Caco-2-based MRP2 Substrate Assessment Service
MRP2 Facilitates Detoxification and Drug Resistance
Multidrug Resistance Protein 2 (MRP2) is a crucial member of the multidrug resistance protein (MRP) family. MRP2 is predominantly localized in the apical membrane of polarized cells, particularly in the canalicular membrane of hepatocytes, where it plays a significant role in detoxification and the excretion of drug metabolites. What has been described above specifically presents these main functions:
-
Detoxification: MRP2 mediates the ATP-dependent transport of lipophilic substances that are conjugated to glutathione, glucuronate, or sulfate.
-
Excretion of Drug Metabolites: MRP2 is responsible for the excretion of drug metabolites into bile.
-
Regulation of Intracellular Concentrations: By transporting various anionic conjugates out of cells, MRP2 helps maintain the intracellular concentrations of drugs and other substances.
-
Contribution to Drug Resistance: MRP2 is involved in the development of multidrug resistance in cancer cells by pumping out chemotherapeutic agents and their conjugates, which can lead to reduced efficacy of cancer treatments.
-
Protection Against Oxidative Stress: MRP2, along with other members of the MRP family, contributes to the control of the glutathione disulfide/glutathione (GSSG/GSH) ratio.
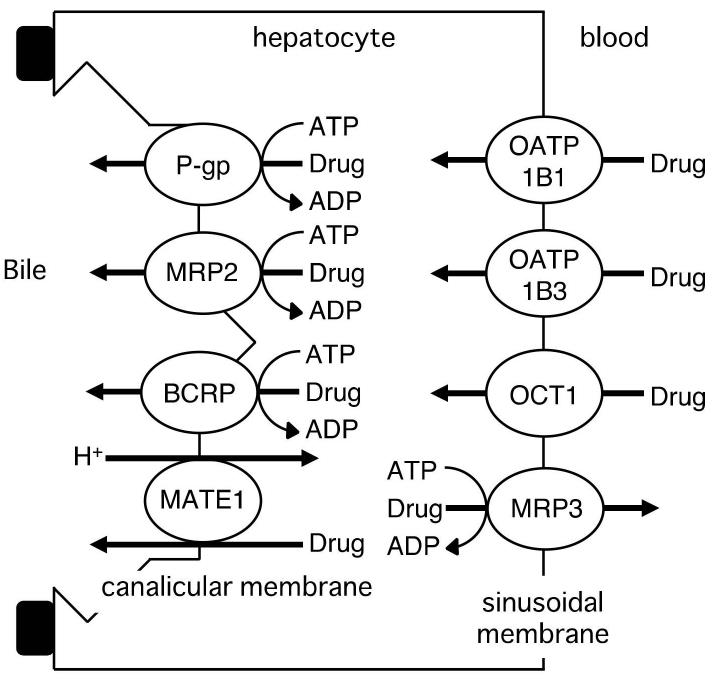 Fig.1 MRP2 in hepatocyte.1,3
Fig.1 MRP2 in hepatocyte.1,3
Caco-2-based MRP2 Substrate Assessment
Creative Biolabs offers MRP2 substrate assessment services based on Caco-2 cells for all clients. The purpose of this assay is to evaluate if a test compound acts as a substrate for MRP2 that is expressed in Caco-2 cells. The permeability of the compound is measured in both the AB and BA directions, under conditions with and without the inclusion of an MRP2 inhibitor (MK571).
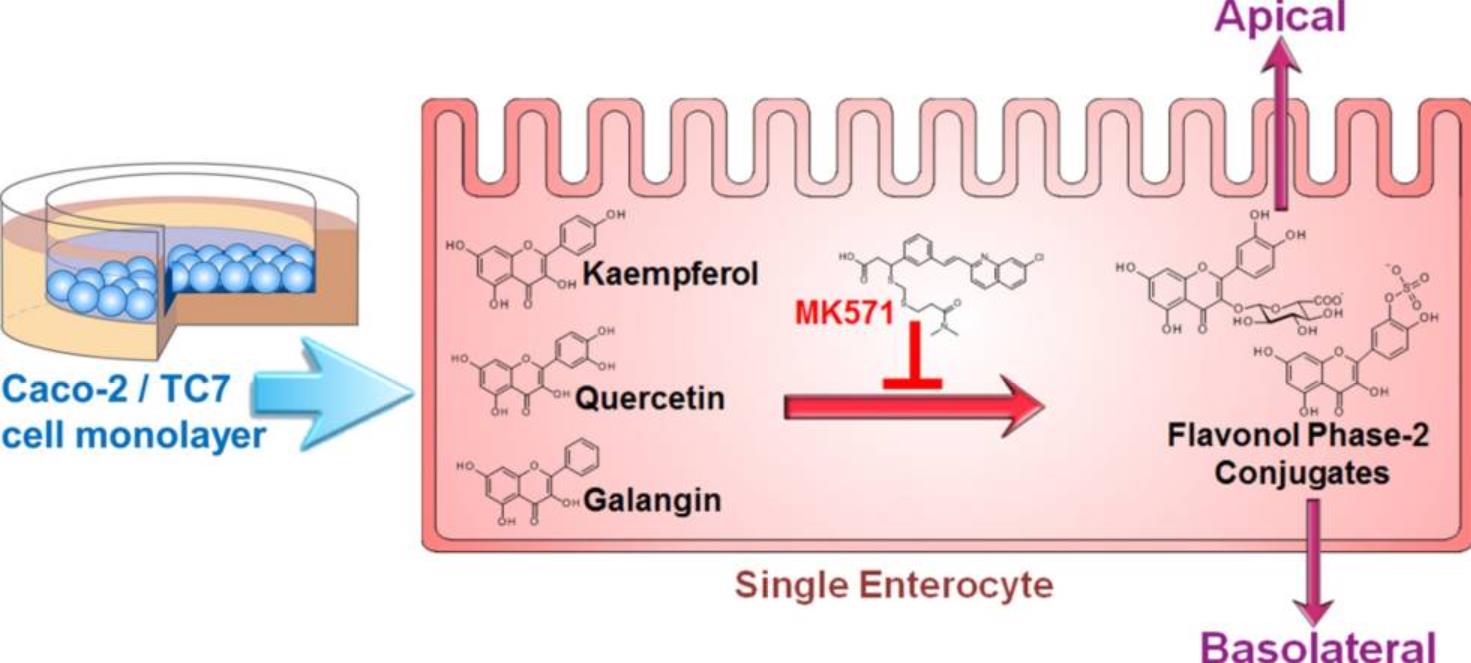 Fig.2 MK571 influences the transport processes of several compounds in the intestinal epithelial cell.2,3
Fig.2 MK571 influences the transport processes of several compounds in the intestinal epithelial cell.2,3
More about MRP2 Substrate Assessment
-
The significance of the MRP2 substrate assessment.
Accessing a compound is a substrate of MRP2 (Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein 2) has several important implications across various fields, including drug development, pharmacokinetics, and clinical applications:
-
Drug-Drug Interaction Assessment: MRP2 is a significant drug transporter that can extrude drugs and their metabolites from cells. Understanding if a compound is an MRP2 substrate is crucial for evaluating potential interactions with other drugs, as competition for MRP2 can lead to reduced efficacy or increased toxicity.
-
Pharmacokinetics Research: Knowledge of a compound's interaction with MRP2 can help predict its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) characteristics, thus providing deeper insights into the drug's fate within the body.
-
Safety Evaluation: Identifying whether a compound is an MRP2 substrate can aid in assessing its potential toxic effects, particularly concerning organ functions like the liver and kidneys, where MRP2 plays a vital role in the elimination of drugs and metabolites.
-
Personalized Medicine: In clinical contexts, patient responses to drugs can vary. Understanding whether a compound is an MRP2 substrate can help in tailoring treatment regimens to enhance efficacy and minimize adverse effects in individual patients.
-
Understanding Membrane Transport Mechanisms: Investigating the interactions between compounds and MRP2 can provide critical information about broader membrane transport mechanisms, aiding in drug design and optimization efforts.
-
The advantages of using the Caco-2 cell model in MRP2 substrate assessment:
-
Standardized Conditions: The use of a stable cell line allows for controlled experimental conditions, making it easier to replicate studies and compare results across different research settings.
-
Predictive Utility: Due to their ability to mimic human intestinal barrier functions, Caco-2 cells are effective for permeability screening, helping to predict the bioavailability of new drug candidates.
MRP2 substrate assessment is important for improving drug development processes, ensuring drug safety and efficacy, and understanding pharmacological interactions. Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing effective support for your research. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us. In addition to MRP2 substrate assessment, we are also willing to offer a variety of services in ADME to meet your needs, such as:
References
-
Uwai Y. "Enantioselective Drug Recognition by Drug Transporters." Molecules 23.12 (2018): 3062.
-
Barrington, R. D., et al. "MK571 inhibits phase-2 conjugation of flavonols by Caco-2/TC7 cells, but does not specifically inhibit their apical efflux." Biochem Pharmacol 95.3 (2015): 193-200.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 MRP2 in hepatocyte.1,3
Fig.1 MRP2 in hepatocyte.1,3
 Fig.2 MK571 influences the transport processes of several compounds in the intestinal epithelial cell.2,3
Fig.2 MK571 influences the transport processes of several compounds in the intestinal epithelial cell.2,3
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure