- Home
- UTC Development
- Bispecific ADC Development
- Fast-internalizing Receptor based Bispecific ADC Development
- CD63 based Bispecific ADC Development
CD63 based Bispecific ADC Development Service
Bispecific antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are designed to be stable in circulation and to release potent cytotoxic drugs intracellularly following antigen-specific binding, uptake, and degradation in tumor cells. Efficient internalization and routing to lysosomes where proteolysis can take place are therefore essential. Based on the well-established ADC and bispecific antibody (bsAb) development platforms, Creative Biolabs offers customized bispecific ADCs development services to achieve your goals.
Background
The Overview of CD63
The CD63 gene is located on human chromosome 12q13 and is the first characterized tetraspanin. Originally, CD63 was discovered as a protein present on the cell surface of activated blood platelets, known as platelet glycoprotein 40 and in early stage human melanoma cells, where it was known as melanoma antigen 491. CD63, being a tetraspanin, interacts with many different proteins either directly or indirectly. Interaction partners include integrins, other tetraspanins, cell surface receptors, kinases, and adaptor proteins.
CD63 is a ubiquitously expressed protein localized within the endosomal system and at the cell surface. In most cells, the major pool of CD63 resides is in late endosomes and lysosomes, and this is why it is also referred to as a lysosomal membrane protein. Lysosomal membrane proteins that exit the trans Golgi network (TGN) can travel to lysosomes via either a direct TGN-to-endosome pathway or an indirect route, involving passage over the plasma membrane and subsequent endocytosis. In general, the sorting of lysosomal membrane proteins depends on tyrosine and dileucine-based consensus motifs within their cytosolic tails. CD63 bears a YXXØ consensus motif in its carboxy terminal cytoplasmic domain with an essential tyrosine residue, 2 hydrophobic XX residues, and the Ø residue being a bulky hydrophobic amino acid. The YXXØ motif is required for endocytosis at the plasma membrane but has also been implicated in direct TGN to lysosome targeting.
 Fig.1 The possible pathway of CD63 trafficking.1
Fig.1 The possible pathway of CD63 trafficking.1
Functions of CD63 in Protein Internalization
Many studies performed in different cell types implicate a role for CD63 in intracellular transport of other proteins. In gastric parietal cells, the co-expression of CD63 causes a redistribution of the H, K-ATPase β-subunit from the cell surface to intracellular compartments. This occurs by CD63-mediated linkage of the H, K-ATPase β-subunit to AP-2, thereby facilitating its clathrin-mediated endocytosis. These results suggest that CD63 might be involved in the recycling of the H, K-ATPase pump between the plasma membrane and intracellular storage compartments.
Our Service
CD63-based Bispecific ADCs Services
CD63, as a high-turnover surface protein, was used in bispecific ADC development. For example, in a HER2 x CD63 bispecific ADC, the binding affinity of the CD63 arm was limited to reduce monovalent target binding and prevent uptake by healthy tissues, thus relatively increasing the targeting properties of the bsAb to tumor cells that co-express HER2 and CD63. The bispecific ADC was armed using lysine conjugation with antimitotic agent duostatin-3 attached to a lysosomal protease-cleavable linker. It demonstrated potent cytotoxicity against HER2-positive tumors in vitro and in vivo, which was not observed with monovalent HER2- and CD63-specific ADCs.
Creative Biolabs is a well-recognized custom ADC development services provider. Our Ph.D. level experts have rich knowledge and extensive experience in generating CD63-based bispecific ADCs. We are confident in providing one-stop service from experiment design, antibody preparation to bio-conjugation to fit your specific demands. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details.
Highlights
- Expertise in ADC Design: Our Ph.D. level experts apply extensive knowledge in developing CD63-based bispecific ADCs, ensuring potent cytotoxic effects on tumor cells.
- Enhanced Dual-Targeting Mechanism: Creative Biolabs develops CD63-based bispecific ADCs that simultaneously target CD63 and other tumor markers, offering superior specificity and reducing off-target effects in cancer therapy.
- Optimized Stability and Circulation: Our bispecific ADCs are meticulously engineered for enhanced stability within the bloodstream, ensuring that the cytotoxic payloads are delivered efficiently to tumor sites without premature release.
- Efficient Payload Delivery via Lysosomal Pathways: Leveraging CD63's role in lysosomal routing, these ADCs enhance internalization and facilitate precise drug delivery, maximizing the cytotoxic impact on tumor cells.
- Customized Development and Conjugation Services: Creative Biolabs provides tailored bispecific ADC services encompassing experiment design, antibody production, and sophisticated bio-conjugation techniques to meet specific clinical and research demands.
- Demonstrated Superior Efficacy in Targeted Therapy: Our CD63-based bispecific ADCs have shown enhanced cytotoxicity against tumors co-expressing HER2 and CD63 in both in vitro and in vivo models, outperforming traditional monospecific ADCs.
FAQ
-
Q: What are CD63-based bispecific ADCs developed by Creative Biolabs?
A: Creative Biolabs specializes in developing CD63-based bispecific ADCs, utilizing the unique properties of CD63 for efficient drug delivery and enhanced cytotoxicity in tumor cells.
-
Q: How does CD63 function in the development of bispecific ADCs?
A: CD63 plays a crucial role in protein internalization and routing to lysosomes, making it an ideal target for ADCs that require precise intracellular drug release.
-
Q: What makes CD63 a significant target in bispecific ADC development?
A: Due to its high turnover and ubiquity in the endosomal system, targeting CD63 enhances the internalization and lysosomal delivery of cytotoxic drugs, increasing the efficacy of bispecific ADCs.
-
Q: How does Creative Biolabs ensure the effectiveness of CD63-based bispecific ADCs?
A: By harnessing advanced platforms for ADC and bispecific antibody development, Creative Biolabs ensures precise conjugation and targeting, optimizing the therapeutic index of CD63-based bispecific ADCs.
-
Q: What specialized services does Creative Biolabs offer for CD63-based bispecific ADCs?
A: Creative Biolabs provides customized development services for CD63-based bispecific ADCs, including antibody selection, conjugation with cytotoxic drugs, and comprehensive in vitro and in vivo testing to ensure efficacy and safety.
Published Data
In this experiment, a bispecific antibody-drug conjugate (bsADC) targeting HER2 and CD63 was developed to improve the delivery of cytotoxic drugs to HER2-positive tumor cells. One arm of the bispecific antibody binds to HER2, a tumor-specific antigen, while the other targets CD63, a protein involved in lysosomal transport. This design enhances lysosomal delivery of the drug. The bsADC conjugated to duostatin-3 showed significant internalization and lysosomal accumulation in HER2-positive cells, leading to potent cytotoxicity. In contrast, monovalent ADCs targeting only HER2 or CD63 were less effective. The results demonstrated that this dual-targeting approach could improve drug delivery to poorly internalizing antigens, offering a novel strategy for treating HER2-positive cancers.
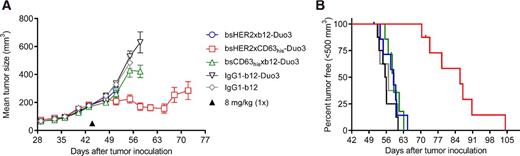 Fig.2 Efficacy of HER2 and CD63 Bispecific ADCS in a SK-OV-3 xenograft model.2
Fig.2 Efficacy of HER2 and CD63 Bispecific ADCS in a SK-OV-3 xenograft model.2
References
- Pols M.; et al. Trafficking and function of the tetraspanin CD63. Experimental Cell Research, 2009, 315(9): 1584-1592.
- de Goeij, Bart ECG, et al. "Efficient payload delivery by a bispecific antibody–drug conjugate targeting HER2 and CD63." Molecular cancer therapeutics 15.11 (2016): 2688-2697.
For Research Use Only. NOT FOR CLINICAL USE.

Online Inquiry
Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
