Enzyme Inhibition Assessment Service
Enzyme Inhibition in Drug-Drug Interactions
Understanding drug-drug interactions is crucial for ensuring safe and effective drug therapy. These interactions can either potentiate or attenuate the therapeutic effect of drugs, leading to either improved or worsened patient outcomes. One of the mechanisms through which drug-drug interactions occur is through enzyme inhibition. Enzymes play a pivotal role in drug metabolism. Co-administration of two drugs may cause one drug or both to inhibit the activity of an enzyme involved in the metabolism of the other drug, thus leading to significant changes in drug concentrations and pharmacological effects.
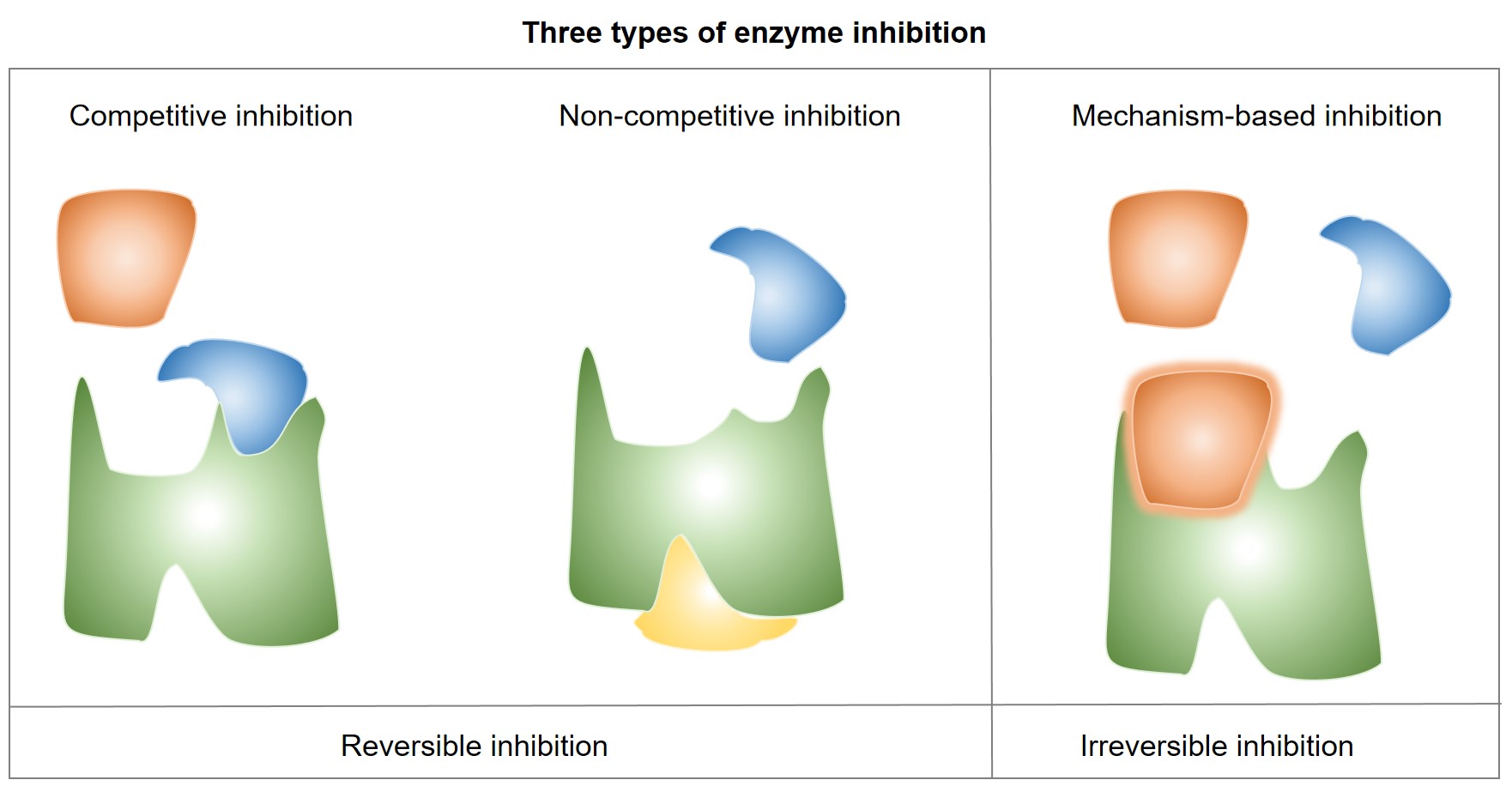
Enzyme Inhibition Assays
At Creative Biolabs, we provide a wide range of enzyme inhibition assays to assess drug-drug interactions. Our team of experts has extensive experience in performing cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibition assays, UGT inhibition assays, and other enzyme inhibition assays. These assays can provide valuable insights into the pharmacokinetic properties of drugs and their potential for interactions with other drugs.
-
CYP Inhibition Assay
CYP enzymes play a vital role in drug metabolism as they are responsible for the oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis of numerous compounds. We perform CYP inhibition assays to evaluate the potential of the drugs to inhibit the activity of these enzymes by using several systems such as hepatocytes, liver microsomes, or recombinant CYP enzymes. The formation of metabolites is assessed using LC/MS/MS analysis.
-
Using liver microsomes, recombinant CYP enzymes, or hepatocytes
-
Various P450 isozymes (e.g., CYP1A, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A)
-
Analysis with LC/MS/MS
-
Evaluation of the inhibition constants (Ki)
-
Evaluation of the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50)
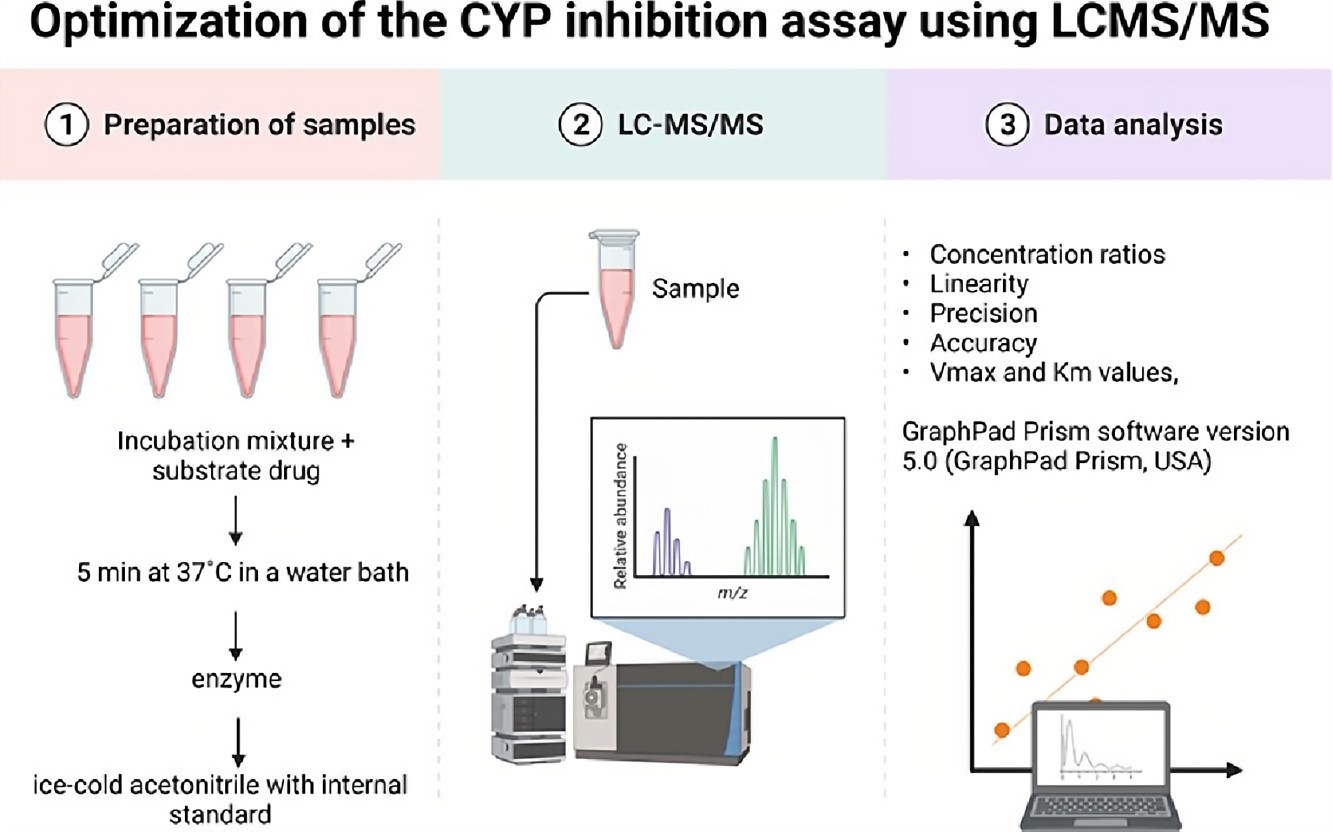 Fig.2 The workflow of CYP inhibition assay.2
Fig.2 The workflow of CYP inhibition assay.2
-
UGT Inhibition Assay
Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) are a family of enzymes that catalyze the conjugation of various compounds, including drugs and endogenous substances, with glucuronic acid. UGT Inhibition assays typically involve incubating the test compound with UGT enzymes and a suitable substrate and then measuring the formation of the glucuronide conjugate to determine the enzyme activity. Our CYP inhibition assays are designed to assess the potential for drugs to inhibit CYP enzymes, which can lead to altered drug metabolism and potentially significant pharmacokinetic interactions.
-
Using recombinant UGT enzyme (e.g., UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A4, UGT1A9, UGT2B7, and UGT2B15)
-
Analysis with LC-MS/MS
-
Evaluation of the IC50
-
Other Enzyme Inhibition Assay
In addition to CYP and UGT enzymes, there are many other enzymes involved in drug metabolism and other biological processes that may be targeted for inhibition, such as N-acetyltransferases, sulfotransferases, and carboxylesterases. At Creative Biolabs, we also offer inhibition studies towards these enzymes as part of our drug-drug interaction services.
References
-
Deodhar, Malavika, et al. "Mechanisms of CYP450 inhibition: understanding drug-drug interactions due to mechanism-based inhibition in clinical practice." Pharmaceutics 12.9 (2020): 846.
-
Abduraman, Muhammad Asyraf, et al. "Optimization of the CYP inhibition assay using LC-MS/MS." MethodsX 9 (2022): 101827.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use



 Fig.2 The workflow of CYP inhibition assay.2
Fig.2 The workflow of CYP inhibition assay.2
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure