Background of F(ab')2
Antibodies are highly specific and affinity immunoglobulins. Thy consists of two heavy chains and two light chains connected by disulfide bonds. Enzymatic or chemical methods can be used to cleave antibodies into different fragments, such as F(ab), F(ab')2, Fc, etc.The F(ab) fragment is obtained by digesting the whole IgG antibody with papain, removing the Fc region and leaving only one antigen-binding site (monovalent). It has a molecular weight of about 50 kDa. The F(ab')2 fragment, on the other hand, is obtained by digesting the whole IgG antibody with pepsin, removing most of the Fc region but retaining part of the hinge region. It still retains two antigen-binding sites (divalent) and has a molecular weight of about 110 kDa.
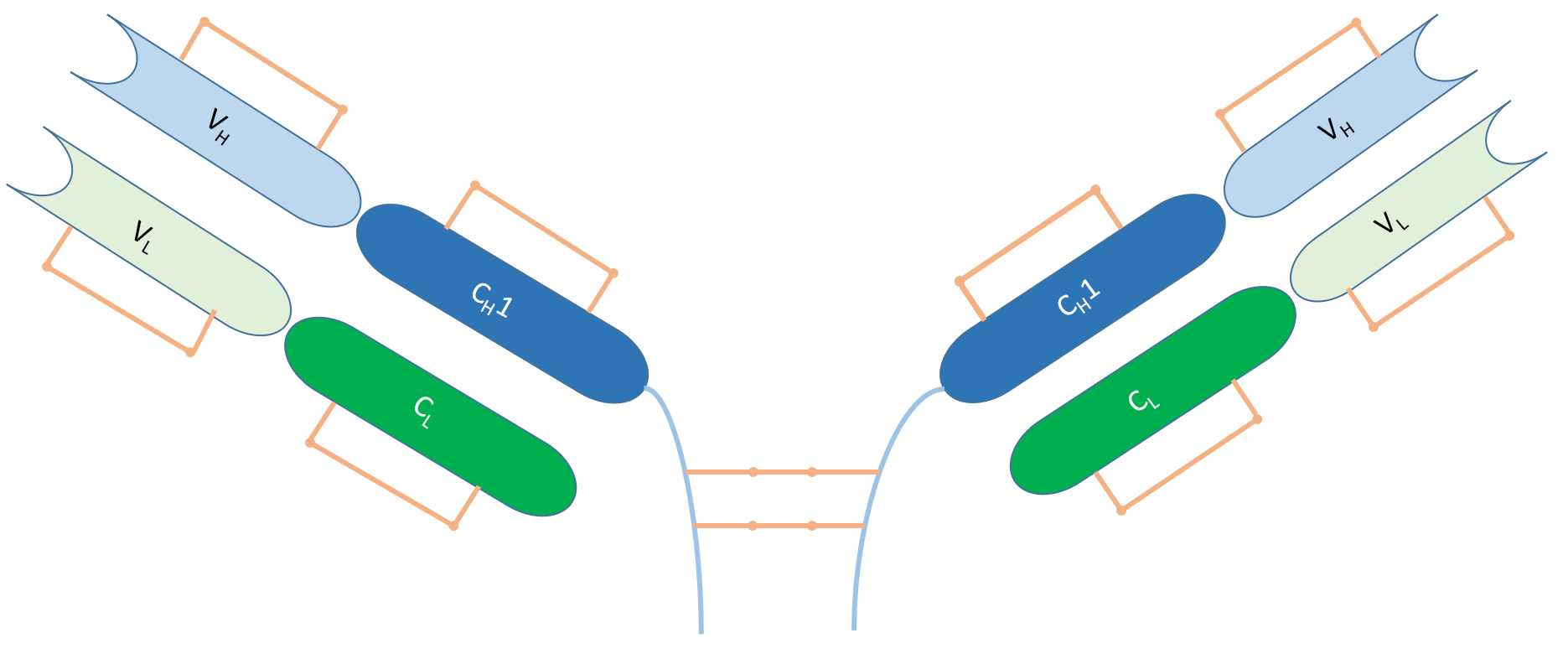
Fig.1 Structure of F(ab')2 Fragment
F(ab')2 fragment antibodies have advantages and disadvantages compared to whole IgG antibodies. On the positive side, they do not cause non-specific binding or immune complex-mediated allergic reactions since they lack the Fc region. Additionally, their smaller molecular weight allows for better tissue penetration, improving the efficiency and sensitivity of antigen recognition. They are also suitable for immunoprecipitation, immunoblotting, and other experiments as they can bind and precipitate antigens simultaneously due to their divalent nature. However, they cannot be recognized by secondary antibodies or complement since they lack the Fc region, making them unsuitable for ELISA, flow cytometry and other experiments. They are easily excreted by the kidneys, have a short half-life, and require increased dosage or frequency due to their smaller molecular weight. Furthermore, they may cross-react with some hinge region-specific Fc receptors as they contain part of the hinge region.
Structural Features of F(ab')2 Fragment Antibodies
Antibodies are composed of two heavy chains and two light chains, each containing a variable region and a constant region. These four chains are connected by disulfide bonds, forming a Y-shaped structure. The upper end of the Y-shaped structure consists of two F(ab) fragments, each comprising a heavy chain and a light chain and containing an antigen-binding site. The lower end of the Y-shaped structure is an Fc fragment, composed of two heavy chains and containing an effector molecule or cell binding site. F(ab')2 fragment antibodies are obtained by digesting the whole IgG antibodies with pepsin, removing most of the Fc region but retaining part of the hinge region. The hinge region, located in the constant region of the heavy chain, connects the two F(ab) fragments and the Fc fragment, providing flexibility and diversity to the antibody. F(ab’)2 fragment antibodies consist of two F(ab) fragments connected by disulfide bonds, resulting in bivalency with a molecular weight of about 110 kDa. While F(ab')2 fragment antibodies can still bind to antigens, they cannot bind to Fc receptors or protein A/G. Fc receptors are proteins on immune cell surfaces that recognize and bind to the Fc region, mediating immune effects. Protein A/G, found on bacterial cell walls, can also bind to the Fc region and serve as affinity chromatography media or detection markers. The structural features of F(ab')2 fragment antibodies make them more suitable than whole IgG antibodies in certain research or therapeutic scenarios. For instance, they offer advantages in situations where non-specific binding must be avoided, tissue penetration needs improvement, or signal strength needs enhancement.
Clinical Data of F(ab')2 Dragment Antibodies
F(ab')2 fragment antibodies are primarily used in the treatment of snake bispecific T cell engagers, autoimmune diseases, tumors and other conditions. The approved F(ab')2 fragment antibody drugs target specific toxins or antigens, neutralizing or blocking their actions to achieve prevention and treatment. They carry a lower risk of non-specific binding and allergic reactions compared to whole IgG antibodies. However, they also have some adverse reactions and limitations that require individualized medication based on different situations.
Table 1. F(ab')2 fragment antibodies approved for marketing
|
Name
|
Target
|
Approval date
|
Indication
|
Population
|
Country or region
|
|
Anavip
|
American rattlesnake venom
|
2018
|
Prevention and treatment of hematological and muscular damage after American rattlesnake bispecific T cell engager
|
Adults and children
|
USA
|
|
CroFab
|
American rattlesnake venom
|
2000
|
Prevention and treatment of hematological, neurological and muscular damage after American rattlesnake bispecific T cell engagers
|
Adults and children
|
USA
|
|
Eculizumab-F (ab')2 (SKY59)
|
C5 complement factor
|
2020
|
Prevention and treatment of relapse and progression of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) and hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS)
|
Adults and children
|
Japan
|
In clinical trials, F(ab')2 fragment antibodies are utilized as carriers, coupled with other molecules or cells, to form novel biologics that enhance specificity, stability, and potency. These biologics are mainly aimed at refractory or malignant tumors, inducing tumor cell apoptosis, inhibiting tumor angiogenesis or activating immune cells for treatment. They are currently undergoing various stages of clinical trials and require further verification of their safety and efficacy.
Table 2. Table 2. F(ab')2 Fragment Antibodies in Clinical Trials
|
Name
|
Target
|
Clinical trial phase
|
Main indication
|
Main research institution
|
|
F(ab')2-CD20-DM1 (SYD985)
|
CD20-positive tumor cell surface antigen
|
Phase III
|
Treatment of HER2-low-expressing advanced breast cancer
|
Synthon Biopharmaceuticals BV
|
|
F(ab')2-EGFRvIII-CAR-T (CNCT19)
|
EGFRvIII-positive tumor cell surface antigen
|
Phase I/II
|
Treatment of EGFRvIII-positive recurrent or refractory glioblastoma
|
BGI Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
|
|
F(ab')2-CD19-CAR-T (CNCT19)
|
CD19-positive tumor cell surface antigen
|
Phase I/II/III/IV/Expansion/Observation/Unknown (different countries or regions)
|
Treatment of CD19-positive recurrent or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, etc.
|
BGI Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
|
References
1. Crivianu-Gaita, V., et al. Aptamers, antibody scFv, and antibody Fab' fragments: an overview and comparison of three of the most versatile biosensor biorecognition elements. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015;85:32-45.
2. Forthal, D.N. Functions of antibodies. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014;2(4):1-17.
3. Lin X, et al. Applications of Nanoparticle-Antibody Conjugates in Immunoassays and Tumor Imaging. AAPS J. 2021 Mar 14;23(2):43.
4. Rosenstein S, et al. Production of F(ab')2 from Monoclonal and Polyclonal Antibodies. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2020 Jun;131(1):e119.
5. Kasturirangan, S., et al. Evaluation of Fab and F(ab')2 fragments and isotype variants of a neutralizing anti-ricin antibody for potency in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010;17(2):210-216.
6. Laffly, E., et al. Selection of a human anti-Botulinum neurotoxin A antibody fragment from a phage display library and its expression as a recombinant F(ab')2 fragment. Toxicon 2005;45(7):869-874.
7. Liu, J.K., et al. Fab and F(ab')2 antibody fragments against viper venom: a strategy for humanization by analyzing antigen contact residues. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014;35(10):1253-1268.
8. Miethe, S., et al. Development of neutralizing scFv-Fc against botulinum neurotoxin A light chain from a macaque immune library. mAbs 2014;6(3):446-459.
Our products and services are for research use only, and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Welcome! For price inquiries, we will get back to you as soon as possible.
To order, please email
INQUIRY





