FolRα Assay Portfolio Service
Biology of FolRα
Folate receptor alpha (FolRα, FRα), a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface glycoprotein, is a member of the folate receptors (FRs) family. FolRα is composed of 257 amino acids. There are four members (FolRα, FolRβ, FolRγ, and FolRδ) of FRs, with molecular weights ranging from 38 to 45 kDa. FolRα, FolRβ, and FolRδ are all GPI-anchored cell-membrane proteins, whereas FolRγ lacks a GPI-anchor region and is a secreted protein. Folate (an essential B vitamin) is necessary for proper cell growth and one-carbon transfer processes mediated by numerous enzymes that are involved in DNA synthesis. The FolRα structure is globular and folate binds in a pocket deep within FolRα. Furthermore, FolRα can be found to secrete as a soluble protein (sFolRα).
The Expression of FolRα
FolRα expression is restricted to a few epithelial tissues. In comparison to noncancerous cells, the expression of FolRα is quite strikingly elevated (100~300 times) in cancerous cells of epithelial origin, particularly the breast, lung, kidney, colon, and brain. However, some exception includes normal epithelia in the placenta, kidneys, and the choroid plexus, where FRs are overexpressed to maintain the necessities required for folates in nucleic acid synthesis and cellular growth. This difference in expression makes FolRα a very attractive therapeutic target for novel anticancer agents that would have limited toxicity in normal tissues.
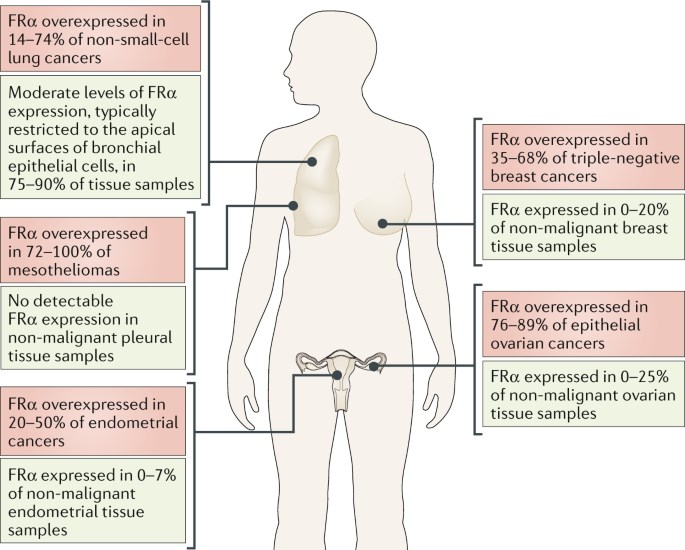 Fig.1 The expression of FolRα in cancers and non-malignant tissues. (Scaranti, 2020)
Fig.1 The expression of FolRα in cancers and non-malignant tissues. (Scaranti, 2020)
FolRα-mediated Internalization of Folates
FolRα is a folate-binding protein located on cellular membranes with high affinity and mediates its intracellular transport via receptor-mediated endocytosis. Folate binds specifically to FolRα creating a receptor-ligand complex. FolRα assisted by low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-related protein 2 (LRP2), gets internalized in caveolar structured early endosomes, which undergo acidification and subsequent fusion with lysosomes. GPI-specific phospholipase D cleaves FolRα from its GPI-anchor. FolRα is released and translocates to the nucleus via an unknown mechanism where it binds cis-regulatory elements of different gene promoters.
The Role of FolRα
-
Central nervous system
Brain folate transport has been primarily characterized at the choroid plexus where folate uptake is mediated by FolRα and proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT). Impaired cerebral folate transport is associated with various types of neurological and neurodevelopmental complications. Accumulating evidence has suggested that disruption of FolRα function also can lead to neural tube defects.
-
Cancer
Following folate uptake and internalization, FolRα can translocate to the nucleus and act as a transcription factor to directly regulate the expression of key developmental genes in cancer cells. In addition, folate uptake can promote cancer cell proliferation, migration, and loss of adhesion through downregulation of the cell-cell adhesion molecule, E-cadherin, promoting cellular motility and metastasis. The folate binding to FolRα results in the association of gp130 and FolRα. Signal transduction through gp130 activates Janus Kinases (JAK)/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) and MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) cascades lead to contribute to cancer malignancy.
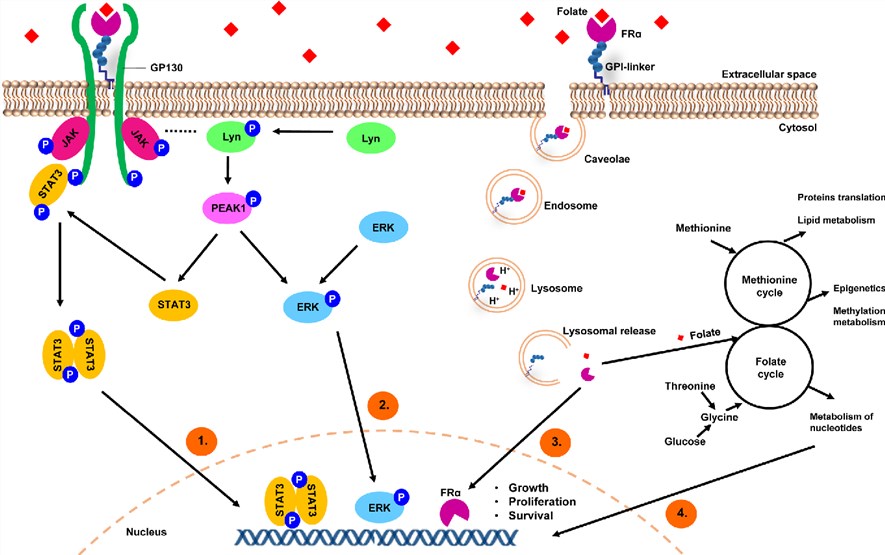 Fig.2 A model depicting FolRα-mediated internalization of folates and regulation of cancer signaling. (Cheung, 2016)
Fig.2 A model depicting FolRα-mediated internalization of folates and regulation of cancer signaling. (Cheung, 2016)
sFolRα
Membrane-associated FolRα can also be released by proteolytic cleavage with membrane-associated protease and GPI-specific phospholipases. This soluble form has been associated with cancer because of its high concentration in the serum of patients with cancer and poor folates levels, whereas healthy individuals exhibit low sFolRα concentrations and high folates levels. The sFolRα may be used as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker.
What Can We Offer?
FolRα is a unique tumor-associated antigen with many characteristics that make it an attractive target for immunotherapy in cancer. Because of the importance of FolRα, Creative Biolabs provides a full set of FolRα assay portfolio services for research, which. including but not limited to:
-
Cell adhesion assay
-
Folate binding and uptake assay
-
Cell proliferation assay
-
Cell apoptosis assay
-
Cell migration and invasion assay
-
Flow cytometry analysis
-
Others. Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, immunohistochemistry, etc.
Creative Biolabs offers a broad range of technologies, platforms, and assays for diagnostic applications and clinical biomarker and endpoint analysis. We have been dedicated to providing one-stop customized tumor marker assay services (e.g., FolRα assay portfolio service). Our scientific team now provides professional and tailored solutions for our worldwide clients. Please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Scaranti, M.; et al. Exploiting the folate receptor alpha in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020, 17(6): 349-359.
-
Cheung, A.; et al. Targeting folate receptor alpha for cancer treatment. Oncotarget. 2016, 7(32): 52553-52574.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 The expression of FolRα in cancers and non-malignant tissues. (Scaranti, 2020)
Fig.1 The expression of FolRα in cancers and non-malignant tissues. (Scaranti, 2020)
 Fig.2 A model depicting FolRα-mediated internalization of folates and regulation of cancer signaling. (Cheung, 2016)
Fig.2 A model depicting FolRα-mediated internalization of folates and regulation of cancer signaling. (Cheung, 2016)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure