LAG-3 Assay Portfolio Service
LAG‑3 is a new generation of immunotherapy targets and plays a balanced regulatory role in the human immune system. With advanced and high-end technologies, rich experienced scientists, Creative Biolabs is an excellent service provider in the field of tumor marker assay. After long years ahead to fully comprehend tumor markers, we launch our LAG-3 assay portfolio service which can be useful for targeted cancer therapy and diagnosis.
Structural Aspects of LAG
LAG-3, also known as CD223, is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is composed of a transmembrane region, an extracellular region and an intracellular region and has a molecular weight of 70 kDa. The gene of LAG-3 contains 8 exons, and the corresponding cDNA encodes a membrane protein, with 498 amino acids.
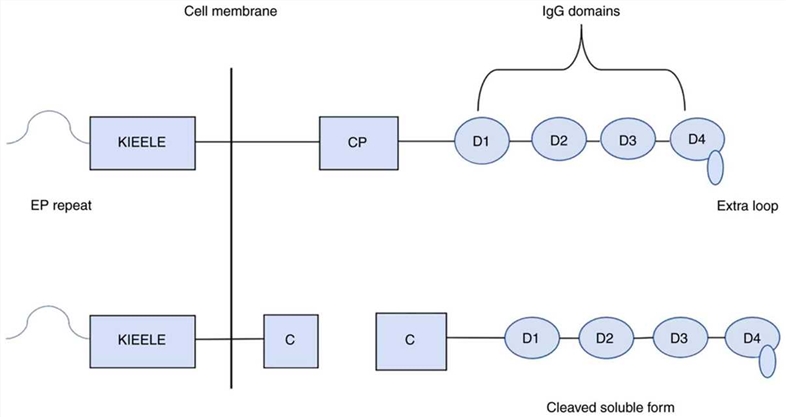 Fig.1 LAG-3 structure. (Shan, 2020)
Fig.1 LAG-3 structure. (Shan, 2020)
The expression of LAG-3 is detected on activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), a subpopulation of NK cells, B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. In addition, LAG-3 is highly expressed in chronic virus infection and various tumors. It is involved in regulating the proliferation and activation of T lymphocytes and effector T lymphocytes, and plays a specific role in maintaining environmental stability in vivo. Overexpression of LAG-3 is also associated with autoimmune diseases, tumors and chronic toxic infectious diseases.
LAG Ligands
-
Galectin-3
Galectin-3, a 31 kDa galactose-binding lectin, was found to interact with LAG-3 and inhibit the secretion of interferon-γ by CD8+ T cells in vitro, which regulates T cell activation and immunoprecipitation.
-
LSECtin
LSECtin is a member of the DC-SIGN family of molecules binding to the four glycosylated sites on LAG-3. It participates in a mechanism that LAG-3 can regulate CD8+ T cells and NK cell function in these environments.
-
α-synuclein
α-synuclein fibrils, a protein aggregation, is a member of the Syn fibrils family. α-synuclein was found to bind to LAG-3, which leads to the intercellular delivery of pathological α-syn fibrils, while blocking their combination with a LAG-3 Ab could significantly reduce the toxicity and the intercellular delivery of pathological α-syn fibrils.
-
Fibrinogen-like protein 1
FGL1 was found to tightly bind to the LAG-3 receptor. When FGL1 binds to the LAG-3 receptor on the surface of T cells, T cell proliferation was inhibited and immune activity was also affected. Moreover, blocking the interaction between FGL1 and LAG-3 could enhance the antitumor effect of T lymphocytes, which has important significance in the research of tumor immunotherapy.
LAG-3 Functions
-
Role in CD4 T Cell Function and Expansion
Researches have shown the role of LAG-3 in regulating the expansion of both CD4 and CD8 T cells and its role as a negative regulator. However, LAG-3 molecules lacking the KIEELE domain could not negatively modulate T cell function in vitro or in vivo.
-
Role of LAG-3 on Regulatory T Cells
Research has demonstrated that LAG-3-blocking antibody mitigates Treg function in vivo, and transfection of antigen-specific CD4 T cells with full-length, but not truncated, LAG-3 could confer in vitro regulatory properties.
-
Role of LAG-3 on CD8 T Cells
Studies using LAG-3 knockout animals have confirmed the role for LAG-3 in regulating CD8 T cell homeostatic proliferation, as well as in the in vivo response to a superantigen.
-
LAG-3 Mechanism of Action
Studies have shown that expression of a non-cleavable form of LAG-3 mediated an irreversible defect in T cell function, showing that LAG-3 cleavage was a major mechanism by which its negative regulatory function was mitigated.
LAG-3 Signaling
-
The interaction of LAG-3 with MHC-II prohibits the binding of the same MHC molecule to a TCR and CD4, thus suppressing TCR signal. LAG-3 transmits an inhibitory signal via the KIEELE motif in the cytoplasmic tail.
-
Crosslinking of LAG-3 and CD3/TCR complex can impair T cell proliferation, cytokines secretion, and calcium ion fluxes.
-
LAG-3 interacts with Gal-3 and LSECtin who expressed on melanoma cells to modulate CD8+ T cell function within the TME.
-
LAG-3 inhibits T cell activation collectively with other immune checkpoints, especially PD-1.
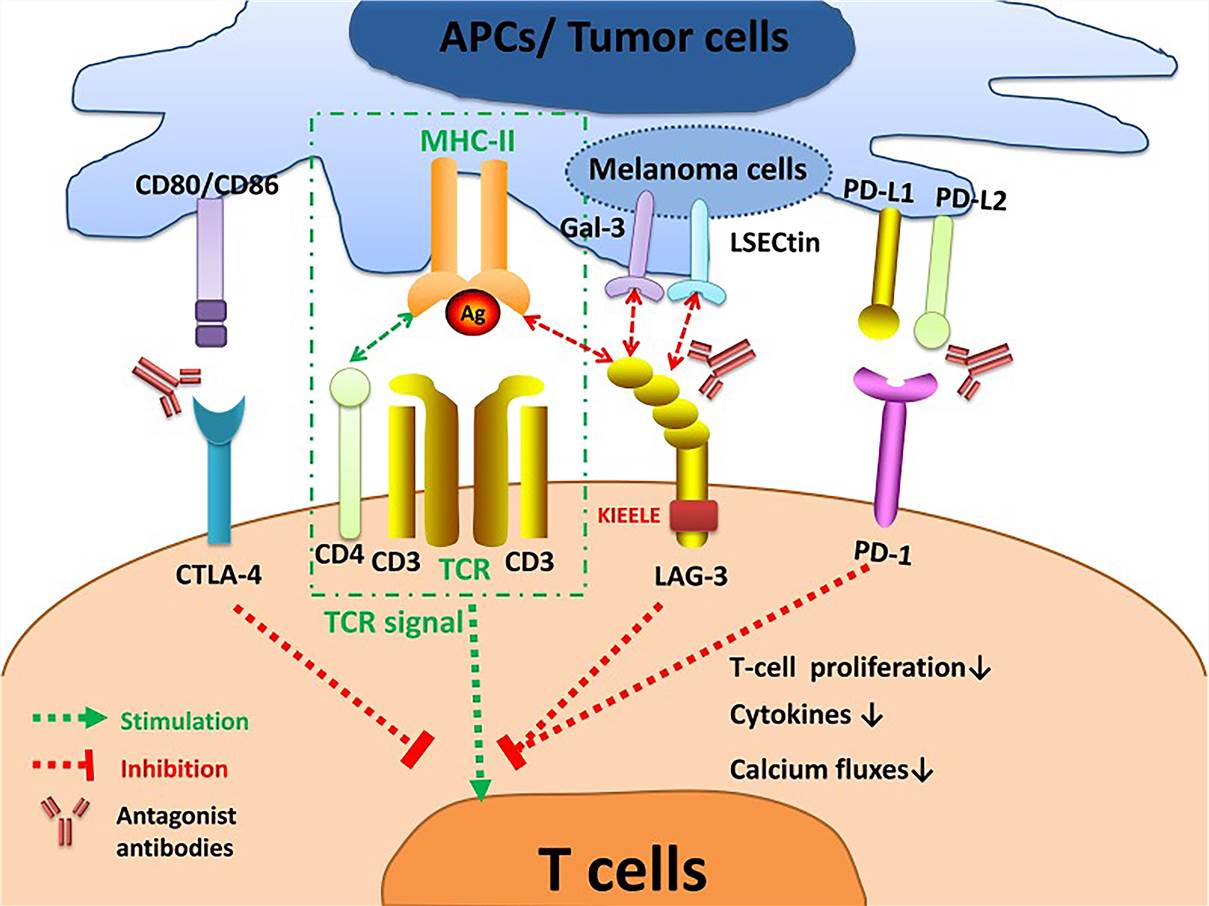 Fig.2 LAG-3 signaling and the interplay with other immune checkpoints. (Long, 2020)
Fig.2 LAG-3 signaling and the interplay with other immune checkpoints. (Long, 2020)
LAG-3 Blockade Assays at Creative Biolabs Including but Not Limited to:
-
Proliferation assay
-
Invasion assay
-
Metastases assay
-
Cytokine assay
-
Apoptosis assay
-
Cytotoxicity assay
-
Immune responses assay
If you are interested in our service, please contact us or directly send us.
References
-
Shan, C.; et al. Progress of immune checkpoint LAG-3 in immunotherapy. Oncol Lett. 2020, 20(5): 207.
-
Long, L.; et al. The promising immune checkpoint LAG-3: from tumor microenvironment to cancer immunotherapy. Genes Cancer. 2018, 9(5-6): 176-189.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 LAG-3 structure. (Shan, 2020)
Fig.1 LAG-3 structure. (Shan, 2020)
 Fig.2 LAG-3 signaling and the interplay with other immune checkpoints. (Long, 2020)
Fig.2 LAG-3 signaling and the interplay with other immune checkpoints. (Long, 2020)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure