CSF1R Assay Portfolio Service
The pre-eminent mechanism of cancer cells employed to evade apoptosis is aberrant co-expression of growth factors and their ligands, forming an autocrine growth loop that promotes tumor formation and progression. Colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) and its receptor CSF1R play an important role in regulating the homeostatic survival of tumor-associated macrophages, which promote tumorigenesis in many human cancers. With advanced and high-end technologies, rich experienced scientists, Creative Biolabs is an excellent service provider in the field of tumor marker assay. After long years ahead to fully comprehend tumor markers, we launch our CSF1R assay portfolio service which can be useful for targeted cancer therapy and diagnosis.
Introduction of CSF1R
CSF1R, also known as CD115 or macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor (M-CSFR), belongs to the type III protein tyrosine kinase receptor family, and exerting its biological functions in response to two competing ligands, namely CSF-1 or interleukin 34 (IL-34), induces homodimerization of the receptor and subsequent activation of receptor signaling. The signaling mediated by CSF1R is crucial for the survival and differentiation of the mononuclear phagocyte system, especially macrophages. CSF1R expression can be detected on tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and the other myeloid cells within the tumor microenvironment such as neutrophils, dendritic cells, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs).
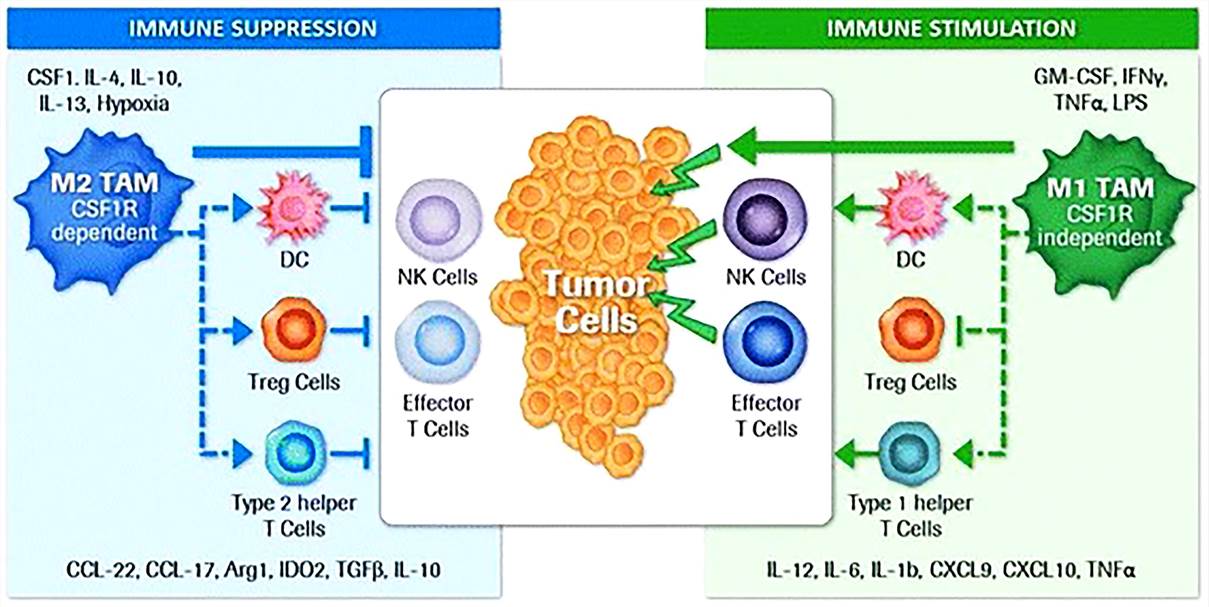 Fig.1 Regulation of immunity by tumor-associated macrophage subtypes. (Cannarile, 2017)
Fig.1 Regulation of immunity by tumor-associated macrophage subtypes. (Cannarile, 2017)
Functions of CSF1R
Binding to CSF-1 or IL-34 induces CSF1R chain dimerization, leading to cross-tyrosine phosphorylation and the direct association of signaling molecules with the receptor through their phosphotyrosine-binding domains. The resultant gene expression program promotes proliferation, differentiation, and survival of the cell. Except for promoting angiogenesis, CSF-1-educated TAMs have an important role in supporting tumor cell survival, proliferation, motility, and drug resistance as well as suppressing anti-tumor immunity. The production and recruitment of TAMs are regulated by the CSF-1/CSF-1R axis.
 Fig.2 CSF-1R signaling in myeloid cells. (Daniela, 2016)
Fig.2 CSF-1R signaling in myeloid cells. (Daniela, 2016)
CSF-1/CSF1R Axis in Cancer
CSF1/CSF1R, the product of the c-fms proto-oncogene, is the primary growth factor regulating the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of cells of the mononuclear phagocytic lineage. Many studies have illustrated that CSF-1/CSF1R plays a certain role in tumor tissues. The expression of CSF-1/CSF1R has been found in several human malignancies including breast, cervical, endometrial, ovarian, lung, prostate, and kidney cancer, as well as in classical Hodgkin's lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Especially, elevated serum levels of CSF-1 have been demonstrated in breast, ovarian, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
CSF1R Blockade Assays at Creative Biolabs Including but Not Limited to:
-
Survival assay
-
Invasion assay
-
Migration assay
-
Proliferation assay
-
Cytotoxic assay
-
Metastatic assay
-
Apoptosis assay
-
Angiogenesis assay
If you are interested in our service, please contact us or directly send us.
References
-
Cannarile, M.A.; et al. Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Immunother Cancer. 2017, 5(1): 53.
-
Achkova, D.; Maher, J. Role of the colony-stimulating factor (CSF)/CSF-1 receptor axis in cancer. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016, 44 (2): 333-341.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Regulation of immunity by tumor-associated macrophage subtypes. (Cannarile, 2017)
Fig.1 Regulation of immunity by tumor-associated macrophage subtypes. (Cannarile, 2017)
 Fig.2 CSF-1R signaling in myeloid cells. (Daniela, 2016)
Fig.2 CSF-1R signaling in myeloid cells. (Daniela, 2016)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure