Identity of Viral Vector
Identity testing of viral vectors is crucial to safeguarding the safety and efficacy of viral vector products. Any deviation from the intended genetic construct could compromise the efficiency and safety of the product. Therefore, identity testing constitutes a vital component of quality control testing in viral vector production, ensuring the safety and efficacy of viral vectors employed in clinical applications.
Physical Characteristics
Major physical characteristics of viral vectors encompass pH, osmolality, and aggregate formation. pH and osmolality are assessed via potentiometry and osmometry, respectively. Aggregate formation is evaluated utilizing dynamic light scattering (DLS). Aggregate formation refers to the propensity of viral particles to clump together, serving as a survival mechanism to resist environmental stress and endure degradation by disinfectants. Viral aggregation can impact the stability of viral vectors in various ways, including:
- Decrease the infectivity of viral vectors: Larger aggregates may hinder effective cell membrane penetration, reducing the vectors' ability to infect cells efficiently.
- Enhance the clearance of viral vectors in vivo: Larger aggregates are more prone to immune system recognition and clearance, potentially limiting gene expression and the duration of therapeutic effects.
- Impact on the safety of viral vectors: Large aggregates pose risks of adverse effects, including toxicity, inflammation, or organ damage.
Viral genome sequencing
The vector genome can be assessed using PCR or high-throughput next-generation genome sequencing (NGS) to verify its positive identity. NGS is employed to sequence all DNA encapsulated within viral particles. Firstly, packaged DNA is extracted from purified, DNase-treated AAV and subjected to NGS. The raw sequencing data is then analyzed to determine the identity. as shown in Fig.1.
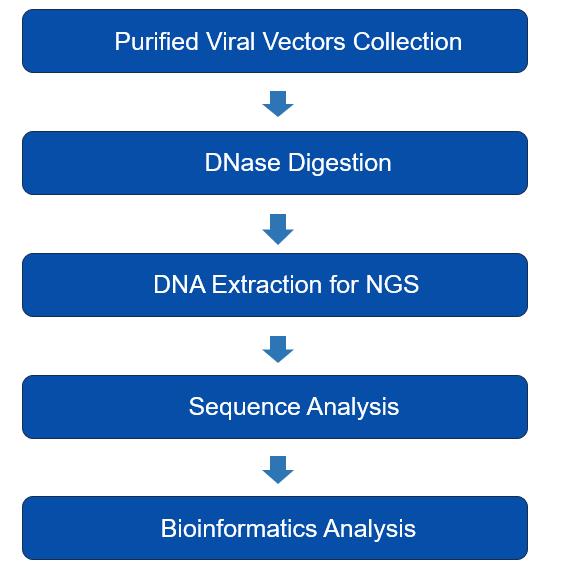 Fig.1 Simplified workflow for viral genome sequencing.
Fig.1 Simplified workflow for viral genome sequencing.
Confirming the Identity of Serotypes
For AAV vectors, various wild-type AAV serotypes are being explored to improve tissue or cell specificity. We utilize serotype-specific antibodies for immunoassays. Methods for serotype identity include Western blotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Western blot techniques are frequently employed to verify product identity in early-stage or preclinical development due to their low start-up and operational costs, as well as their ease of use. When higher throughput and reduced manual handling are needed due to sample volume, ELISA is often preferred.
SERVICES
Creative Biolabs leverages our high-sensitivity platform technology to perform rigorous identity testing during viral vector production. The safety and efficacy of viral vectors are ensured through accurate testing and identification. Feel free to reach out to us for further information on viral vector identity studies.
