Transporter Interaction Assessment Service
Drug Transporters
Drug transporters are proteins present in cell membranes that play a crucial role in mediating the passage of drugs and other xenobiotics across various biological barriers in the body, such as the blood-brain barrier, intestines, liver, and kidneys. These transporters can be broadly classified into two main types based on their function: efflux transporters (ATP-binding cassette transporters, ABC) and uptake transporters (solute carrier transporters, SLC). Drug-transporter interactions affect drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, leading to altered pharmacokinetics, drug efficacy, and potential drug-drug interactions. Therefore, a comprehensive analysis of transporter interactions is essential to optimize drug therapy and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Transporter Types
-
ABC Transporters: P-glycoprotein (P-gp), MRPs (e.g. MRP1, MRP2, MRP3) BSEP, BCRP, etc.
-
SLC transporters: OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, MATE1, MATE2, MCT10, etc.
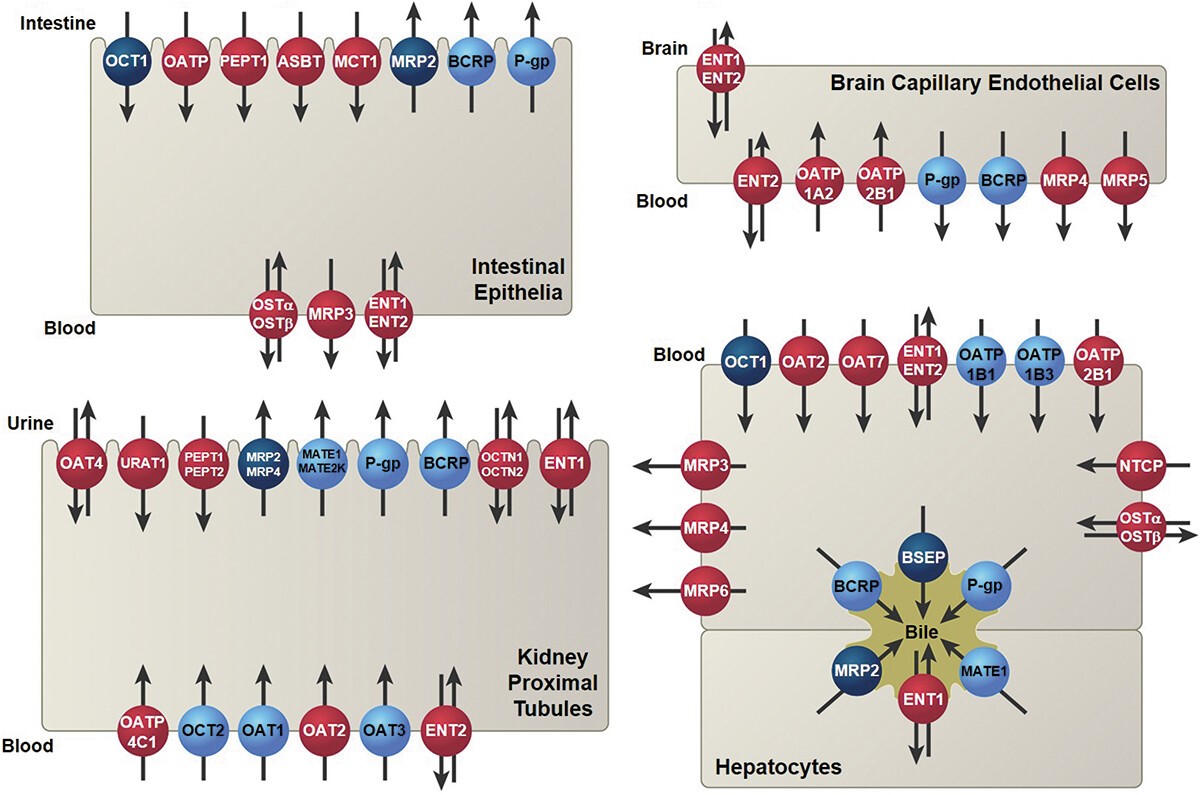 Fig.1 Summary of various drug transporters in ADME organs.1
Fig.1 Summary of various drug transporters in ADME organs.1
Methods for Transporter Interaction Assessment
To characterize drug transporter interactions, we conduct the following assays.
Inhibition assay is used to determine the ability of a drug to inhibit the function of a specific transporter. The drug of interest is tested for its ability to inhibit the transporter by competing for the binding site or blocking the transporter's activity. In the Inhibition Assay, we measure the ability of a test drug to inhibit the activity of a transporter by incubating the transporter with a known probe substrate alone or in the presence of a selective inhibitor or a test drug.
Substrate assay is used to determine if a test drug is a substrate for a particular transporter. We measure the ability of a test drug to be transported by a drug transporter by incubating the transporter with the test drug in the absence or presence of a selective inhibitor.
We perform inhibition assay and substrate assay in Caco-2, MDCK, LLC-PK1, HEK293, membrane vesicles, and various stably transfected transporter-overexpressing cell lines. Additionally, transporter knockout cell lines allow for determining the potential impact of specific transporters in drug absorption and disposition without dependence on chemical inhibitors.
-
Analysis Method
-
Scintillation counting (Radiochemical detection)
-
LC-MS/MS analysis (Non-radiochemical detection)
Services
At Creative Biolabs, we provide a comprehensive range of transporter interaction assessment services that can be tailored to the specific needs of any project. These services are designed to evaluate drug-transporter interactions, offering valuable insights into drug pharmacokinetics and potential drug-drug interactions. Our team of experts utilizes state-of-the-art technology and methodologies to accurately assess transporter activity and substrate specificity, as well as deliver reliable results to support your research.
-
Uptake Transporter Assay
Our uptake transporter assay is used to evaluate the substrate potential and transporter inhibition potential of drugs by specific uptake transporters in cell lines expressing these transporters. Our uptake transporters for testing include OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, MATE1, MATE2-K, OATP1A2, OATP2B1, OAT2, OAT4, OCTN2, PEPT1, PEPT2, NTCP, etc.
-
Uptake Transporter Inhibition assessment studies
-
Uptake Transporter Substrate assessment studies
-
Efflux Transporter Assay
Our assay is conducted in cell lines expressing specific efflux transporters such as P-gp, BCRP, MRP2, and so on. These efflux transporters play a crucial role in drug efflux from cells, potentially leading to drug resistance and altered drug concentrations in tissues.
-
Efflux Transporter Inhibition assessment studies
-
Efflux Transporter Substrate assessment studies
-
Vesicular Transport Assay
Vesicular transport assays involve the use of inside-out membrane vesicles isolated from cells that overexpress specific transporters. The use of vesicular transport assays allows for the evaluation of a specific test article as a transport substrate or inhibitor in a simplified system, providing valuable information on the transport mechanisms of drugs and their potential for drug-drug interactions.
-
Inhibition assessment studies
-
Substrate assessment studies
Reference
-
Elsby, Robert, et al. "Studying the right transporter at the right time: an in vitro strategy for assessing drug-drug interaction risk during drug discovery and development." Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology 18.10 (2022): 619-655.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Summary of various drug transporters in ADME organs.1
Fig.1 Summary of various drug transporters in ADME organs.1
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure