MUC16 Assay Portfolio Service
Structure of MUC16
Mucins are high molecular weight glycoproteins that are synthesized by epithelial cells and serve several functions that include lubrication, cell signaling, and the formation of chemical barriers. MUC16 (also named CA125), a member of the mucins family, is overexpressed in breast, ovarian and pancreatic tumors and plays an important role in progression and metastasis. MUC16 has cytoplasmic, transmembrane, and extracellular components that harbor variable O- and N-glycosylation sites. The peptide component of MUC16 has approximately 22,152 amino acids. The N-terminal domain of MUC16 has 12,000 amino acids and exclusively harbors O-glycosylation. A considerable portion of its peptide component is composed of the tandem repeat region with 60+ repeats of 156 amino acids. MUC16 harbors about 56 sea-urchin, enterokinase, and agrin (SEA) domains. SEA domain is a shared feature among mucins, and this domain is involved in the cleavage and association of MUC16 subunits. The transmembrane domain is followed by a 32 amino acids cytoplasmic tail with possible phosphorylation sites. MUC16 is cleaved from an extracellular site with approximately 12 amino acids from the plasma membrane. The cleavage product is a 17 kDa molecule that harbors the repetitive MUC16 epitope throughout its tandem repeat domains.
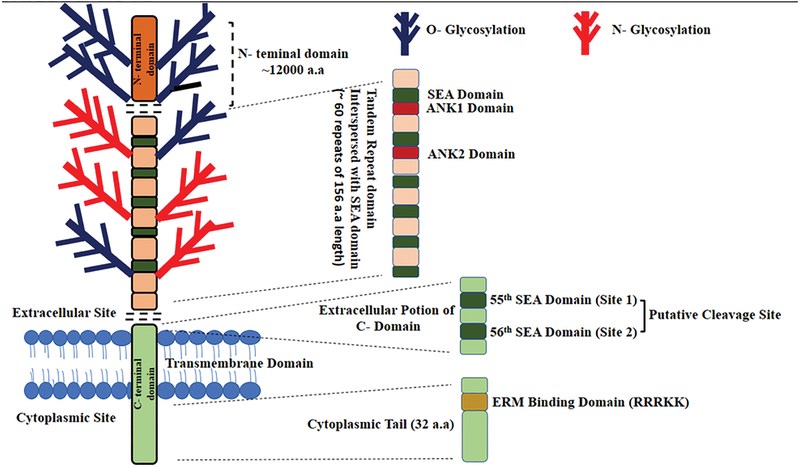 Fig.1 MUC16 structure. (Aithal, 2018)
Fig.1 MUC16 structure. (Aithal, 2018)
Role of MUC16 in Cells
MUC16 is overexpressed in many cancer types and plays an active role in ovarian tumorigenesis. The evidence indicates MUC16 is correlative with the development and worse prognosis of cancer.
-
Immunoprotection of cancer cell cells. Natural killer (NK) cells and monocytes are unable to attack tumor cells expressing high levels of MUC16. Due to its extended structure and overall negative charge, MUC16 may inhibit intimate interactions between NK and cancer cells. Imunoprotective effect by MUC16 may also arise from its interaction with the NK cell inhibitory receptor, Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 9 (Siglec 9).
-
Proliferation. Interaction of MUC16 with cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase-Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) can result in increased proliferation, cancer stem cell phenotype, and enhanced metastasis by upregulation of cyclin-D1 and genes (such as LMO2 and NANOG).
-
Pro-metastasis. Mesothelin and selectins can mediate metastasis of cells expressing MUC16 by glycosylation-dependent binding of MUC16.
Clinical Applications
-
A diagnostic marker for ovarian cancer.
Due to its aberrant overexpression, MUC16 is a promising target for diagnosis. Despite the identification of numerous new biomarkers, MUC16 is still superior to the majority of novel biomarkers, including human epididymis protein 4 (HE4). MUC16 is an indicator to monitor cancer recurrence and distinguish benign pelvic masses from ovarian cancer.
-
Therapy
-
Immunotherapy. Owing to the clinical importance of MUC16, several studies have attempted to target MUC16 therapeutically by antibodies. In-depth research should be carried out to enhance the efficacy of antibody-based therapeutics.
-
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. Immunotherapy based on CAR T-cell holds promise as an alternative avenue for MUC16 based immunotherapy.
-
Targeting MUC16-other molecular Interactions. Efforts to disrupt the functional cooperation of MUC16 and its interacting partners are viewed as an interesting therapeutic intervention. MUC16-mesothelin interaction is of unusually high affinity. Anti-mesothelin antibodies that interfere with mesothelin MUC16 binding have been developed as immunotherapeutic agents.
 Fig.2 MUC16 interactome and possible therapeutic intervention. (Das, 2015)
Fig.2 MUC16 interactome and possible therapeutic intervention. (Das, 2015)
What Can We Offer?
MUC16 as a biomarker plays an important role in the screening, treatment, and follow-up phases of ovarian cancer management. Recent studies indicate that MUC16 can contribute to ovarian tumor growth and metastasis. Creative Biolabs provides a full set of MUC16 assay portfolio services, which including but not limited to
-
Cell proliferation assay (such as CCK8, MTT, EDU, colony formation assays)
-
Cell migration assay and invasion assay
-
Growth kinetics assay
-
Apoptosis assay
-
Cell conjugation assay
-
Slot blot galectin-3 binding assay
-
Barrier function assay
-
Others. Western blotting and lectin blotting, immunoprecipitation analysis, ELISA, flow cytometry analysis, immunohistochemistry.
Creative Biolabs is committed to providing a series of customized tumor marker assay services (e.g., MUC16 assay portfolio service). We are proud to offer all range of services list to meet your various demands. We are consistent to deliver efficient and high-quality services within the shortest timeline. Please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Aithal, A; et al. MUC16 as a novel target for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018, 22(8): 675-686.
-
Das, S.; Batra, S.K. Understanding the unique attributes of MUC16 (CA125): potential implications in targeted therapy. Cancer Res. 2015, 75(22): 4669-4674.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 MUC16 structure. (Aithal, 2018)
Fig.1 MUC16 structure. (Aithal, 2018)
 Fig.2 MUC16 interactome and possible therapeutic intervention. (Das, 2015)
Fig.2 MUC16 interactome and possible therapeutic intervention. (Das, 2015)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure