BTLA Assay Portfolio Service
Immune checkpoint blockade therapy has become a major effective way to fight cancer. B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) expresses in most lymphocytes and induces immunosuppression by inhibiting B and T cell activation and proliferation. With advanced and high-end technologies, rich experienced scientists, Creative Biolabs is an excellent service provider in the field of tumor marker assay. After long years ahead to fully comprehend tumor markers, we launch our BTLA assay portfolio service which can be useful for targeted cancer therapy and diagnosis.
Introduction of BTLA
BTLA, a co-inhibitory molecule similar to programmed death 1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), is a transmembrane glycoprotein, belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. The expression of BTLA is detected on the surface of various immune cells, such as B cells, T cells including naive T cells, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs), natural killer cells. Its gene is localized in the q13.2 region of chromosome 3 and consists of 5 exons with a total length of 870 bp and the extracellular domain is the immunoglobulin domain, and the intracellular domain contains three conserved motifs: one is the proximal motif which has sequence YDND, an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), and an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif.
 Fig.1 Structure of the BTLA protein. (From Wikipedia)
Fig.1 Structure of the BTLA protein. (From Wikipedia)
Biological Function of BTLA
-
Pro-survival function of BTLA: The motif of sequence YDND contains tyrosine and binds to growth factor receptor binding 2 (Grb-2), then interacting with the p85 subunit of PI3K.
-
Inhibitory effects: The ITIM phosphorylate after BTLA binds to HVEM, thereby ITIM recruit and activate the protein tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2, attenuating tyrosine kinase activated by T cell receptor.
-
BTLA can weaken the activation of transcription factor NF-κB and NFAT and inhibit the activity of transcription factor AP-1, inhibiting the proliferation and differentiation of T cells.
-
BTLA can prevent Toll-like receptors in dendritic cells from being over-activated, reduce cytokine production of NKT cells and follicular Th cells.
BTLA/HVEM Signaling
Herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), the BTLA ligand, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily. Immune effects are mediated by the association of BTLA with HVEM directly bridges the CD28 and TNFR families. The detailed signal shows as follows: SHP-1 and SHP-2 were recruited in T cells due to engagement of BTLA, then downregulating TCR signaling and delivering inhibitory signals. The recruitment of PI3K protein subunit p85 and the stimulation of the PI3K signaling pathway occurs resulting from the Grb-2 association motif binds to Grb-2. In addition, BTLA/HVEM signaling is bidirectional. BTLA/HVEM engagement induces HVEM-mediated NF-κB activation in antigen-presenting cells, thereby providing pro-inflammatory and pro-survival signals.
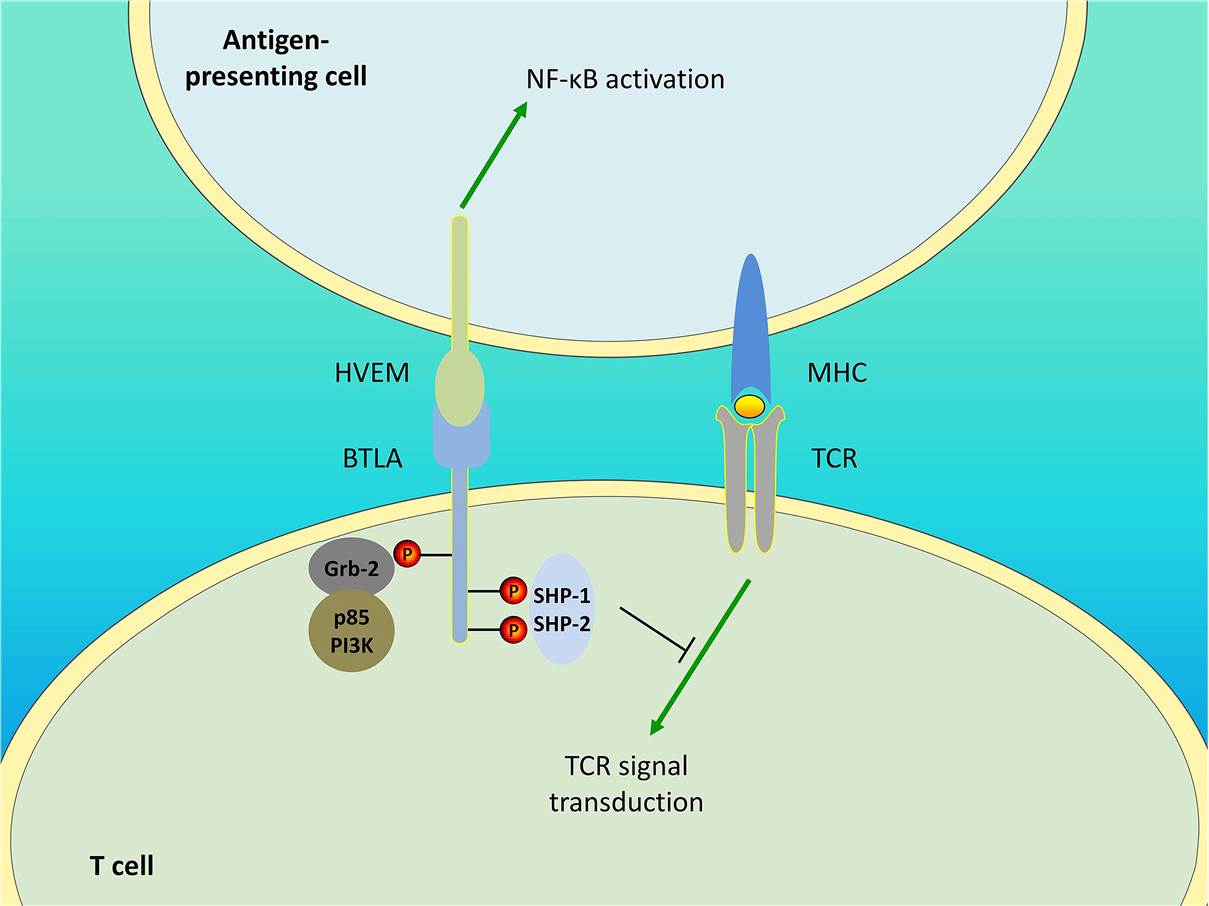 Fig.2 Bidirectional signaling between BTLA and HVEM. (Ning, 2021)
Fig.2 Bidirectional signaling between BTLA and HVEM. (Ning, 2021)
BTLA Blockade Assays at Creative Biolabs Including but Not Limited to:
-
Migration assay
-
Proliferation assay
-
Invasion assay
-
Metastases assay
-
Cytokine assay
-
Apoptosis assay
-
Cytotoxicity assay
-
Immune responses assay
If you are interested in our service, please contact us or directly send us.
References
-
Deng, Z.; et al. The role of B and T lymphocyte attenuator in respiratory system diseases. Front Immunol. 2021,12: 635623.
-
Ning, Z.; et al. Roles of BTLA in immunity and immune disorders. Front Immunol. 2021, 12: 654960.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Structure of the BTLA protein. (From Wikipedia)
Fig.1 Structure of the BTLA protein. (From Wikipedia)
 Fig.2 Bidirectional signaling between BTLA and HVEM. (Ning, 2021)
Fig.2 Bidirectional signaling between BTLA and HVEM. (Ning, 2021)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure