ND-L02-s0201
Introduction to siRNA
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), also known as silencing RNAs, have been widely used as RNA-based therapeutic drugs for the treatment of rare or orphan genetic disorders. Pilot studies have demonstrated that siRNAs can catalyze many enzymes and can inactivate a group of RNA molecules. Many attempts have been made in the generation of siRNA-based therapeutics for treating various human diseases in the past few years. Meanwhile, a panel of chemical modification assays for RNA have been also developed that play an important role in regulating their function and keep them stable. Moreover, a number of delivery systems have been established and used as carriers for the delivery of siRNA to target cells. In addition, several siRNAs properties, such as siRNA safety and stability, the activation of the immune response, as well as off-target silencing, have been evaluated by using different types of advanced technologies.
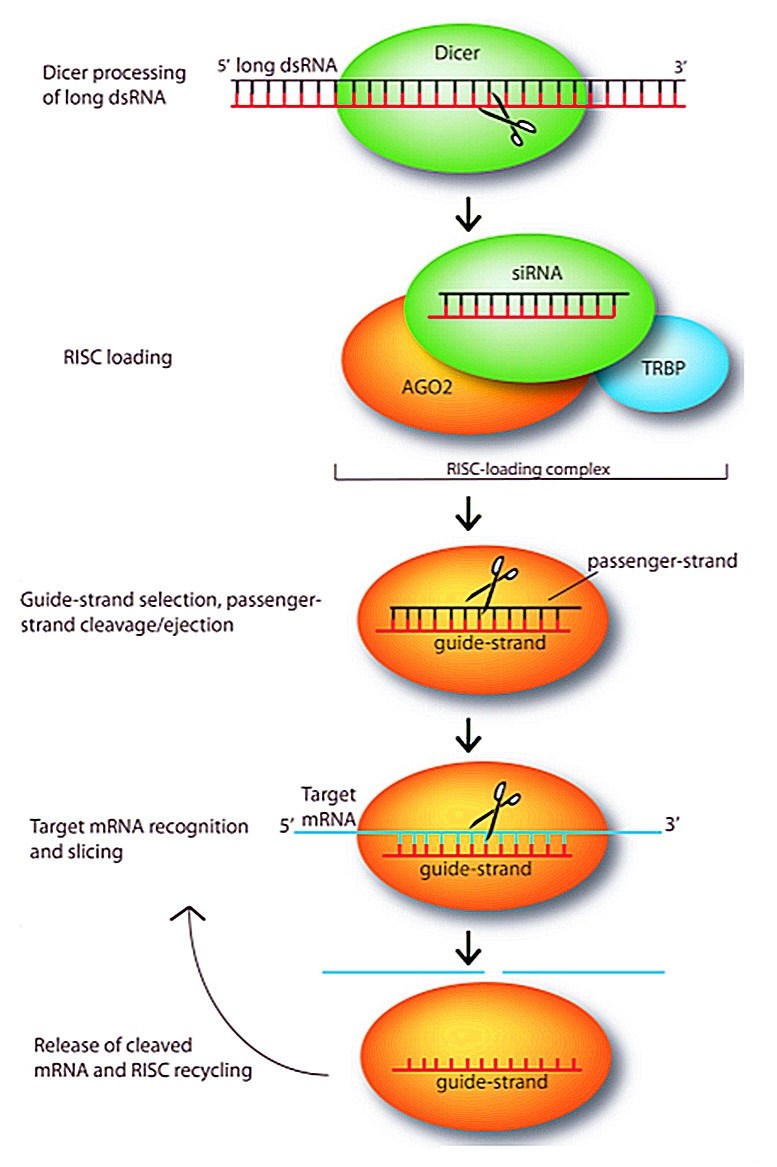 Figure 1. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) mediate the silencing of target genes by guiding sequence-dependent slicing of their target mRNAs. (Gavrilov, 2012)
Figure 1. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) mediate the silencing of target genes by guiding sequence-dependent slicing of their target mRNAs. (Gavrilov, 2012)
The ND-L02-s0201 in Disease Treatment
ND-L02-s0201, also called BMS-986263, is a therapeutic drug generated by using heat shock protein 47 (HSP47) siRNA. It has been evaluated for treating a wide variety of diseases, including hepatic fibrosis. For instance, lung fibrosis and liver fibrosis models have been established for testing its efficacy and screening potential biomarkers in the clinic. The results have shown that ND-L02-s0201 is capable of inhibiting the expression of HSP47 and then blocking the collagen synthesis, which may reverse fibrosis and provide a new gene therapy for fibrotic diseases.
Furthermore, a large scale of clinical trials has been conducted on both healthy adult individuals and patients suffering from various kinds of fibrotic diseases, including but not limited to: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and cystic fibrosis (CF). In phase I clinical trials, a double-blind and randomized single-dose study has been used to assess the safety and toxicity of ND-L02-s0201 in healthy volunteers. Meanwhile, the immunogenicity of ND-L02-s0201 has been analyzed by using anti-drug antibody (ADA) assays in normal human subjects. In phase II/III clinical trials, the biologic activity and pharmacokinetics of ND-L02-s0201 in patients with IPF have been evaluated. The data have indicated that intravenous injection (IV) administration of ND-L02-s0201 with a dose of 90 mg for three weeks is well-tolerated. There is no difference in tolerability or PK profiles for both healthy groups and patient groups.
Reference
- Gavrilov, K.; et al. (2012). Therapeutic siRNA: Principles, Challenges, and Strategies. The Yale journal of biology and medicine. 85(2): 187.
