CD30 Assay Portfolio Service
CD30 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNF-receptor) superfamily and is characteristically expressed in some hematopoietic malignancies, such as Hodgkin lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. The signaling of CD30 activates nuclear factor-kappa B (NFkB) transcription factor, leading to pleiotropic regulation of gene function. With advanced and high-end technologies, rich experienced scientists, Creative Biolabs is an excellent service provider in the field of tumor marker assay. After long years ahead to fully comprehend tumor markers, we launch our CD30 assay portfolio service which can be useful for targeted cancer therapy and diagnosis.
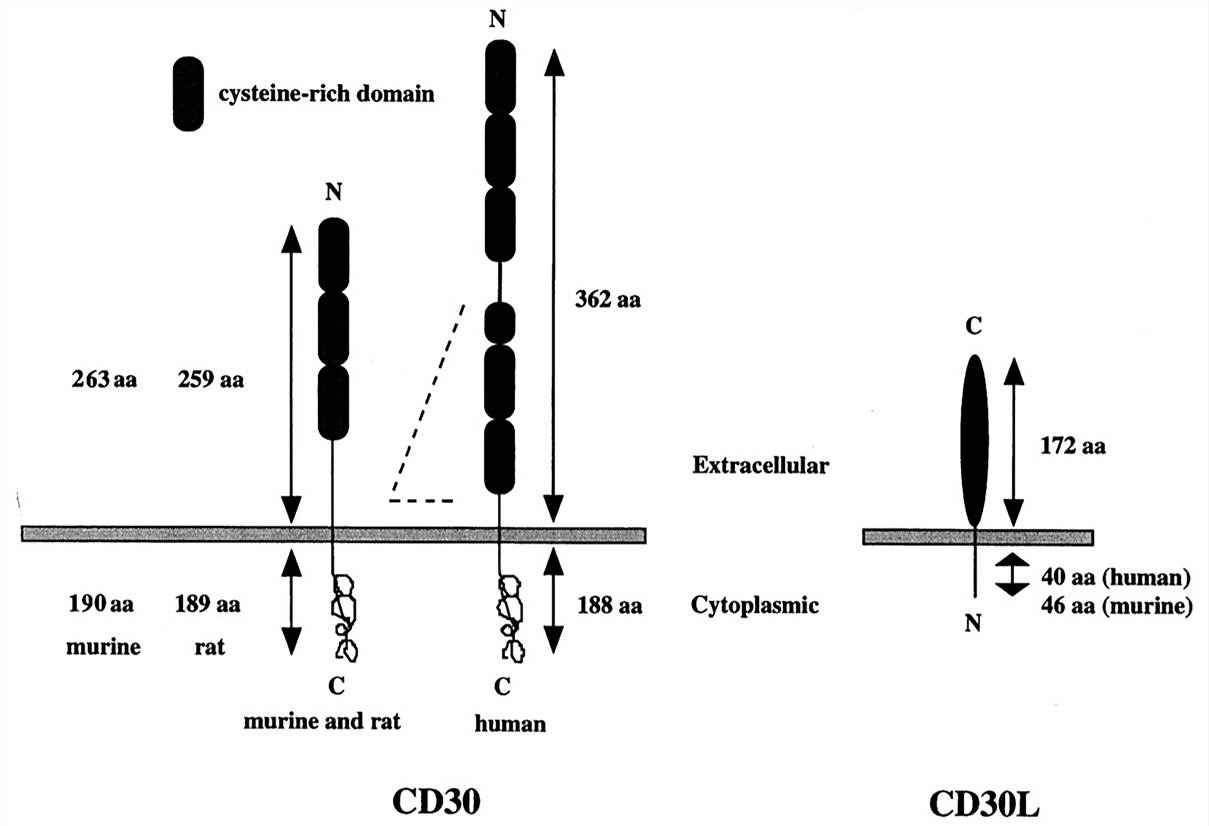 Fig.1 Schematic organization of CD30 and CD30L. (Horie, 1998)
Fig.1 Schematic organization of CD30 and CD30L. (Horie, 1998)
Biology of CD30
CD30, one of several members of the TNF-receptor family, is expressed on various types of germ cell tumors, Lymphomas, and multiple myeloma. CD30L, the ligand of CD30, is expressed in follicular B cell lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma, and adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Both are cell surface glycoproteins.
CD30 is a 120 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein consisting of an intracellular domain, an extracellular domain, and a transmembrane domain. The extracellular domain of CD30 is characterized by 6 cysteine-rich stretches of amino acids, which help to form a scaffold of disulfide bonds, creating an elongated structure. In addition, The intracellular cytoplasmic tail domain is characterized by several serine/threonine residues.
Function of CD30
-
CD30 expression following TCR stimulation needs CD28 or IL-4R signaling, and CD30 signals enhance T cell proliferation at low levels of in vitro TCR stimulation.
-
CD30 signaling regulates peripheral T cell responses, controlling T cell survival and down-regulating cytolytic capacity.
-
CD30 also regulates thymocyte survival.
Signaling Pathways of CD30
The effects of CD30 are mediated by a number of several signaling pathways.
-
Stimulation of CD30 molecule leads to trimerization and signal mediation through tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated proteins (TRAF1, TRAF2, and TRAF5), to stimulate the NFkB pathway.
-
CD30 ligation signal pathways play an important role in anti-apoptotic and pro-survival benefits in the neoplastic cell.
-
A positive feedback loop exists between the MAPK/ERK pathway and the nuclear transcription factor JunB, which is contributed to cell survival and the upregulation of CD30 expression.
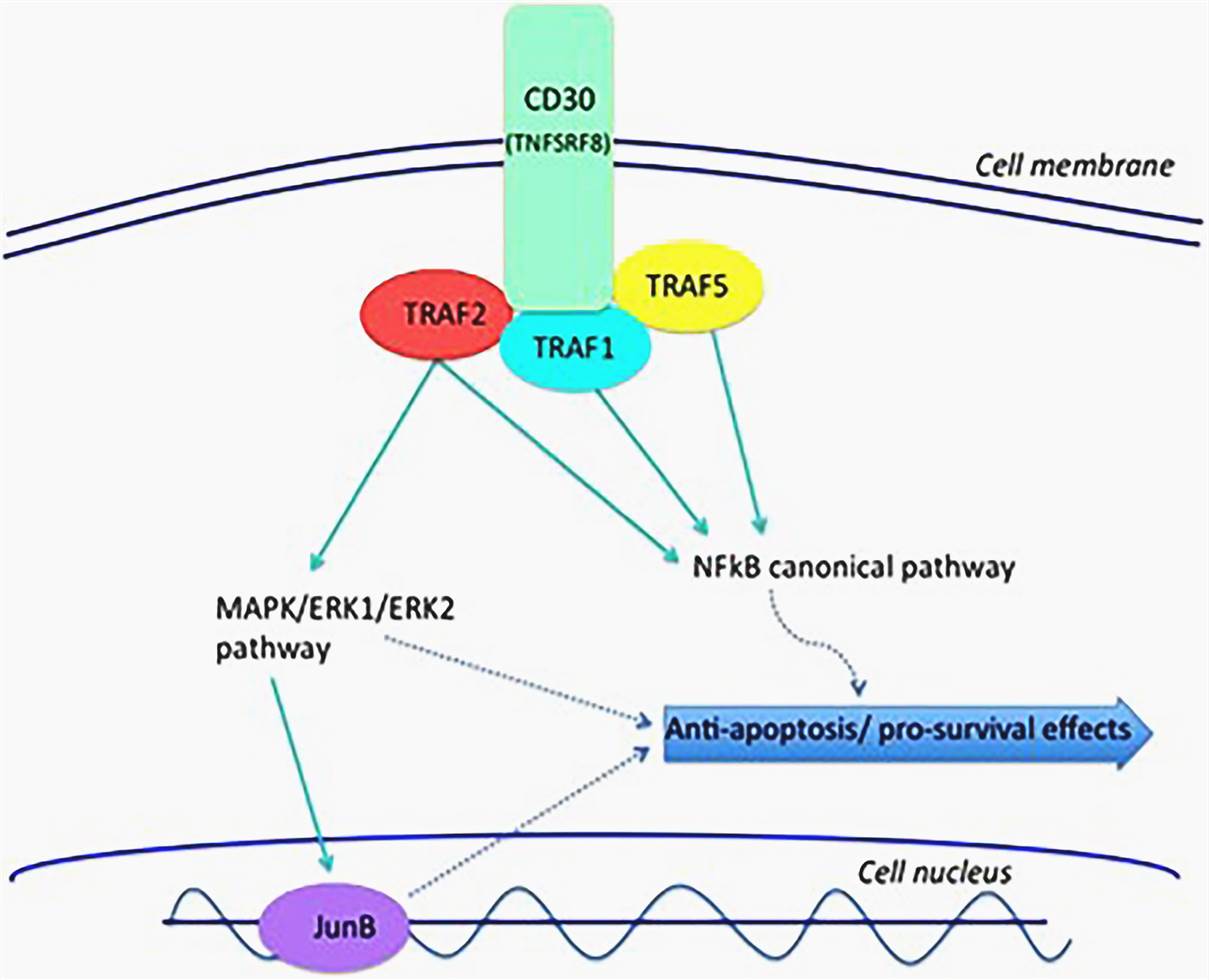 Fig.2 CD30 mediates its effects through a number of diverse signaling pathways. (Van der Weyden, 2017)
Fig.2 CD30 mediates its effects through a number of diverse signaling pathways. (Van der Weyden, 2017)
CD30 Blockade Assays at Creative Biolabs Including but Not Limited to:
-
Cytotoxicity assay
-
Proliferation assay
-
Apoptosis assay
-
Activation assay
-
Cytokines assay
If you are interested in our service, please contact us or directly send us.
References
-
Horie, R.; et al. CD30: expression and function in health and disease. Semin Immunol. 1998, 10(6): 457-70.
-
Van der Weyden, C.A.; et al. Understanding CD30 biology and therapeutic targeting: a historical perspective providing insight into future directions. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7: e603.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Schematic organization of CD30 and CD30L. (Horie, 1998)
Fig.1 Schematic organization of CD30 and CD30L. (Horie, 1998) Fig.2 CD30 mediates its effects through a number of diverse signaling pathways. (Van der Weyden, 2017)
Fig.2 CD30 mediates its effects through a number of diverse signaling pathways. (Van der Weyden, 2017)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure