Reactive Metabolite Screening Service
Why Reactive Metabolite Assay?
Reactive metabolite screening is a crucial aspect of drug development and toxicology research. It involves the identification and assessment of potentially toxic metabolites, which are produced when drugs or other xenobiotics are metabolized by the body. Reactive metabolites are capable of reacting with biological macromolecules, such as DNA, RNA, or proteins, leading to potential toxicities or mutagenic effects, including DNA damage, protein modification, and lipid peroxidation. Therefore, it is essential to identify and evaluate these metabolites to avoid potential safety concerns in later stages of development.
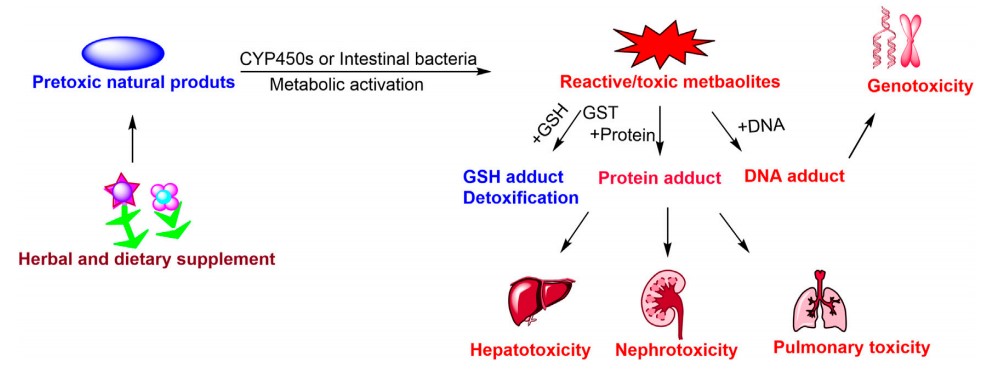 Fig.1 The toxicities of reactive metabolites.1
Fig.1 The toxicities of reactive metabolites.1
A reactive metabolite screening assay involves incubating the drug with liver microsomes or hepatocytes and then measuring the formation of reactive metabolites using various analytical techniques. At Creative Biolabs, our team of experts utilizes state-of-the-art technology and methods to screen for reactive metabolites. We offer a range of assays, including glutathione trapping assay, cysteine trapping assay, cyanide trapping assay, and stable isotope labeling approaches, to comprehensively evaluate the potential for reactive metabolite formation. These assays allow us to detect and quantify reactive metabolites formed during the incubation of drugs with liver microsomes or hepatocytes. By screening for reactive metabolites, we aim to assess the potential safety risks associated with a drug candidate. Our assays provide valuable insights into the metabolic fate of drugs and identify any potential toxicities that may arise during their use.
There are several methods we offer to screen for reactive metabolites:
-
Glutathione Trapping Assay
Glutathione (GSH) is a common target for reactive metabolites, as it can form adducts with electrophilic intermediates. We offer the GSH trapping service that typically involves incubating the test compound with liver microsomes or hepatocytes in the presence of GSH, which acts as a trapping agent for reactive metabolites. The metabolite-GSH conjugates formed are then analyzed using analytical techniques such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to identify the reactive metabolites and assess their potential risks.
In addition, we offer cysteine (Cys) trapping and cyanide (KCN) service as an alternative study of GSH trapping.
Covalent binding assays are considered the most accurate tool in drug development due to their ability to predict the potential toxicity of a drug candidate. These assays are typically performed using radiolabeled compounds, such as 3H or 14C. However, it is rare to conduct it in early-stage development because of the long and costly processes.
Reactive metabolites can lead to cellular damage and cytotoxicity. By exposing cells to the test compound and measuring cell viability or other markers of cell damage, such as ATP levels or LDH release, reactive metabolites can be identified.
Reference
-
Wang, Yi-Kun, et al. "Metabolic activation of the toxic natural products from herbal and dietary supplements leading to toxicities." Frontiers in pharmacology 12 (2021): 758468.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 The toxicities of reactive metabolites.1
Fig.1 The toxicities of reactive metabolites.1
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure