As a world-leading service provider of antibody generation and development, Creative Biolabs has already established a comprehensive series of in vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibody development services targeting a wide range of biomarkers. Here, we focus on the APC marker of ovarian cancer.
APC Marker
APC (Adenomatous polyposis coli), also called DP2.5 (Deleted in Polyposis 2.5), is a negative regulator that regulates beta-catenin concentrations and interacts with E-cadherin, which contribute to cell adhesion. APC protein in humans is encoded by the APC gene, and the mutations in the APC gene may result in colorectal cancer. APC is identified as a tumor suppressor gene, which can prevent the uncontrolled growth of cells that may lead to cancerous tumors. APC protein plays an essential role in several cellular processes that determine whether a cell might develop to form a tumor. It contributes to controlling how often a cell divides, how the cell polarizes and the morphogenesis of the 3D structures, how it attaches to other cells within a tissue, or whether a cell moves within or away from a tissue. APC protein also facilitates to ensure the correctness of chromosome number in cells that produced through cell division. APC protein controls the activity of β-catenin, the regulation of which prevents genes that stimulate cell division from being activated too often and prevents cell overgrowth. APC protein also associates with other proteins that are involved in cell attachment and signaling, to accomplish its biological functions.
The Role of APC in Ovarian Cancer
It has been proven that epigenetic modifications, including DNA methylation, nucleosome positioning, histone modifications and non-coding RNAs, are early and common events in tumor. As the main mechanism of epigenetic modifications, DNA methylation plays a vital role in carcinogenesis and cancer progression. The reduced expression of the APC protein, through gene promoter hypermethylation, has been demonstrated to play a vital role in the carcinogenesis. APC promoter hypermethylation is reported to likely be associated with the increased risk of ovarian cancer. It is related to histological type, but not with tumor stage or tumor grade. Wnt signaling pathway contributes to the development, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of cells, while APC gene methylation is linked to the APC gene suppression which can cause deregulation in Wnt signaling pathway. It has also been shown that APC protein was decreased in ovarian cancer compared to the normal ovary.
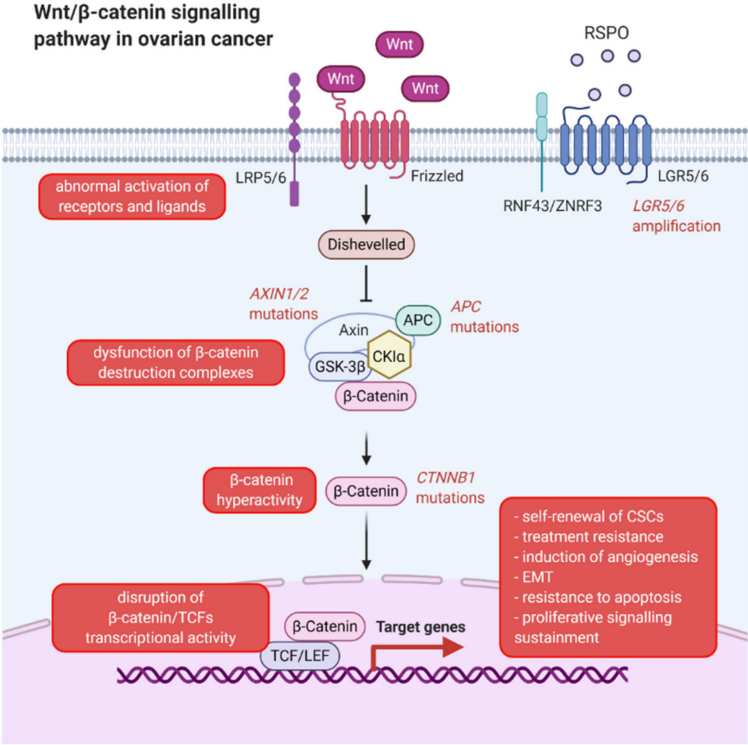 Fig.1 Critical role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in ovarian cancer.1
Fig.1 Critical role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in ovarian cancer.1
Antibodies are core elements for antibody-based immunoassays for detecting and quantifying antigens of interest in all kinds of samples such as the serum, urine, and tissue preparations. With advanced technology and years of experience, Creative Biolabs has launched a whole series of APC-specific antibody development services for the diagnosis and prognosis of ovarian cancer. Additionally, Creative Biolabs also provides diagnostic immunoassay development services targeting this marker. We offer one-stop services from antibody generation to kit production. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Reference
For Research Use Only.
