BAFF Assay Portfolio Service
Introduction
B cell-activating factor (BAFF), also known as B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand superfamily member 13B (TNFSF13B), is a cytokine belonging to the TNF ligand family that activates B cells. BAFF is first synthesized as type II transmembrane proteins, mainly in myeloid and stromal cells, and further processed by furin convertase cleavage into trimeric soluble cytokines BAFF 3-mer. Twenty soluble BAFF 3-mers can be further oligomerized into a virus-like particle, called BAFF 60-mer. BAFF expression is increased in the presence of type I interferon (IFNs) including IFN-γ, interleukin (IL)-10 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, as well as by Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), TLR4 or TLR9 stimulation.
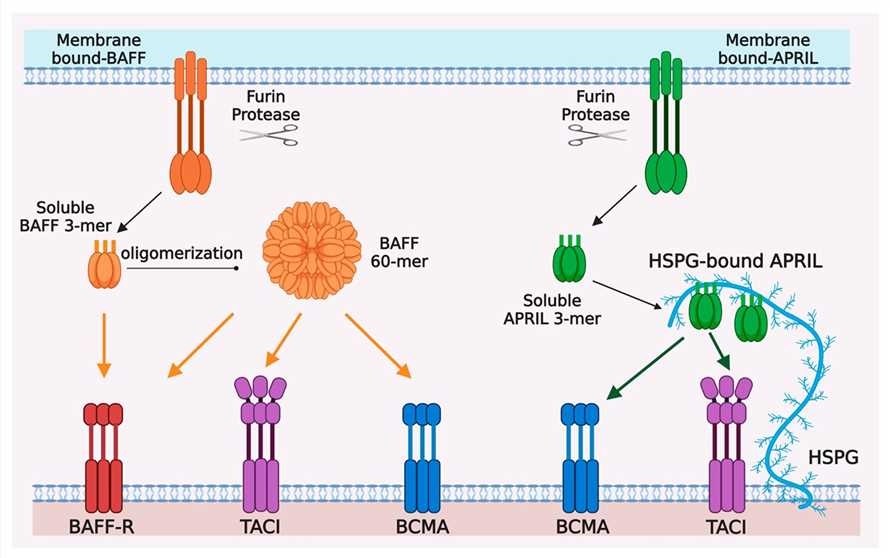 Fig.1 Ligand-receptor interactions in the BAFF/APRIL system. (Xu, 2020)
Fig.1 Ligand-receptor interactions in the BAFF/APRIL system. (Xu, 2020)
BAFF System Molecules
The so-called "BAFF system molecules", which consist of two ligands, BAFF and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL), and three receptors, are critical for B cell homeostasis. BAFF and APRIL are type II transmembrane proteins and they share some receptor specificity. BAFF binds to 3 receptors that are primarily expressed on B cells: BAFF receptor (BAFF-R), B cell maturation antigen (BCMA), and transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI). Both BAFF and APRIL bind two receptors BCMA and TACI. APRIL does not bind BAFF-R but binds heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG) in both the extracellular matrix and on the surface of cells like plasma cells, triggering APRIL multimerization. The expression of all three receptors is restricted mainly to B lymphocyte lineage cells. BAFF and APRIL are cytokines that share biological functions, they promote B cell survival and maturation and are expressed as membrane-bound or soluble proteins.
 Fig.2 BCR and BAFF-R signaling cascades. (Pieper, 2013)
Fig.2 BCR and BAFF-R signaling cascades. (Pieper, 2013)
BAFF and Disease
BAFF induces signals which interfere with mechanisms regulating the selection of B cells. Excess of BAFF promotes the development of autoreactive B cells. Some studies have shown that overproduce BAFF have high numbers of mature B cells and antibodies, including autoantibodies, and develop an autoimmune disease.
-
Hematological malignancies
BAFF may contribute to cancer progression through the amplification of pro-inflammatory signaling. They can activate multiple signaling pathways including NF-κB, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI-3K)/AKT and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways in myeloma cells and upregulate their expression of anti-apoptotic proteins. In addition, studies have shown that TACI-mediated signaling could contribute to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. As an essential component of the lymphoma microenvironment, BAFF has long been recognized as a 'sanctuary site' for lymphoma cells during traditional chemotherapy.
BAFF Assay Portfolio Service for Research
BAFF is considered an important player in many pathophysiological conditions, including inflammation, autoimmune disorders, primary immunodeficiencies. Increased expression and serum levels of BAFF were demonstrated in many types of hematological and solid tumors making BAFF a possible new biomarker in malignancies. Creative Biolabs provides a full set of BAFF assay portfolio services for research, which including but not limited to
-
NF-κB activation assay
-
In vitro B-cell stimulation assay
-
ELISA assay for BAFF
-
Cell proliferation assay
-
Cell apoptotic assay
-
Cell migration assay and wound healing assay
-
Immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry
-
Flow cytometry: cell surface antigens and apoptosis
-
Western blotting
Creative Biolabs has been dedicated to providing one-stop tumor marker assay services (e.g., BAFF assay portfolio service). We are experienced in the specialized development of high-complexity assay solutions to support complete custom solutions for biochemical and cell-based assays. This facilitates pharma and biotech preclinical research in all therapeutic areas and the development of companion diagnostics and clinical biomarkers, particularly in oncology. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Xu, S.; Lam, K.P. Transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI): another potential target for immunotherapy of multiple myeloma?. Cancers (Basel). 2020, 12(4): 1045.
-
Pieper, K.; et al. B-cell biology and development. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013, 131(4): 959-971.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Ligand-receptor interactions in the BAFF/APRIL system. (Xu, 2020)
Fig.1 Ligand-receptor interactions in the BAFF/APRIL system. (Xu, 2020)
 Fig.2 BCR and BAFF-R signaling cascades. (Pieper, 2013)
Fig.2 BCR and BAFF-R signaling cascades. (Pieper, 2013)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure