ROR1 Assay Portfolio Service
Structure
Receptor tyrosine kinase orphan receptors 1 (ROR1) are transmembrane proteins within the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. Human ROR1 is located on chromosomal region 1p31.3 and consists of 937 amino acids (908 after cleavage of the signal peptide) with an estimated molecular weight of 105 kDa. However, post-translational modification of ROR1 adds numerous N-glycosylation regions causing the final protein molecular weight to be about 130kDa. The structure of human ROR1 consists of an extracellular immunoglobulin-like (Ig) domain at the amino terminus, followed by a cysteine-rich domain known as a Frizzled domain (FZD) or CRD, and then a Kringle domain (KRD) into a transmembrane domain. The FZD is thought to mediate receptor-ligand interaction. On the intracellular side, ROR1 possesses a tyrosine kinase domain (TKD), two serine/threonine-rich domains (Ser/Thr), and a proline-rich domain (PRD).
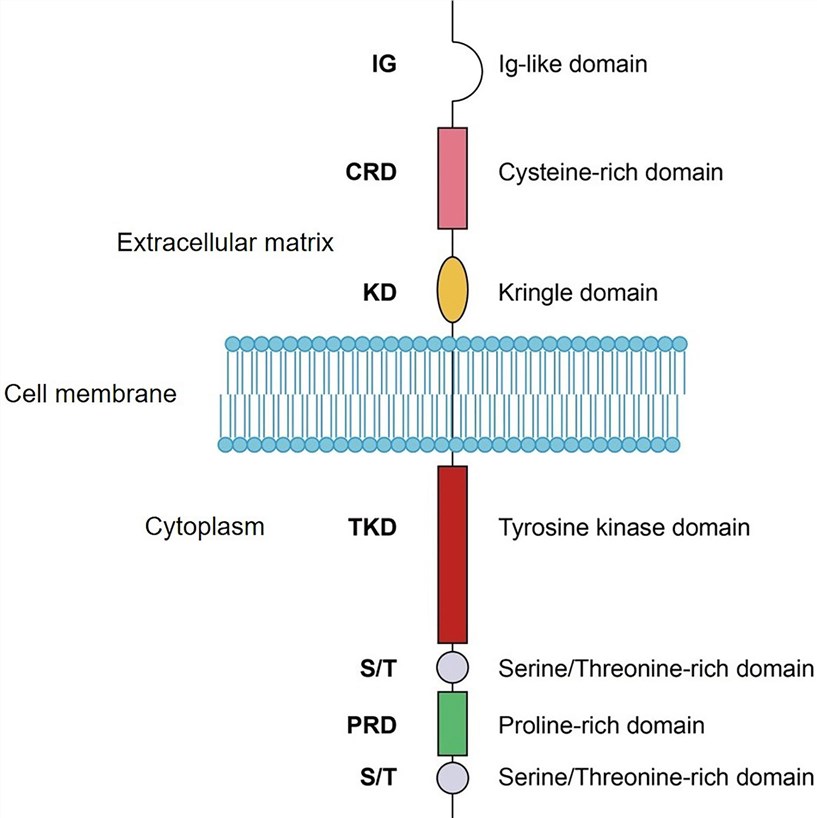 Fig.1 Schematic domain structure of ROR1. (Zhao, 2021)
Fig.1 Schematic domain structure of ROR1. (Zhao, 2021)
The Expression of ROR1
-
In normal tissues.
ROR1 is expressed predominantly during embryogenesis. ROR1 is not expressed in most postpartum tissues, except for adipose tissues that express ROR1 weakly, and some tissues from the endocrine glands, gastrointestinal tract, and immature B lymphocytes. The function of ROR1 in these adult tissues is currently unknown.
-
In malignancies.
ROR1 was first identified as an onco-embryonic gene in hematological malignancies. Strong expression of ROR1 was initially identified in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. In addition, ROR1 is also overexpressed in mantle cell lymphoma and acute lymphocytic leukemia. High expression of ROR1 is also observed in a wide variety of solid malignancies, such as colon, lung, breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers.
WNT/ROR1 Signaling Pathway
ROR1-mediated signaling has been reported in a number of cell lines. ROR1 has an intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity, and activation of ROR1 kinase activity also requires engagement with its ligand such as WNT5A. The vast majority of studies have associated ROR1 with the activation of β-catenin-independent WNT signaling responses triggered by binding of the non-canonical WNT ligand WNT5A. WNT/ROR1 signal transduction is mediated by the phosphorylation of ROR1 by several kinases which on the one hand results in the inhibition of anti-apoptotic pathways, while on the other hand activates downstream pathways such as WNT/PCP, MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT or NF-κB. These either trigger cytoskeletal rearrangements associated with enhanced tumor cell migration, or induce a transcriptional response leading to the expression of genes that promote cell proliferation, survival, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), or therapy resistance.
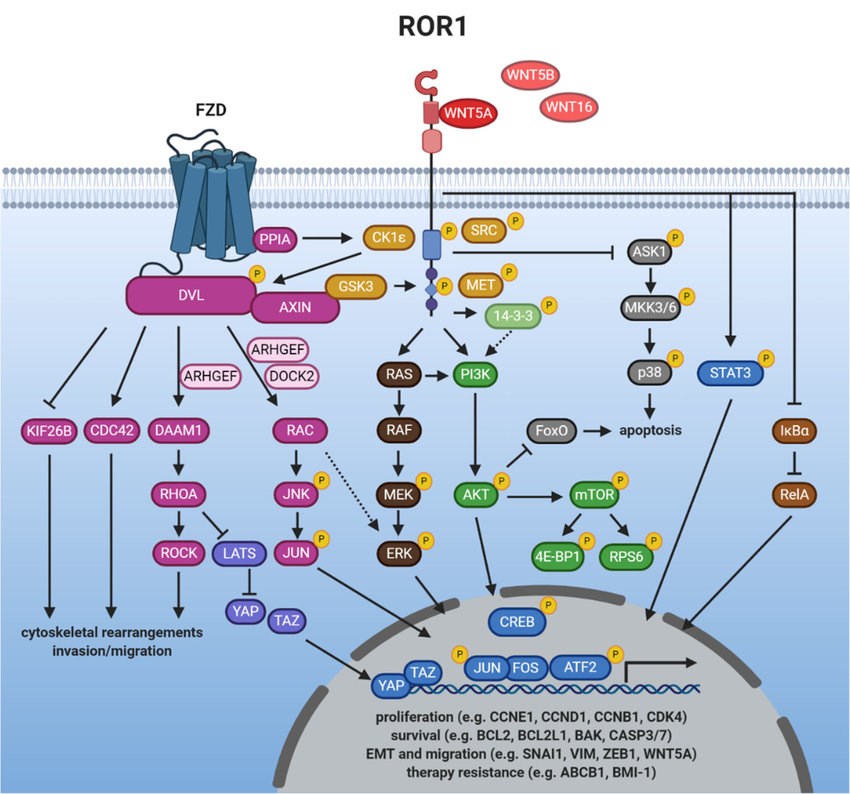 Fig.2 ROR1 signaling. (Menck, 2021)
Fig.2 ROR1 signaling. (Menck, 2021)
Therapeutic Strategies Targeting ROR1
ROR1 is a useful biomarker for cancer diagnosis and targeted therapy. The large extracellular region of ROR-1 provides large numbers of epitopes for different immune responses such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and apoptosis for immunotherapy. Most targeted cancer therapies use either small molecule drugs or monoclonal antibody (mAb)-based strategies. mAbs block ligand binding directly and activate the immune system to eliminate tumor cells. Small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are ATP-competitive inhibitors that target the catalytic domains in tyrosine kinases.
What Can We Offer?
ROR1 is expressed in a number of malignancies and plays an important role in cancer progression and represents an ideal druggable target for cancer therapy. Creative Biolabs provides a full set of ROR1 assay portfolio services for research, including but not limited to
-
EMT assay (cell proliferation assay, cell migration assay, cell invasion assay, EMT marker assay, and colony formation assay)
-
Annexin-V/PI apoptosis assay
-
CDC and ADCC assays
-
Short interfering RNA assay
-
Luciferase reporter assay (for the ROR1 promoter binding examination)
-
Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay and immunoblotting
Due to the many requests we received from our customers, we are very proud to offer custom tumor marker assay services to assist our clients. Our dedicated team is experienced in immunoassay and molecular test development. We can offer you aggressive development timelines and competitive pricing. Please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Zhao, Y.; et al. Tyrosine kinase ROR1 as a target for anti-cancer therapies. Frontiers in Oncology. 2021, 11: 680834.
-
Menck, K.; et al. The WNT/ROR pathway in cancer: from signaling to therapeutic intervention. Cells. 2021, 10(1): 142.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Schematic domain structure of ROR1. (Zhao, 2021)
Fig.1 Schematic domain structure of ROR1. (Zhao, 2021)
 Fig.2 ROR1 signaling. (Menck, 2021)
Fig.2 ROR1 signaling. (Menck, 2021)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure