Introduction of CD3
CD3 is a protein complex composed of four distinct chains (γ, δ, ε, and ζ) that associate with the T cell receptor (TCR) and mediate signal transduction upon antigen recognition. CD3 is expressed on the surface of all mature T-cells and is essential for their activation and function. CD3 is a well-established target for T cell-engaging BsAbs, as it can trigger potent antitumor responses regardless of the TCR specificity and the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) status of the tumor cells.
Introduction of B7H3
B7H3, also known as CD276, is a member of the B7 family of immunoregulatory proteins. B7H3 has two isoforms in humans, one with two immunoglobulin-like domains (2Ig-B7H3) and one with four immunoglobulin-like domains (4Ig-B7H3), both encoded by a gene on chromosome 15. B7H3 is expressed in various normal tissues, but its expression is upregulated in many types of cancers, where it plays a dual role in modulating immune responses and promoting tumor progression. B7H3 has been reported to have both co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory effects on T cells, depending on the context and the receptor involved. B7H3 also has non-immunological functions in cancer cells, such as enhancing proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, metastasis, and drug resistance.
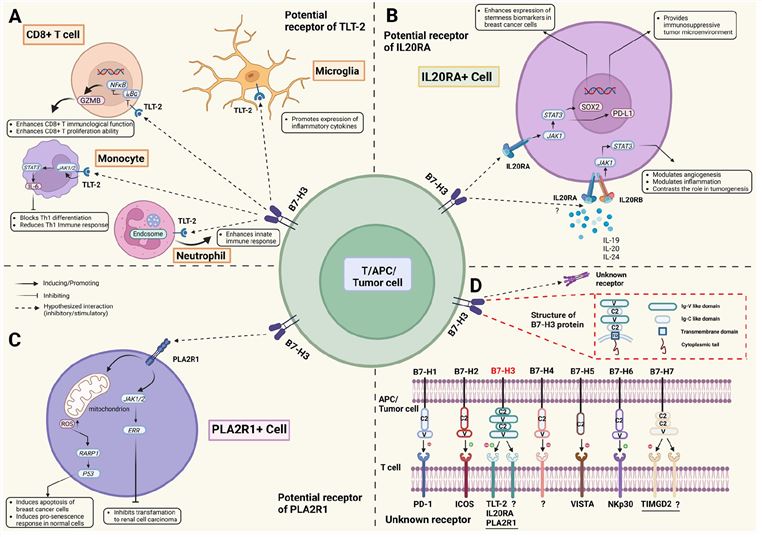
Fig.1 Structures, distributions, interactions, and biological functions of B7H3 and putative receptors (Jin C, 2021)
Signaling Pathways Involved in Bispecific Antibodies Targeting CD3 and B7H3
The main signaling pathway involved in BsAbs targeting CD3 and B7H3 is the TCR signaling pathway, which is initiated by the crosslinking of CD3 with BsAbs bound to B7H3 on tumor cells. This leads to the phosphorylation of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) in the CD3ζ subunits by Src family kinases, such as Lck and Fyn. The phosphorylated ITAMs then recruit and activate ZAP70, a tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates several downstream substrates, such as LAT, SLP-76, PLCγ1, Vav1, and Itk. These molecules form a signalosome that activates multiple signaling cascades, such as MAPK, NF-κB, PI3K/Akt, and Ca2+ pathways. These pathways regulate various aspects of T cell activation, such as proliferation, differentiation, survival, cytokine production, and cytotoxicity.
Another signaling pathway that may be involved in BsAbs targeting CD3 and B7H3 is the B7H3 signaling pathway, which is still poorly understood. The receptor for B7H3 has not been conclusively identified yet, but several candidates have been proposed, such as TREML2, CD28H, and TLT-2. Depending on the receptor and the context, B7H3 may exert either co-stimulatory or co-inhibitory effects on T cells. For example, B7H3 was shown to enhance T cell proliferation and cytokine production through TREML2, CD28H, or TLT-2, but to inhibit T cell activation and function through Siglec or CEACAM1. The exact mechanism by which BsAbs targeting CD3 and B7H3 modulate the B7H3 signaling pathway is unclear, but it may involve blocking the interaction between B7H3 and its receptor, altering the expression or localization of B7H3, or inducing conformational changes in B7H3 that affect its signaling capacity.
Clinic Status of Bispecific Antibodies Targeting CD3 and B7H3
Currently, there are no BsAbs targeting CD3 and B7H3 that have been approved for clinical use, but several candidates are under investigation in preclinical or clinical trials. The main companies or institutions that are developing these BsAbs include MacroGenics and Tuebingen University. The main indications for these BsAbs are solid tumors, such as melanoma, prostate cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer, renal cell carcinoma, glioblastoma, and sarcoma. MGD009 and CC-3 are two bispecific antibodies that target CD3 on T cells and B7H3 on tumor cells, thereby inducing T cell activation and tumor cell killing. They have similar mechanisms of action and applications, but different structural formats and development stages.
Table 1. Comparison of MGD009 and CC-3
|
Name
|
Format
|
Developer
|
Phase
|
Indication
|
|
MGD009
|
Dual-affinity Re-targeting
|
MacroGenics
|
I/II
|
Solid tumors (lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer, etc)
|
|
CC-3
|
IgG
|
Tuebingen University
|
Preclinical
|
Gastrointestinal tumors (pancreatic cancer, liver cancer, stomach cancer, etc)
|
MGD009 is a dual-affinity re-targeting format bispecific antibody, consisting of two polypeptide chains, each with an Fv fragment targeting CD3 or B7H3, linked by a disulfide bond. MGD009 also has an Fc fragment that enhances its stability and half-life. CC-3 is an IgG format bispecific antibody, consisting of three polypeptide chains, each with an Fv fragment targeting CD3 or B7H3, linked by a disulfide bond. CC-3 does not have an Fc fragment but can modulate its potency by changing the affinity of the Fv fragments.
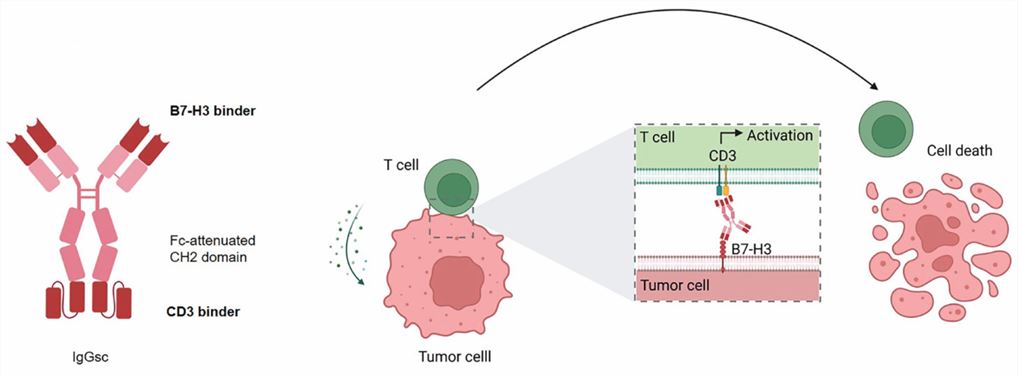
Fig.2 Schematic illustration and mechanism of action of the B7H3xCD3 bsAb CC-3 (Lutz MS, 2023)
References
1. Jin C, et al. B7-H3: A Novel Target for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2021 May 4;12:701006.
2. Ma J, et al. Bispecific antibodies: a new dawn for cancer immunotherapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Feb 5;6(1):50.
3. Labrijn AF, et al. Therapeutic bispecific antibodies: the clinical landscape and challenges in development, manufacturing, and delivery. Antibody Therapeutics. 2019 Dec;2(4):141-60.
4. Fan G, et al. Bispecific antibodies and their applications in tumor immunotherapy. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2015 Dec 19;14:74-81.
5. Seckinger A, et al. Target expression, generation, preclinical activity, and pharmacokinetics of the BCMA-T cell bispecific antibody EM801 for multiple myeloma treatment. Cancer Cell. 2017 Mar 13 ;31 (3) :396 -410.
6. Zhang W, et al. Development of a novel anti-B7-H3 monoclonal antibody with antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 2020 Jan ;19 (1) :119 -29.
7. Liu C, et al. Targeting the immune checkpoint B7-H3 for next-generation cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022 Jul;71(7):1549-1567.
8. Lutz MS,et al. IgG-based B7-H3xCD3 bispecific antibody for treatment of pancreatic, hepatic and gastric cancer. Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 14;14:1163136.
9. Ma J, et al. Bispecific anti-CD3 x anti-B7-H3 antibody mediates T cell cytotoxic ability to human melanoma in vitro and in vivo. Invest New Drugs. 2019 Oct;37(5):1036-1043.
Our products and services are for research use only, and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Welcome! For price inquiries, we will get back to you as soon as possible.
To order, please email
INQUIRY











