Probiotic Modification of Gut Microbiota
Probiotics are live microorganism and they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut flora. Creative Biolabs offers high-quality services for prebiotic modification of gut microbiota to facilitate your microbe research.
Probiotic
-
Definition
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines probiotics as "live microorganisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host."
-
Source
Live probiotic cultures are part of fermented dairy products, other fermented foods, and probiotic-fortified foods.
-
Lactic acid bacteria (LABs), a kind of food fermenting bacteria, can prevent food spoilage and improve the nutritive value of the foods.
-
Fermented products that contain lactic acid bacteria (LAB): vegetables such as pickled vegetables, bread-like products made without wheat or rye flour, fermented cereal-fish-shrimp mixtures and fermented meats.
-
Side Effect
Though probiotics are considered safe, there still have some concerns about their safety in certain cases:
-
Within immunodeficiency, short bowel syndrome, central venous catheters, and cardiac valve disease, and premature infants, may be at higher risk for adverse events.
-
Lactobacillus spp. has been suggested to contribute to obesity in humans.
-
Mechanisms of Action
-
Colonization resistance. Probiotics inhibit colonization of pathogenic bacteria by releasing antimicrobial peptides, lowering luminal pH and/or directly interacting with pathogens.
-
Modulating immunity. Probiotics have a distinct immunomodulatory effect to reduce colonic inflammation or enhance antitumor immunity.
-
Enhanced gut barrier function. Probiotics increase mucin production and tight junction protein expression and promoted epithelial restitution.
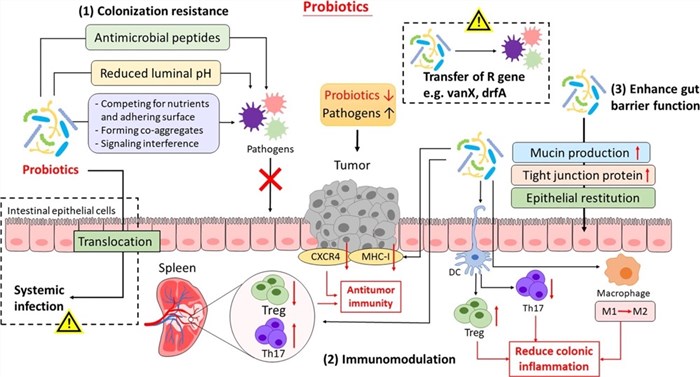 Fig.1 Mechanisms of action of probiotic. (Fong, 2020)
Fig.1 Mechanisms of action of probiotic. (Fong, 2020)
Probiotic Modification of Gut Microbiota
-
Probiotics are used to manipulate gut microbiota, and exert both anti-cancerous and anti-mutagenic activities.
-
Probiotics effectively protect the intestinal mucosa barrier in colorectal cancer after surgical procedures.
-
Probiotics are used as a therapeutic method to prevent infections with colorectal cancer in the postoperative period.
-
Next-generation probiotics (NGPs) are considered a novel potential therapeutic strategy to improve colorectal cancer (CRC).
Probiotics have been suggested as preventive and therapeutic measures to restore the healthy composition and function of the gut microbiome. Nevertheless, much data from human microbiome research lead to the identification of novel indigenous microbial species and tools to positively induce alterations in the gut microbial communities. Scientists at Creative Biolabs yield insights into the biology and potential manipulation of the microbiome in the human host by well-designed experiments in in vitro or in vivo models. We also provide metagenomic, metatranscriptomic and metabonomics technology to globally explore interactions between probiotics, intestinal microbes and the mammalian gastrointestinal tract.
Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive and professional Gut Microbiota Engineering Services to meet all the needs of our customers. If you have interest, please contact us for further discussion about your gut microbiota engineering needs.
References
-
Fong, W.; et al. Gut microbiota modulation: a novel strategy for prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2020, 4925-4943.
-
Floch, M. H.; et al. Modification of the gut microbiota to promote human health. Clinical Insights: Probiotics, Prebiotics and Gut Health. 2014, 15-34.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Mechanisms of action of probiotic. (Fong, 2020)
Fig.1 Mechanisms of action of probiotic. (Fong, 2020)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure