T and B Cell-based Radio Immuno Assay (RIA)
Radioimmunoassay (RIA) is a sensitive, quantitative immunoassay used to determine molecules in biological samples, especially to trace various substrates in a specimen. Creative Biolabs offers multiple radioimmunoassays to analyze cancer epitopes by monitoring the epitope-induced specific T and B cell responses, including cytokine release and antibody production.
Introduction of Radioimmunoassay
The principle of radioimmunoassay is based on specific antibody-antigen binding reactions and the competition between analytes and standard antigens for the limited binding sites on antibodies. Two different approaches are available for measuring molecules in biological samples, one is double-antibody RIA, and another is coated-tube RIA. In the double-antibody dependent assay, a first antibody is used to capture antigens, and a second antibody is adopted to precipitate the first antibody and antigen-formed complex from the reaction solution, facilitating removing unbound labeled standards to monitor radioactivity. Another approach is pre-coating the primary antibody on the bottom of the test tube to capture the corresponding antigens. Therefore, the unbound labeled antigens are easily separated by collecting the supernatant.
 Fig.1 Principle of radioimmunoassay.1
Fig.1 Principle of radioimmunoassay.1
Radioimmunoassay Services at Creative Biolabs
Radioimmunoassay employs antibodies to monitor and quantitate the number of analytes in a sample. Creative Biolabs provides high-quality antibodies to conduct standard radioimmunoassay with validated performance.
Workflow
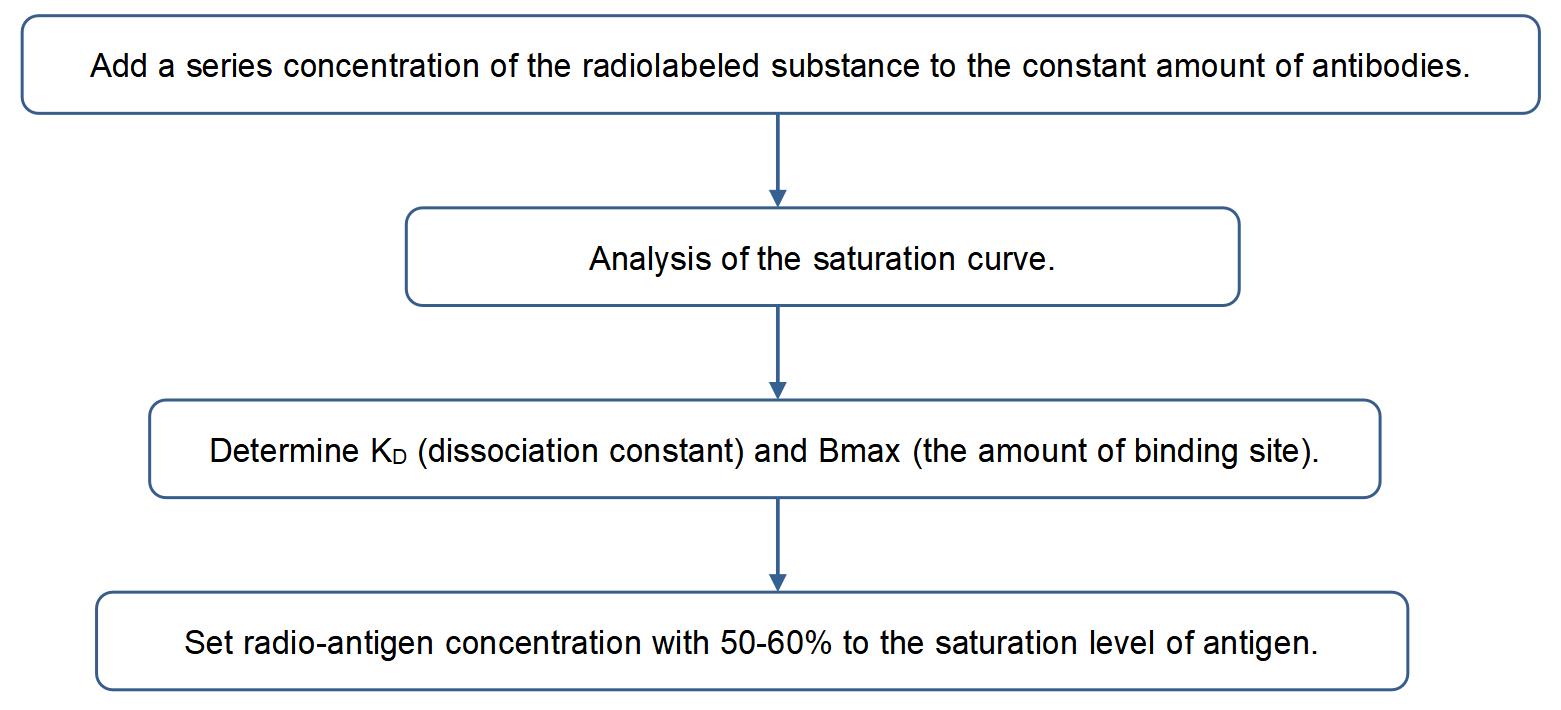
Titration Experiment--Define the Proper Concentration of Radiolabeled Antigen
Determine the Analytes Concentration by Competition Assay
In the competition assay, the unlabeled antigens compete with binding sites on antibodies with radio-labeled antigens. The measurement of analyte concentration in the sample and known series diluted standard substrate are performed in the same experiment.
 Fig.2 Using RIA to evaluate the specific monoclonal antibody as a reporter for hepatocellular carcinoma.2
Fig.2 Using RIA to evaluate the specific monoclonal antibody as a reporter for hepatocellular carcinoma.2
Data Analysis
✔ A gamma counter is used to determine the concentration of an unbound labeled ligand by monitoring the counts per minute.
✔ The count is inversely proportional to the count of antigens that exist in the sample tested.
Deliveries of Our Service
1) High-quality antibodies are produced for the detection assay.
2) A purified standard substrate and a validated dilution range for the standard curve.
3) Assess the binding interaction between epitope and antibodies, providing:
-
Qualitative Binding Data
-
Dissociation Constant, KD
-
Association Constant, KA
-
The Number of Binding Sites, Bmax
-
IC50
4) Detect the cytokines secreted from immune cells.
Highlights
-
High sensitivity up to picogram quantities.
-
Accurate and precise data.
-
Detect a wide range of analytes.
As a leader in the field of immunotherapy development, Creative Biolabs offers a variety of cancer epitope characterization methods according to specific T and B cell immunity. Our experts and technicians are here to make tailored assays to clients' respective studies. Please contact us or consult our experts online.
References
-
Hao, P. P.; et al. Evaluation of (131)I-anti-angiotensin II type 1 receptor monoclonal antibody as a reporter for hepatocellular carcinoma. PloS one. 2014, 9(1): e85002.
-
Ranjan, Koushlesh.; et al. Application of Molecular and Serological Diagnostics in Veterinary Parasitology. The Journal of Advances in Parasitology. 2016, 2. 80-99.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Principle of radioimmunoassay.1
Fig.1 Principle of radioimmunoassay.1


 Fig.2 Using RIA to evaluate the specific monoclonal antibody as a reporter for hepatocellular carcinoma.2
Fig.2 Using RIA to evaluate the specific monoclonal antibody as a reporter for hepatocellular carcinoma.2
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure