TIM-3 Assay Portfolio Service
Immunotherapy is being an increasingly therapeutic modality to treat cancer and represents the key treatment for the disease. T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (TIM-3) is a potential target in cancer immunotherapy due to its expression on a variety of T cells. With advanced and high-end technologies, rich experienced scientists, Creative Biolabs is an excellent service provider in the field of tumor marker assay. After long years ahead to fully comprehend tumor markers, we launch our TIM-3 assay portfolio service which can be useful in targeted cancer therapy and diagnosis.
TIM-3 Signaling
TIM-3, also known as HAVCR2, belongs to the TIM gene family. Currently, the model of Tim-3 signaling is that on T-cell activation, Tim-3 is recruited to the immunological synapse where Bat3 binds to the cytoplasmic tail of Tim-3 and recruits the active, catalytic form of Lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (Lck). The expression of TIM-3 was detected in non-small cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, cervical cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, ovarian cancer, head and neck cancer, and so on.
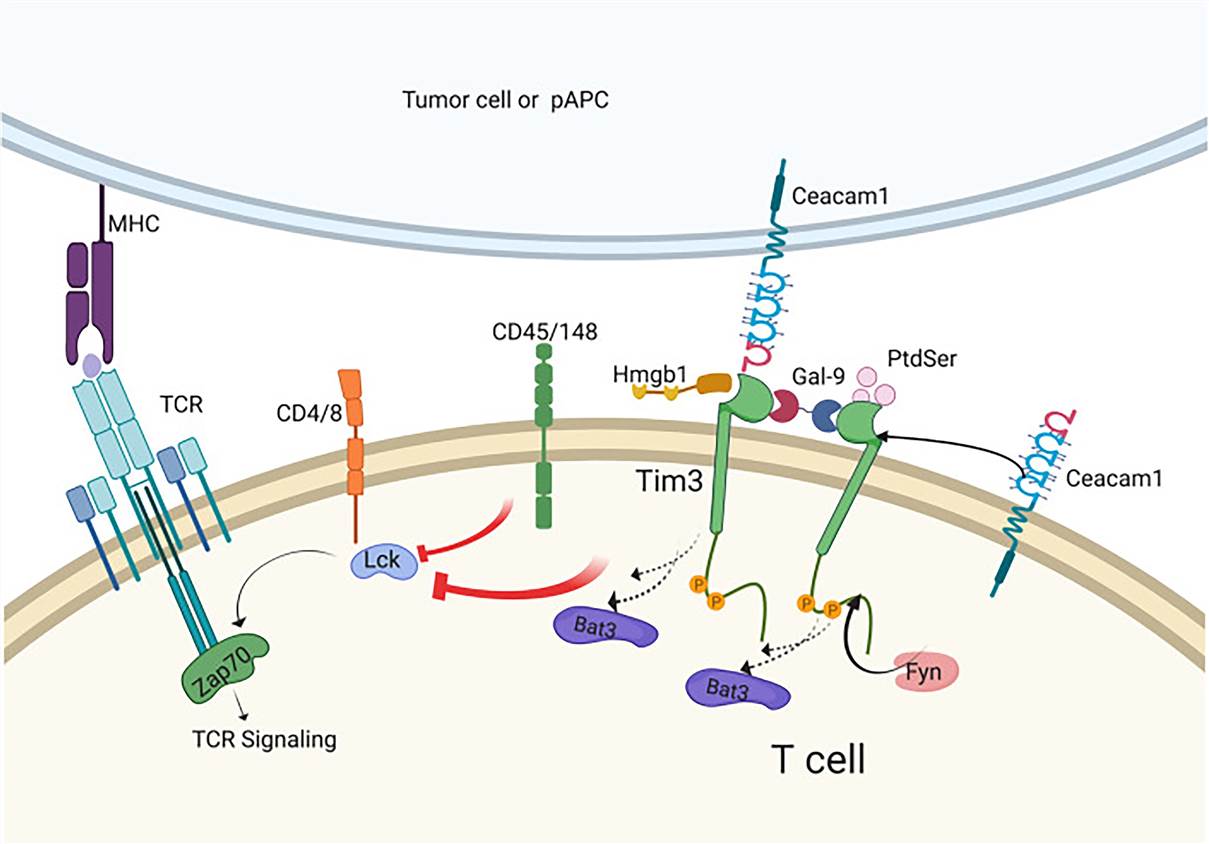 Fig.1 Tim-3 signaling in T cells. (Acharya, 2020)
Fig.1 Tim-3 signaling in T cells. (Acharya, 2020)
Tim-3 Ligands
Tim-3 has been identified as four distinct ligands related to cancer: galectin-9, phosphatidylserine (PtdSer), high-mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1), and Carcinoembyronic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule-1 (CEACAM-1).
-
Galectin-9
Galectin-9, a soluble protein, contains two tandemly linked carbohydrate recognition domains, specifically recognizing the structure of N-linked sugar chains in the Tim-3 IgV domain. The interaction of Tim-3-galectin-9 can suppress immune responses and facilitate tumor growth. The in vitro studies revealed that galectin-9 suppresses metastatic potential via promoting cancer cell aggregation, limiting invasion, detachment from the tumor, and attachment to the vascular endothelium. In addition, Galectin-9 can induce apoptosis and inhibit the growth of HCC cells.
-
PtdSer
Unlike the other Tim-3 ligands, PtdSer, a non-protein ligand for Tim-3, binds to the FG-CC′ loops of the Tim-3 IgV domain. PtdSer is a phospholipid, which serves as a ligand for all Tim family members. Tim-3-PtdSer interaction can mediate phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by Tim-3-expressing CD8+ DCs and subsequent cross-presentation of the apoptotic cell-associated antigens to CD8+ T cells.
-
HMGB1
HMGB1, a ligand for Tim-3, can be secreted by tumor cells among other cell types. Researche has reported that the complex formation of HMGB1 with nucleic acids and with other molecules can be inhibited by direct interaction with Tim-3. However, The relative roles of Tim-3-HMGB1 interaction in the regulation of the response to different chemotherapeutic agents remain to be determined.
-
CEACAM-1
CEACAM1, which is expressed by T cells, DCs, monocytes, macrophages and tumor cells, such as melanoma, is also a ligand for Tim-3. CEACAM1 can bind Tim-3 both intracellularly and extracellularly. The inhibitory function of Tim-3 is compromised in the absence of Ceacam1 expression. Additionally, Ceacam1-Tim-3 interaction suppresses effector T cell function and is required for maintaining T cell tolerance.
TIM-3 in AML and MDS
TIM-3 expression has been found to correlate with disease progression of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myelogenous leukemia (AML).
-
The Tim-3-galectin-9 interaction promotes autocrine leukemic stem cell (LSC) self-renewal.
-
The Tim-3-galectin-9 interaction may directly influence downstream signaling pathways, including the NF-kB and β-catenin pathways.
-
The binding of an anti-TIM-3 antibody to TIM-3 on the surface of LSCs/blasts may facilitate antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis by myeloid cells/macrophages expressing FcγRs and promotion of M1 phenotype.
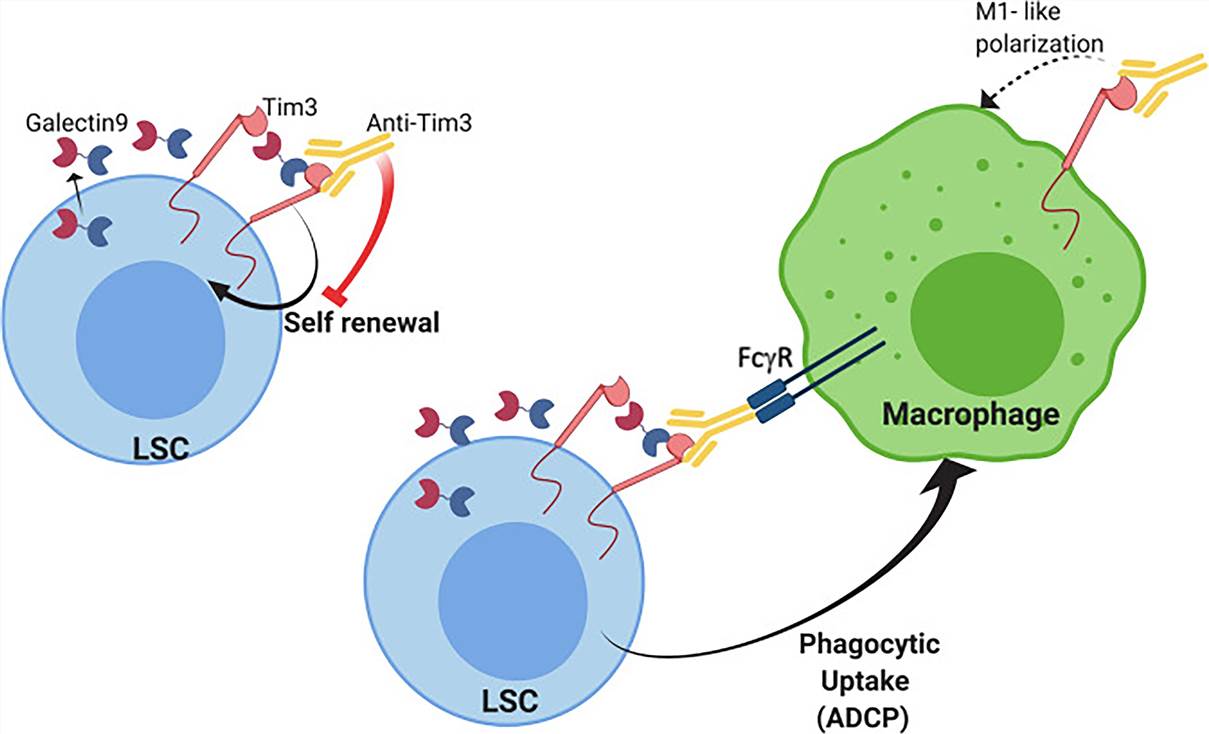 Fig.2 Tim-3 mAb mechanism of action in AML/MDS. (Acharya, 2020)
Fig.2 Tim-3 mAb mechanism of action in AML/MDS. (Acharya, 2020)
TIM-3 Blockade Assays at Creative Biolabs Including but Not Limited to:
-
Invasion assay
-
Metastases assay
-
Cytokine assay
-
Apoptosis assay
-
Cytotoxicity assay
-
Immune responses assay
If you are interested in our service, please contact us or directly send us.
Reference
-
Acharya, N.; et al. Tim-3 finds its place in the cancer immunotherapy landscape. J Immunother Cancer. 2020, 8(1): e000911.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Tim-3 signaling in T cells. (Acharya, 2020)
Fig.1 Tim-3 signaling in T cells. (Acharya, 2020)
 Fig.2 Tim-3 mAb mechanism of action in AML/MDS. (Acharya, 2020)
Fig.2 Tim-3 mAb mechanism of action in AML/MDS. (Acharya, 2020)
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure