LMP1 Assay Portfolio Service
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is a vital effector of EBV-mediated B cell transformation. LMP1 exhibits potent oncogenic properties, and takes a key role in epithelial cells and B cells. Therefore, LMP1 obtains considerable attention as a good therapeutic target and potential prognostic biomarker. With advanced and high-end technologies, rich experienced scientists, Creative Biolabs is an excellent service provider in the field of tumor marker assay service. After long years ahead to fully comprehend tumor markers, we launch our LMP1 assay portfolio service which can be useful for targeted cancer therapy and diagnosis.
EBV
EBV is a tumorigenic human herpes virus that is implicated in a number of human malignant diseases of either B-cells or epithelial and other cells. The EBV-related B-cell cancers include Hodgkin's disease (HD), endemic Burkitt's lymphoma (BL), and lymphoid tumors appearing in immunosuppressed patients; the epithelial cell cancers include gastric cancers and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Different patterns of latent EBV gene expression are observed in these tumors, which can alter the phenotype and cause oncogenic transformation of EBV-infected cells. LMP1 from EBV has been identified as the main transforming oncoprotein of EBV.
Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1)
LMP1 signals of EBV-associated cancers are involved in the regulation of proliferation, immortalization, invasion, immune evasion, and angiogenesis of tumor cells. Researches identified LMP1 protein as an integral membrane protein and consists of three domains critical for EBV-mediated B-cell growth transformation: a short cytoplasmic N-terminus (amino acids 1-23), six transmembrane spanning regions (amino acids 24-186), and a large cytoplasmic C-terminal tail (amino acids 187-386). LMP1 functions as a constitutively active tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR), and activates a number of signaling pathways, including NF-κB, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and interferon regulatory factor pathways. Functionally, through these signaling events, LMP1 has been confirmed that transforming rodent fibroblast cells can cause B lymphocyte immortalization in vitro in certain instances, and induce hyperplasia in transgenic mice. In addition, LMP1 resembles CD40, it can substitute for CD40 in vivo, to enhance B lymphocyte proliferation.
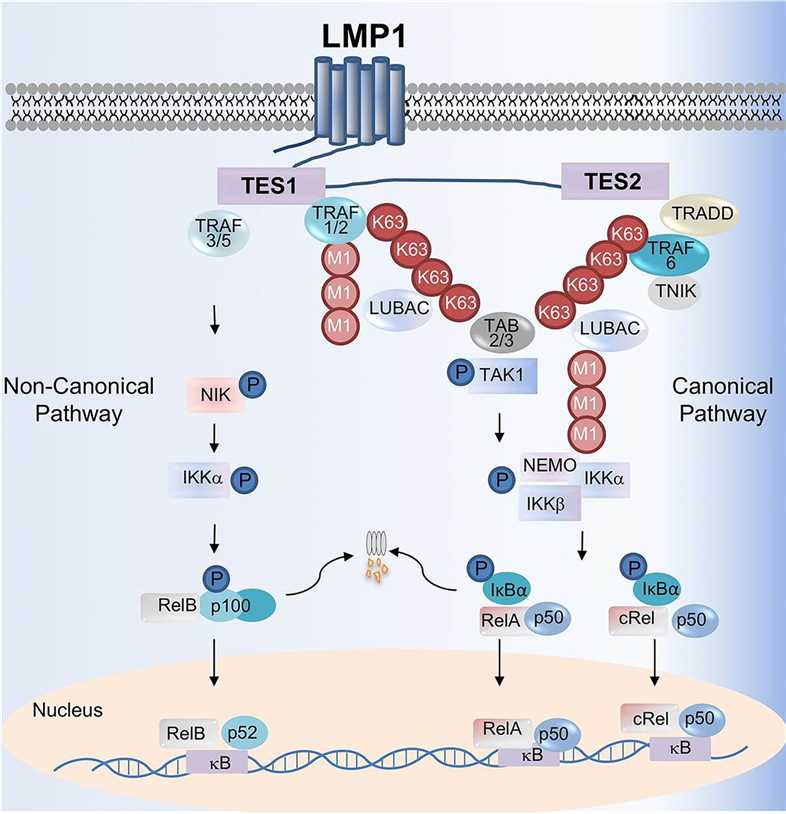 Fig.1 LMP1-mediated canonical and noncanonical NF-κB activation pathways. (Wang, 2017)
Fig.1 LMP1-mediated canonical and noncanonical NF-κB activation pathways. (Wang, 2017)
LMP1 Stimulation Assays at Creative Biolabs including but Not Limited to:
-
Pro-inflammatory cytokines assay
-
Apoptosis assay
-
Cell motility assay
-
Cell invasion assay
-
Cell migration assay
-
Cell proliferation assay
-
Angiogenesis assay
-
Cellular micro-RNAs (miRs) assay
-
Variants and NPC assay
-
Epithelial-mesenchyme-transition (EMT) assay
-
G1-S cell-cycle checkpoint assay
-
Expression of key tumor suppressor genes assay
If you are interested in our service, please contact us or directly send us.
References
-
Wang, L.W.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus LMP1-mediated oncogenicity. J Virol. 2017, 91(21): e01718-16.
-
Dawson, C.W.; et al. The role of the EBV-encoded latent membrane proteins LMP1 and LMP2 in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Semin Cancer Biol. 2012, 22(2): 144-53.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 LMP1-mediated canonical and noncanonical NF-κB activation pathways. (Wang, 2017)
Fig.1 LMP1-mediated canonical and noncanonical NF-κB activation pathways. (Wang, 2017)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure