CD25 Assay Portfolio Service
The abundance of regulatory T cells (Treg) is related to poor prognosis and diminished anti-tumor immunity in human cancers. Studies have shown that CD25 is a potential target for Treg depletion in human and mouse malignancies. With advanced and high-end technologies, rich experienced scientists, Creative Biolabs is an excellent service provider in the field of tumor marker assay. After long years ahead to fully comprehend tumor markers, we launch our CD25 assay portfolio service which can be useful for targeted cancer therapy and diagnosis.
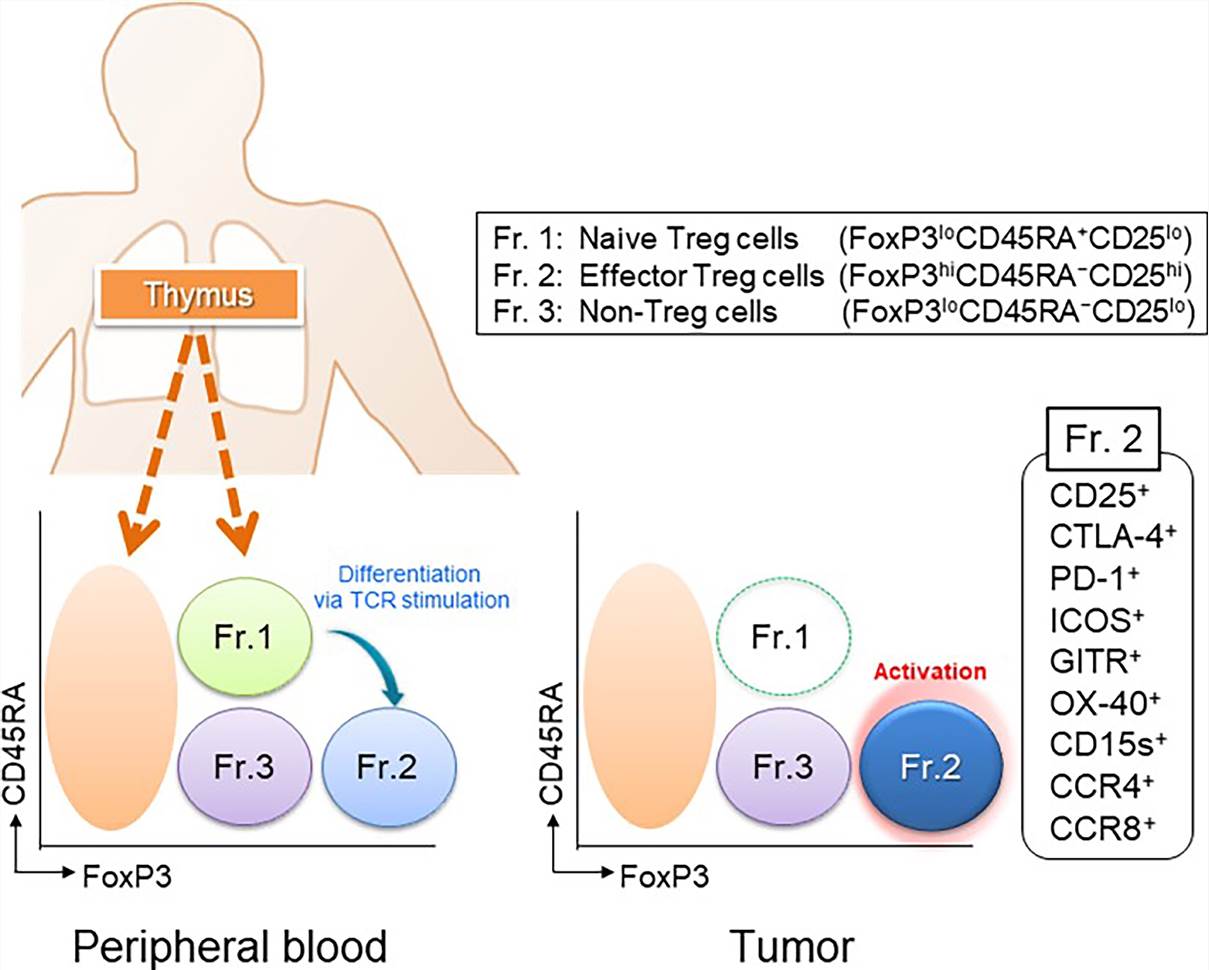 Fig.1 Classification of human Treg cells. (Ohue, 2019)
Fig.1 Classification of human Treg cells. (Ohue, 2019)
Treg
Treg is a kind of T-cell population that can functionally suppress the immune response via influencing the activity of another cell type and inhibit antitumor immune response in tumor‐bearing hosts. It suppresses immune functions through various mechanisms, such as consumption of IL‐2, CTLA‐4‐mediated suppression of APC function, production of immune-suppressive metabolites, and production of immunosuppressive cytokines. Additionally, Treg has a vital role in the control of autoimmunity, immune homeostasis, and anti-tumor immunity.
CD25
IL-2 is a key cytokine in regulating the activation and proliferation of immune cells. Under most physiological conditions, IL-2 exerts its biological effects through binding to the high-affinity IL-2R, consisting of IL-2Rα, IL-2Rβ, and γc, which is primarily found on activated T conventional and Treg cells.
CD25, also known as IL-2Rα, is part of the heterotrimeric IL-2 receptor that regulates normal immune function and is widely expressed on the surface of leukemias and lymphomas. IL2R are immediately overexpressed by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after T cell receptor (TCR) activation. Unlike other T cell subsets, CD25 was expressed in the high levels in the majority of Treg, while CD122 and CD132 were expressed in the intermediate levels.
Mechanism of CD25 Upregulation in Cells
Mechanism of CD25 upregulated expression in T cells occurs via different pathways. Allo-antigen or mitogen binding to T cells activates their T cell receptors, initiating a calcium influx leading to a cascade resulting in CD25 upregulation and phosphorylation of protein kinase C. In addition, the expression of CD25 by T cells is stimulated by contact with IL2, which induces a positive feedback loop that involves the binding of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 to the CD25 gene locus3. Except for its effects on IL2RA expression, the binding of IL2 to its heterotrimeric receptor stimulates effector function and T cell growth. This process occurs via signal transduction pathways following translocation and phosphorylation of dimerized STAT5 proteins, activated p70 S6 kinase, or mitogen-activated protein kinase to the nucleus, stimulating transcription.
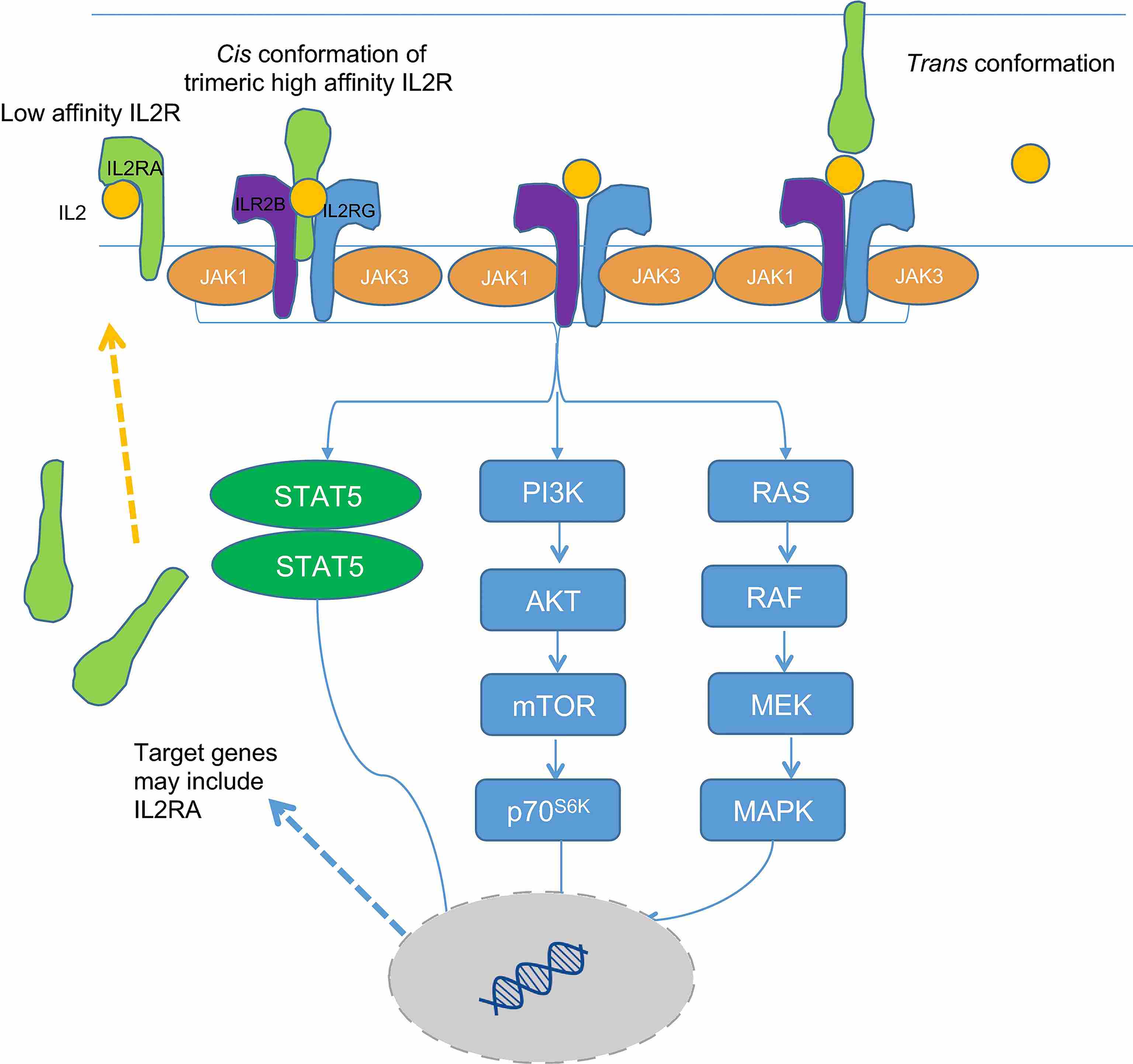 Fig.2 Representation of IL2R activation pathways in a stimulated T cell. (Flynn, 2017)
Fig.2 Representation of IL2R activation pathways in a stimulated T cell. (Flynn, 2017)
CD25 Blockade Assays at Creative Biolabs Including but Not Limited to:
-
Proliferate assay
-
Cytotoxicity assay
-
Activation assay
-
Cytokine assay
-
Immune modulation assay
If you are interested in our service, please contact us or directly send us.
References
-
Flynn, M.J.; et al. The emerging role of anti-CD25 directed therapies as both immune modulators and targeted agents in cancer. Br J Haematol. 2017, 179(1): 20-35.
-
Ohue, Y.; et al. Regulatory T (Treg) cells in cancer: can Treg cells be a new therapeutic target? Cancer Sci. 2019, 110(7): 2080-2089.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Classification of human Treg cells. (Ohue, 2019)
Fig.1 Classification of human Treg cells. (Ohue, 2019) Fig.2 Representation of IL2R activation pathways in a stimulated T cell. (Flynn, 2017)
Fig.2 Representation of IL2R activation pathways in a stimulated T cell. (Flynn, 2017)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure