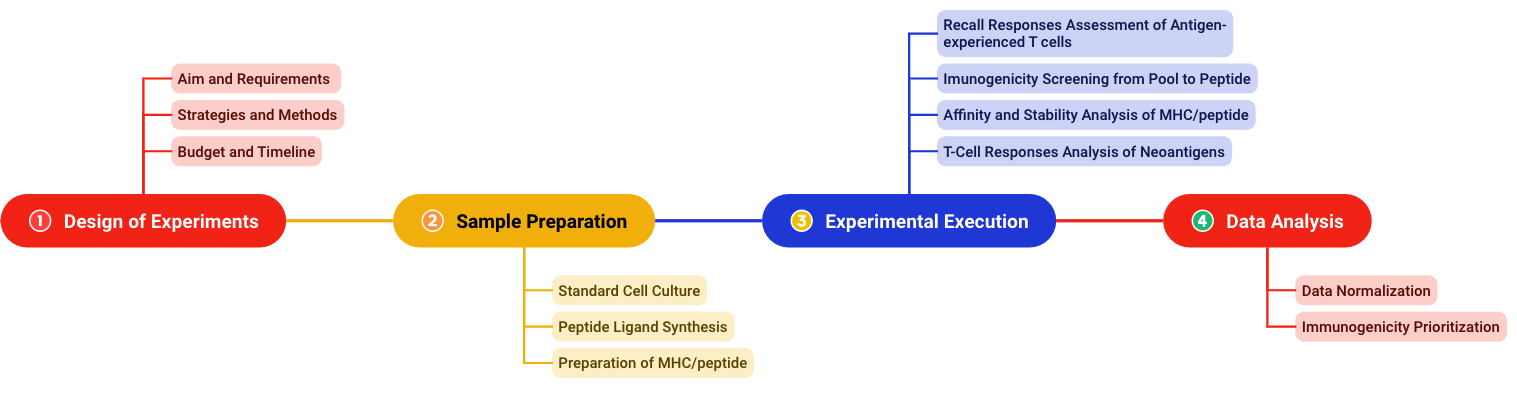 Fig.2 Experimental workflow for immunogenicity assessment. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.2 Experimental workflow for immunogenicity assessment. (Creative Biolabs)
Key Benefits
-
High-throughput neoantigen screening
-
A one-stop solution from sample preparation to immunogenicity prioritization
-
Comprehensive data analysis with expert professional bioinformatics software
Results Display
Aim: To define the peptide-eliciting immunogenicity of candidate peptides.
Method: Candidate peptides were assembled in eleven pools to be tested with antigen-experienced and stimulated PBMC cells in the IFN-γ ELISpot assay.
Result: Pool 4 and Pool 9 both had a high immunogenicity and were analyzed for subsequent single peptide screens. 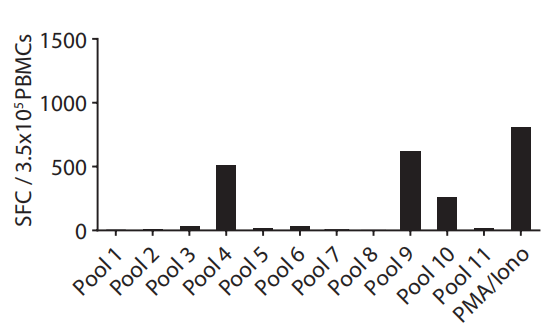 Fig.3 Immunogenicity assessment of peptide pools.2 Fig.3 Immunogenicity assessment of peptide pools.2
|
Aim: To measure the immunogenicity of candidate single peptides.
Method: Candidate single peptide-pulsed T2-A3 cells were incubated with expanded and stimulated T cells in the IFN-γ ELISpot assay.
Result: Peptide RLFLGLAIK was identified to have a high immunogenicity. 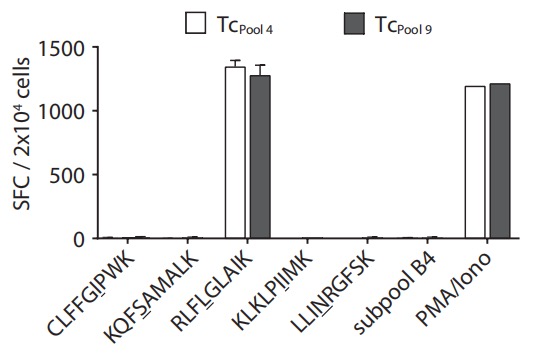 Fig.4 Immunogenicity assessment of neoantigens.2 Fig.4 Immunogenicity assessment of neoantigens.2
|
Aim: To measure the cytotoxicity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) induced by candidate peptide-pulsed dendritic cells (DCs).
Method: Candidate peptide-pulsed DCs incubated with CTLs which were stimulated with recombinant human IL-2. The calcein-positive living tumor cells were tested in the calcein-releasing cytotoxicity assay.
Result: CTLs stimulated with peptide 9-pulsed DCs showed the strongest cytotoxicity against tumor cells. 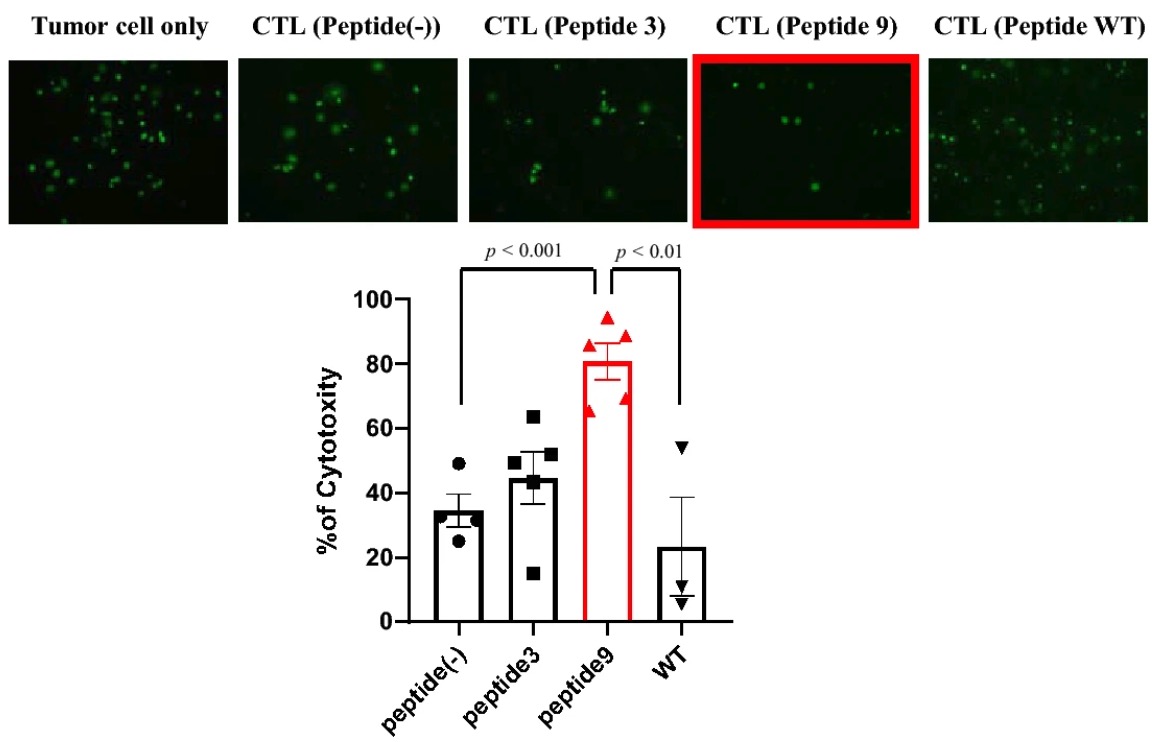 Fig.5 Cytotoxicity results of CTLs induced by neoantigen-pulsed mDCs.3 Fig.5 Cytotoxicity results of CTLs induced by neoantigen-pulsed mDCs.3
|
Aim: To evaluate the IFNγ-producing ability of CTLs induced by candidate peptide-pulsed DCs
Method: Candidate single peptide and wildtype control peptide were pulsed into DCs. CTLs induced by candidate peptide-pulsed DCs and stimulated with recombinant human IL-2 were tested against the autologous tumor cells in the IFN-γ ELISpot assay.
Result: CTLs induced by peptide 9-pulsed DCs had a strong IFNγ-producing ability. 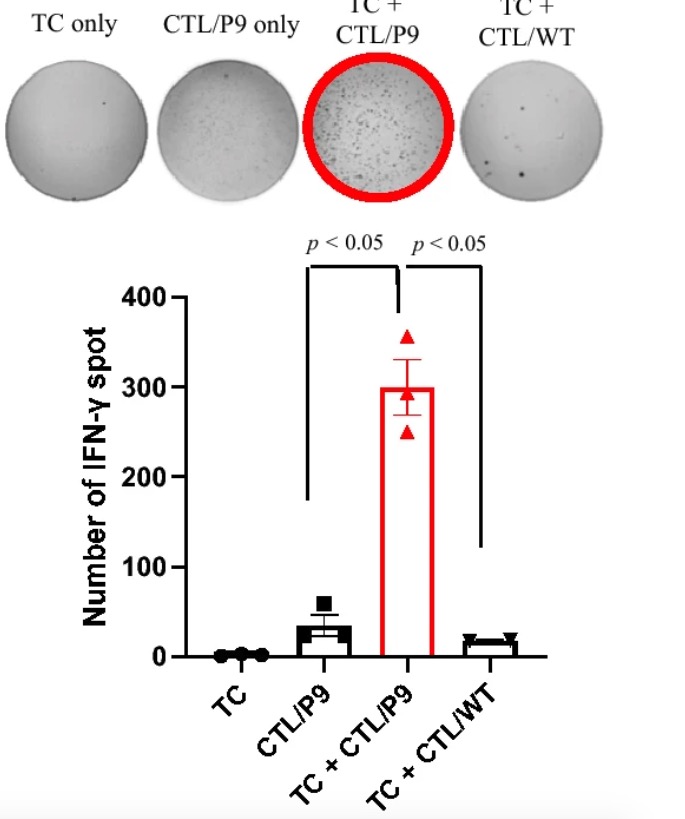 Fig.6 IFNγ-release responses induced by peptide 9-pulsed mDC stimulated with CTLs against autologous tumor cells.3 Fig.6 IFNγ-release responses induced by peptide 9-pulsed mDC stimulated with CTLs against autologous tumor cells.3
|
Creative Biolabs has established an experienced and professional team to help our clients with the immunogenicity assessment of neoantigens. We wish to cooperate with you to develop a neoantigen-based approach to cancer immunotherapy.
References
-
Okada, Masahiro, Kanako Shimizu, and Shin-ichiro Fujii. "Identification of neoantigens in cancer cells as targets for immunotherapy." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.5 (2022): 2594.
-
Bräunlein, Eva, et al. "Functional analysis of peripheral and intratumoral neoantigen-specific TCRs identified in a patient with melanoma." Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer 9.9 (2021).
-
Morisaki, Takafumi, et al. "Neoantigens elicit T cell responses in breast cancer." Scientific reports 11.1 (2021): 13590.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Neoantigen presentation and immune responses.1
Fig.1 Neoantigen presentation and immune responses.1
 Fig.2 Experimental workflow for immunogenicity assessment. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.2 Experimental workflow for immunogenicity assessment. (Creative Biolabs)
 Fig.3 Immunogenicity assessment of peptide pools.2
Fig.3 Immunogenicity assessment of peptide pools.2 Fig.4 Immunogenicity assessment of neoantigens.2
Fig.4 Immunogenicity assessment of neoantigens.2 Fig.5 Cytotoxicity results of CTLs induced by neoantigen-pulsed mDCs.3
Fig.5 Cytotoxicity results of CTLs induced by neoantigen-pulsed mDCs.3 Fig.6 IFNγ-release responses induced by peptide 9-pulsed mDC stimulated with CTLs against autologous tumor cells.3
Fig.6 IFNγ-release responses induced by peptide 9-pulsed mDC stimulated with CTLs against autologous tumor cells.3 Download our brochure
Download our brochure