CD22 Assay Portfolio Service
Structure and Expression of CD22
CD22 is a member of the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin type lectin (Siglec) family of immunomodulatory receptors. CD22 is a type I transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of 140 kDa. It consists of seven extracellular immunoglobulin domains and a 141-amino acid cytoplasmic tail. The extracellular domain of CD22 binds to α 2,6-linked sialic acid ligands linked to galactose, which are expressed on a number of cell types including erythrocytes, monocytes, certain endothelial cells, T cells and B cells. The transmembrane and cytoplasmic regions are equipped with signaling motifs, primarily based on immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition (ITIM). CD22 expression is restricted in B cells and has its main function on conventional B cells (also called B2-cells). On B cells, expression of CD22 is first apparent at the pro-B cell stage of B cell development in the bone marrow, reaching its highest expression, by the mature B cell stage in the periphery. CD22 maintains its high expression on naive B2, B1, marginal zone, memory and regulatory B cells. Like many other critical B cell receptors, the expression of CD22 is lost upon differentiation of B cells to plasma cells, with the intermediate expression on plasmablasts.
Functions of CD22
CD22 appears to have two distinct functions. First, CD22 has properties of an adhesion molecule and has high specificity for sialic acid in the α2,6-linkage (2,6Siα). Second, CD22 mediates a negative impact on the B cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway by dephosphorylating the associated cascade components via protein tyrosine phosphatases. On B cells, CD22 and Siglec-G mediate inhibition of BCR-induced signaling to inhibit B cell activation by dampening the calcium (Ca2+) response. In resting B cells, the conformation of the BCR is closed and CD22 is forming homo-oligomers (cis-interaction) distinct from the BCR. BCR signaling triggers depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores in the endoplasmic reticulum. This activates the opening of Ca2+ release-activated channels and triggers Ca2+ influx. When sialic acids expressed by antigen-presenting cells (APC) bind to CD22, the tyrosine residues of the ITIMs are phosphorylated. Ligation of the phosphorylated ITIMs to Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-1 and -2 (SHP-1 and SHP-2) induces a down-regulation of BCR-mediated signaling. CD22 activates the Ca2+ pump plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase-4 (PMCA4) and thereby controls Ca2+ efflux.
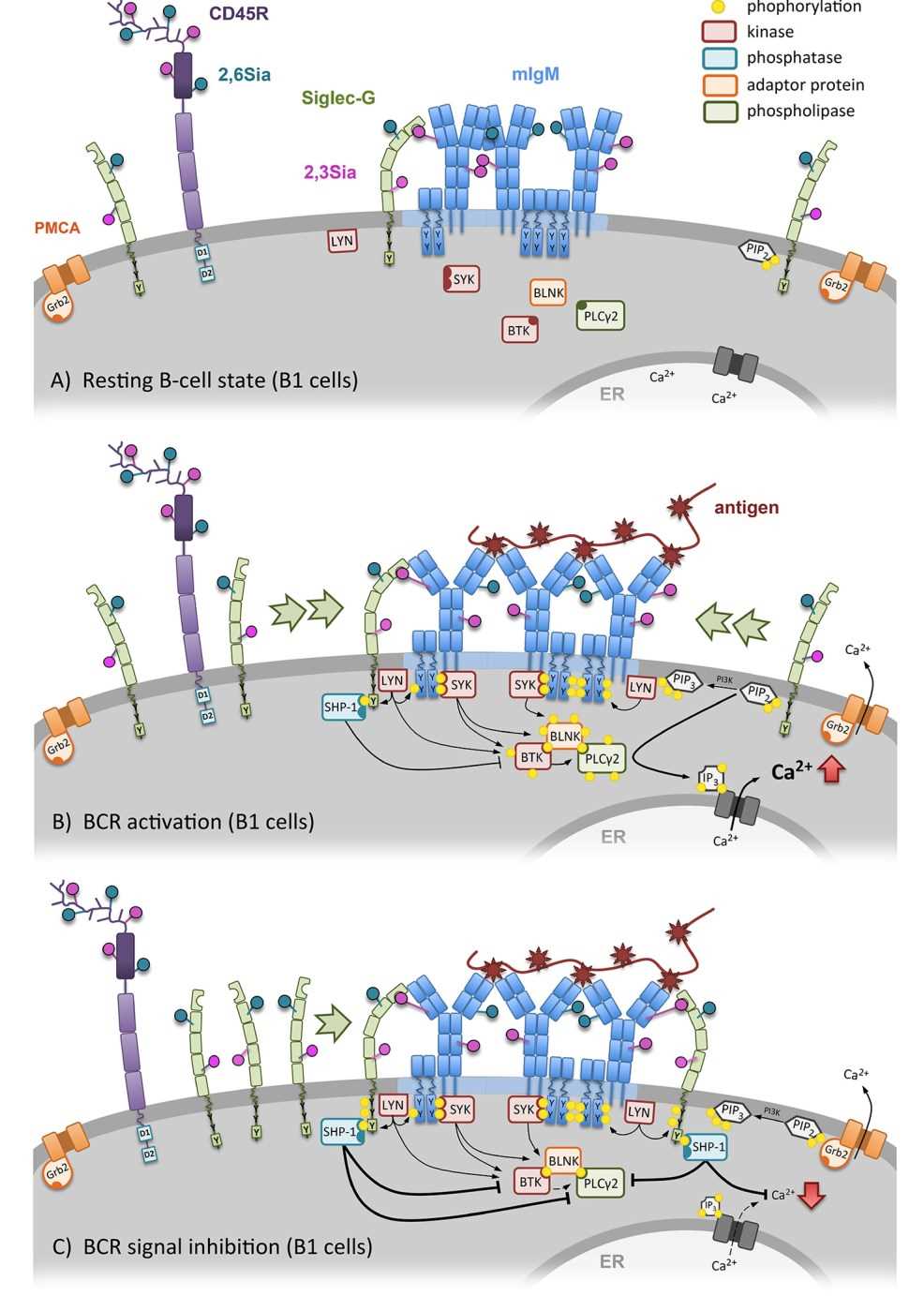 Fig.1 CD22 dependent regulation of the BCR signal. (Meyer, 2018)
Fig.1 CD22 dependent regulation of the BCR signal. (Meyer, 2018)
Roles of CD22 in Diseases
-
Cancer. Expression of CD22 by B-cell malignancies has been reported to vary from 60% to 85% depending on the histologic type. Monoclonal antibodies against CD20 have been widely used for the treatment of multiple lymphoid malignancies. CD22 is a targeted antigen of CAR-T cells in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and lymphoma trials.
-
Autoimmunity. CD22 contributes to the regulation of autoimmunity. Recent studies in mouse models have suggested a role for defects and loss of functionality in CD22 in the pathogenesis of the autoimmune disease, including systemic lupus erythematosus. Some recent data suggest that targeting Siglecs (such as CD22) and other inhibitory receptors on B cells is a promising new therapeutic approach for autoimmune diseases.
What Can We Offer?
As CD22 expression is restricted to B cells, it can serve as an important target for immunotherapy of B cell-mediated autoimmune diseases and B cell-related lymphomas. Because of the importance of CD22, Creative Biolabs provides a full set of CD22 assay portfolio services for research, which including but not limited to
-
In vitro B cell Siglec-engaging tolerance-inducing antigenic liposomes (STALs) assay
-
Ca2+ influx assay
-
Cell adhesion assay
-
CD22-Fc binding assay
-
Cell proliferation assay
-
Cytotoxicity assay
-
Cytokine assay
-
ELISA
-
Others. Western blotting, flow cytometry analysis, immunohistochemistry.
As a globally-oriented biotech company, Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing one-stop customized tumor marker assay services (e.g., CD22 assay portfolio service). We are proud to offer an expanding selection of assays and work with you to develop an optimum assay for your target. Our scientific team now provides professional and tailored solutions for our worldwide clients. Please feel free to contact us.
Reference
-
Meyer, S.J.; et al. B cell Siglecs-News on signaling and its interplay with ligand binding. Frontiers in Immunology. 2018, 9 (2820).
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 CD22 dependent regulation of the BCR signal. (Meyer, 2018)
Fig.1 CD22 dependent regulation of the BCR signal. (Meyer, 2018)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure