Membrane Adsorption Assay
In the past few decades, membrane adsorption hasn't been a widely adopted method to remove endotoxin due to its lower binding capacity than that of traditional methods, such as chromatography. It has been reported that as the initial endotoxin concentration was increased, the removal efficiency was decreased demonstrating the limited binding capacity using a nylon membrane. The removal efficiency was only 65%, even if at the lowest endotoxin concentration of 387 EU/mL. Recently, the membrane adsorbers with high-efficiency endotoxin removal and binding have been synthesized. For example, amphiphilic carbonaceous particles (ACPs) incorporated in polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) matrix absorbers have been successful at removing endotoxins from BSA protein solutions at >99.8%.
With the rich project experience, mature and reliable expert team in terms of endotoxin removal, Creative Biolabs provides membrane adsorption assay which exploits the phenomenon of selective adsorption to remove endotoxin.
Membrane Adsorption
Membrane adsorption exploits the same mechanisms used in affinity and ion-exchange chromatography. The preparation of the membrane adsorber entailed four steps: (1) first activation; (2) coating with PVA; (3) second activation; (4) ligand immobilization. Fig.1 depicts an illustration of the immobilization strategy.
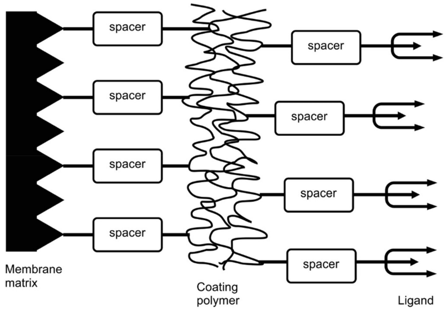 Fig.1 Schematic representation of membrane adsorber structure. (Almeida, 2016)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of membrane adsorber structure. (Almeida, 2016)
Source of the Membrane
-
Nylon
-
PEVA
-
PVA
-
PVDF
-
Cellulose
-
Cellulose acetate
Comparative of Different Membrane
|
Membrane
|
Properties
|
|
Nylon
|
The highly porous structure provides a large contact area for endotoxin adsorption; mechanic stability allows the adsorber to withstand high pressures; the availability of reactive groups, such as OH, NH2, SH, COOH, is convenient for ligand immobilization; thermal and chemical stability.
|
|
PEVA
|
Non-specific endotoxin binding; different ligands for the removal of endotoxins, such as polymyxin B, histamine, histidine, protamine, poly (L-lysine), poly (ethylene imine), dimethylamine, deoxycholate and others, having moderate or high efficiency, can be immobilized.
|
|
PVA
|
Different ligands for the removal of endotoxins, such as polymyxin B, histamine, histidine, protamine, poly (L-lysine), poly (ethylene imine), dimethylamine, deoxycholate and others, having moderate or high efficiency, can be immobilized.
|
|
Cellulose
|
Different ligands for the removal of endotoxins, such as polymyxin B, histamine, histidine, protamine, poly (L-lysine), poly (ethylene imine), dimethylamine, deoxycholate and others, having moderate or high efficiency, can be immobilized.
|
|
Cellulose acetate
|
Deacetylation of cellulose acetate is required to increase the number of reactive hydroxyl groups, which can modify membrane pore size distribution and reduce the material´s mechanical stability.
|
Features
-
Reduction of processing time and initial investment
-
Minor or zero loss of the product
-
Great improvement of flow rates and the elimination of diffusion limitations
-
Decrease chance of product contamination, reduction of process time and decrease buffer volume
Creative Biolabs offers improvements of one or more of the above methods, or a combination of multiple methods to achieve the viable needs for your endotoxin removal project. If you are interested in our membrane adsorption assay, please feel free to contact us or directly send us an inquiry.
References
-
Mason, S.; et al. Current technologies to endotoxin detection and removal for biopharmaceutical purification. Authorea. 2019.
-
Almeida.; et al. Membrane adsorber for endotoxin removal. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2016, 52(1): 171-178.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Schematic representation of membrane adsorber structure. (Almeida, 2016)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of membrane adsorber structure. (Almeida, 2016)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure