CA15-3 Assay Portfolio Service
Aberrantly glycosylated MUC1 is overexpressed in several epithelial cancers and plays a vital role in the progression of many diseases. CA15-3 is the soluble product of the mucin 1 (MUC1) gene and is the most widely used serum marker in patients with breast cancer. With advanced and high-end technologies, rich experienced scientists, Creative Biolabs is an excellent service provider in the field of tumor marker assay. After long years ahead to fully comprehend tumor markers, we launch our CA15-3 assay portfolio service which can be useful for targeted cancer therapy and diagnosis.
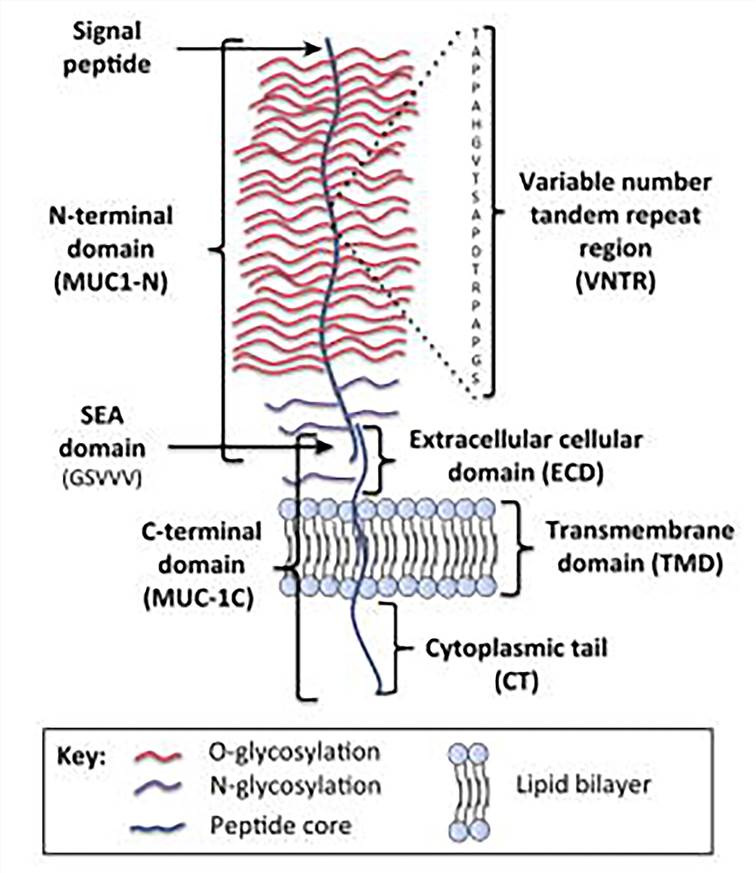 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the structure
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the structure
of MUC1. (Nath, 2014)
MUC1
MUC1, also known as CA15-3, episialin, PEM, H23Ag, EMA, and MCA, belongs to the human mucin family and is a single-pass type I transmembrane protein with a heavily glycosylated extracellular domain that extends up to 200-500 nm from the cell surface. Classically, MUC1 protects the external surfaces of epithelial tissue layers lining ducts and lumens in different parts of the body to the underlying epithelia by playing roles of protection, lubrication and hydration. However, compared to normal breast epithelial cells, aberrantly glycosylated MUC1 is overexpressed in breast cancer. It is also overpressed in various epithelial cancers and becomes a potential target for cancer therapy.
Expression of Tumor-associated MUC1
The altered expression of MUC-1 is involved in the pathogenesis of cancer metastasis and formation.
-
The carboxy-terminal subunit is implicated to drive cancer formation and cell proliferation.
-
The amino terminal subunit interacts with adhesion proteins such as ICAM-1 to play a role in the formation and progression of cancer.
-
The extended N-terminal domain of MUC-1 is related to block access of immune cells to tumors.
-
Direct targeting of MUC-1 with either synthetic peptides or antibodies was found to decrease the growth of tumors in mouse models.
When MUC1 is overexpressed in cancer cells, the loss of cell polarity can cause tumor-associated MUC1 to be redistributed within the cytoplasm and over the cell surface. Meanwhile, lack of cell polarity also can cause the redistribution of cell surface growth factors located in the basolateral surface of epithelial cells.
 Fig.2 MUC1 overexpression and loss of polarity in cancer cells. (Nath, 2014)
Fig.2 MUC1 overexpression and loss of polarity in cancer cells. (Nath, 2014)
CA15-3
CA15-3 is the soluble product of the MUC1 gene and is the most widely used serum marker of breast cancer. Elevated CA15-3 level is predictive of poor response to chemotherapy in locally advanced disease and is found in most patients with metastatic breast cancer.
CA15-3 Blockade Assays at Creative Biolabs Including but Not Limited to:
-
Proliferation assay
-
Metabolism assay
-
Invasion assay
-
Metastasis assay
-
Angiogenesis assay
-
Apoptosis assay
-
Chemoresistance assay
-
Inflammation assay
If you are interested in our service, please don't hesitate to contact us or directly send us.
Reference
-
Nath, S.; et al. MUC1: a multifaceted oncoprotein with a key role in cancer progression. Trends Mol Med. 2014, 20(6): 332-342.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the structure
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the structure Fig.2 MUC1 overexpression and loss of polarity in cancer cells. (Nath, 2014)
Fig.2 MUC1 overexpression and loss of polarity in cancer cells. (Nath, 2014)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure