B Cell-based Cross Blocking Assay
Antibody-mediated Blocking Assay
If an antibody binds to an antigen and blocks other antibodies or receptor proteins binding to the antigen, it is called a blocking antibody. Therefore, a blocking assay is also called an antibody competition assay. Cross blocking assays are usually used for antibody classification based on epitope specificity. The blocking function is also applied to control allergic disorders. Therefore, Cross blocking assay is functional to identify human monoclonal antibodies with broad and synergistic neutral functions against various infections.
As a world-leading company for high-quality antibody discovery and production, Creative Biolabs offers the blocking assay to clients to study cancer antigens and determine immunodominant epitopes using epitope-specific antibodies.
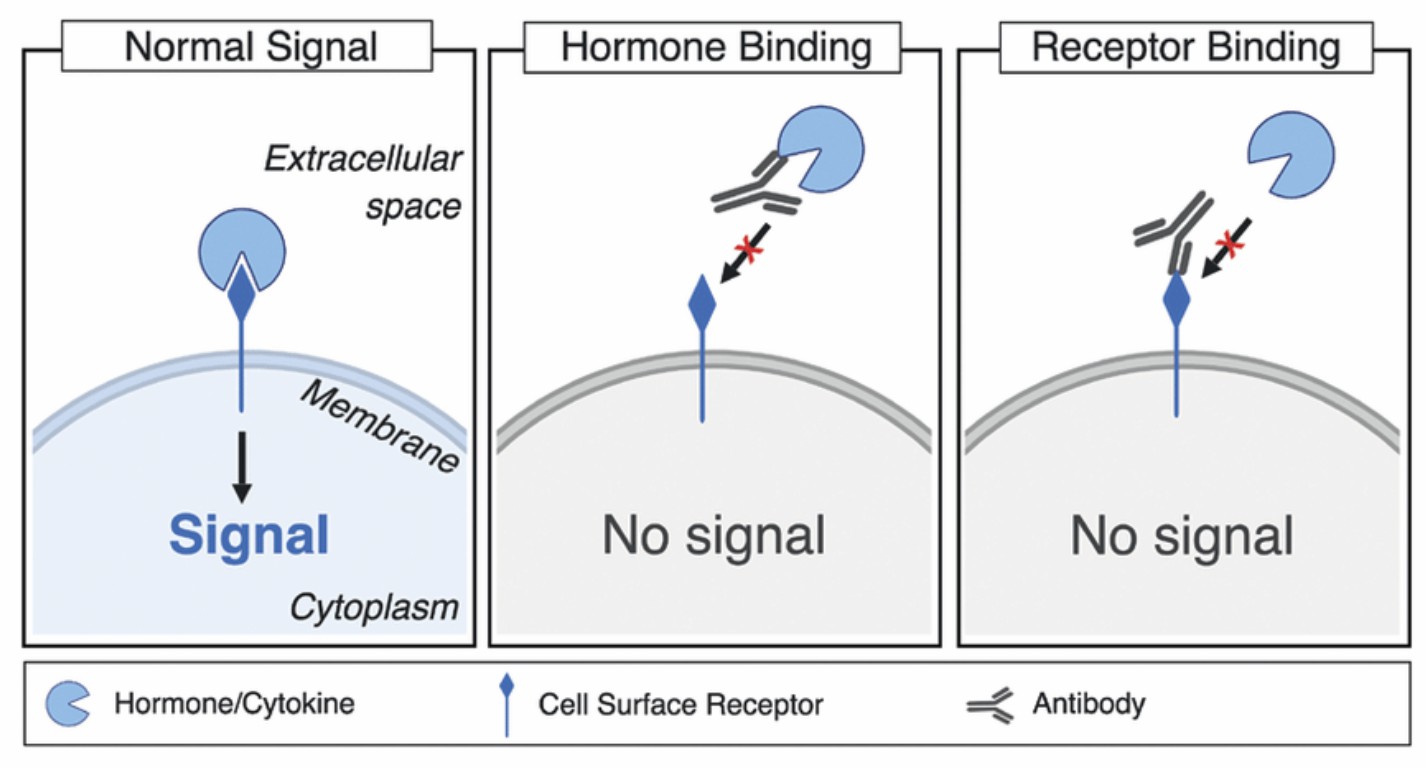 Fig.1 Mechanisms of specific antibody-mediated blocking action of receptor-ligand binding.1
Fig.1 Mechanisms of specific antibody-mediated blocking action of receptor-ligand binding.1
Cross Blocking Assay Services at Creative Biolabs
The blocking assay is a promising method for identifying B-cell epitopes in tumor antigens and is widely used for screening antigenic peptide segment libraries. Creative Biolabs provides a scientific blocking assay for cancer epitope analysis.
Workflow
 Fig.2 Workflow (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.2 Workflow (Creative Biolabs)
Antibody Preparation
-
Epitope-specific Antibody
Immunize mice with target epitope peptides.
Purification and assessment.
-
Human Antibodies
Isolation protein antigen-specific single B cell.
Cloning and expression of specific human mAbs.
 Fig.3 Isolate antigen-reactive antibodies from the recovered patients.5
Fig.3 Isolate antigen-reactive antibodies from the recovered patients.5
Types of Our Cross Blocking Assay
-
The competition ELISA assay. The peptides are immobilized on the plate, and the first native unlabeled mAbs/receptors are added to the plate at saturating titters. Next, the other labeled mAbs diluted to serial concentrations are added to the same wells. After inoculation, the peptide-labeled mAbs complex is detected by color reaction. The blocking rate is calculated by comparing OD in the presence and absence of competitor mAbs.
 Fig.4 Illustration of the competitive ELISA assay for cross blocking.2
Fig.4 Illustration of the competitive ELISA assay for cross blocking.2
-
The classical sandwich ELISA-based cross-blocking assay.
 Fig.5 Applying classical sandwich ELISA for cross block assay.4
Fig.5 Applying classical sandwich ELISA for cross block assay.4
-
Mixing mAbs with an epitope protein probe at a specific ratio. The blocking rate can also be conducted by inoculating with epitope protein-expressing cells to compete for binding and measured by cell image.
-
Blocking the receptor to the epitope ligand.
 Fig.6 The neutralizing antibody blocks RBD binding with its ACE2 receptor.3
Fig.6 The neutralizing antibody blocks RBD binding with its ACE2 receptor.3
Detection Techniques
With advanced technologies, we provide various methods to detect antibody binding to specific antigen peptides.
With the versatile blocking assay, it is efficient to identify the minimal epitope sequence of a conformational B-cell epitope and identify an immunodominant epitope within a protein antigen. Creative Biolabs provides a variety of blocking antibodies and tailored blocking assays to meet your special demands. To learn more, please contact us for more detailed information.
References
-
Lee, Jungmin.; et al. Minimizing side effects, maximizing returns: what makes a smart therapeutic design? The Biochemist. 2019, 41: 28-32.
-
Li, Y.; et al. Development and evaluation of a monoclonal antibody-based competitive ELISA for the detection of antibodies against H7 avian influenza virus. BMC veterinary research. 2021, 17(1): 64.
-
Tan, C. W.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2-spike protein-protein interaction. Nature biotechnology. 2020, 38(9): 1073–1078.
-
Abdiche, Y. N.; et al. Antibodies Targeting Closely Adjacent or Minimally Overlapping Epitopes Can Displace One Another. PloS one. 2017, 12(1): e0169535.
-
Chen, X.; et al. Human monoclonal antibodies block the binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020, 17: 647–649.
For Research Use Only | Not For Clinical Use


 Fig.1 Mechanisms of specific antibody-mediated blocking action of receptor-ligand binding.1
Fig.1 Mechanisms of specific antibody-mediated blocking action of receptor-ligand binding.1
 Fig.2 Workflow (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.2 Workflow (Creative Biolabs)
 Fig.3 Isolate antigen-reactive antibodies from the recovered patients.5
Fig.3 Isolate antigen-reactive antibodies from the recovered patients.5
 Fig.4 Illustration of the competitive ELISA assay for cross blocking.2
Fig.4 Illustration of the competitive ELISA assay for cross blocking.2
 Fig.5 Applying classical sandwich ELISA for cross block assay.4
Fig.5 Applying classical sandwich ELISA for cross block assay.4
 Fig.6 The neutralizing antibody blocks RBD binding with its ACE2 receptor.3
Fig.6 The neutralizing antibody blocks RBD binding with its ACE2 receptor.3
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure