Drug-Drug Interaction Analysis Services
Mechanism of Drug-Drug Interaction
When two or more drugs are administered simultaneously, they may interact with each other, impacting the efficacy and safety of the medications. Drug metabolism plays a crucial role in drug-drug interactions, as it can greatly influence drug concentrations in the body, subsequently affecting their therapeutic effects and potential side effects. A significant focus of research in Drug-Drug Interactions is on the induction or inhibition of enzymes and transcription factors responsible for drug metabolism. For example, if a drug inhibits the metabolism of another drug, the concentrations of the second drug may increase, potentially leading to increased therapeutic effects or side effects. Conversely, if a drug induces the metabolism of another drug, the concentrations of the second drug may decrease, potentially reducing its therapeutic effectiveness. Through understanding these interactions, researchers can develop improved drug combinations and dosing regimens that enhance therapeutic outcomes while reducing potential risks.
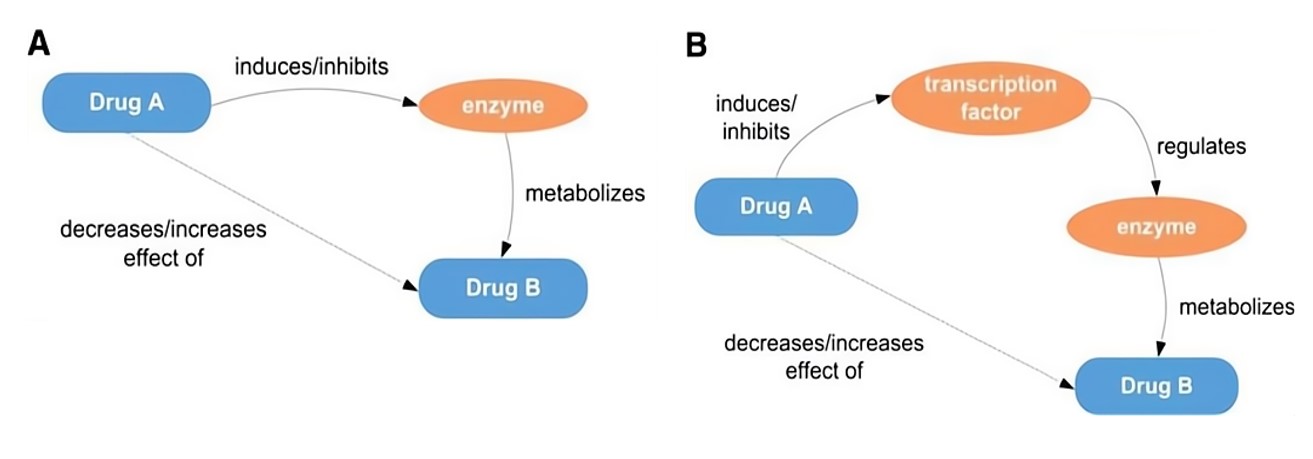 Fig.1 Drug-drug interactions through induction/inhibition of (A) enzymes; (B) transcription factors.1
Fig.1 Drug-drug interactions through induction/inhibition of (A) enzymes; (B) transcription factors.1
Protein Binding Assays
Creative Biolabs, a leading provider of biotechnology services, offers a comprehensive range of services to help researchers understand and predict drug-drug interactions. Our services cover enzyme inhibition and induction assessment, reaction phenotyping assessment, reactive metabolite screening, and transporter interaction assessment. These services are designed to help researchers identify potential interactions between drugs and enzymes/transporters, assess reaction phenotypes, and profile metabolites. Our expertise and state-of-the-art facilities ensure accurate and reliable results, supporting your drug discovery and development efforts.
Our enzyme inhibition assessment service employs a range of in vitro techniques to evaluate the inhibitory potential of drugs on key enzymes involved in drug metabolism, such as CYP450 and UGT enzymes.
Our service utilizes in vitro systems to assess the ability of test drugs to induce specific drug-metabolizing enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes. This information is crucial in predicting drug-drug interactions that may result from enzyme induction and in designing optimized drug-dosing strategies.
Our reaction phenotyping assessment service aims to identify the enzyme phenotype involved in the in vitro metabolism of drugs and determine the relative contributions of various isozymes in metabolism. This typically involves incubating drugs with human liver microsomes or other relevant biological matrices.
Creative Biolabs also offers comprehensive metabolite profiling services that involve the comprehensive analysis of metabolites produced by the body in response to drug exposure. By analyzing the metabolites produced during drug metabolism, we provide a deeper understanding of how a drug is metabolized, which can help predict potential drug-drug interactions.
We provide a series of in vitro models for assessing transporter-mediated drug-drug interactions, such as Caco-2 cells, MDCK cells, and HEK-293 cells- transfected with SLC transporters. These models are used for the characterization of the inhibition potential of drugs towards a wide range of transporters, including MDR1, BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, MDR1, P-glycoprotein, and BCRP.
Reference
-
Tari, Luis, et al. "Discovering drug-drug interactions: a text-mining and reasoning approach based on properties of drug metabolism." Bioinformatics 26.18 (2010): i547-i553.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Drug-drug interactions through induction/inhibition of (A) enzymes; (B) transcription factors.1
Fig.1 Drug-drug interactions through induction/inhibition of (A) enzymes; (B) transcription factors.1
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure