Creative Biolabs is offering the most comprehensive services for antibody development projects. With strict regulation and effective execution, we are dedicated to providing the most valuable solutions to complete your projects.
HighlightsCreative Biolabs is offering the most comprehensive services for antibody development projects. With strict regulation and effective execution, we are dedicated to providing the most valuable solutions to complete your projects.
HighlightsCreative Biolabs is offering the most comprehensive services for antibody development projects. With strict regulation and effective execution, we are dedicated to providing the most valuable solutions to complete your projects.
HighlightsCreative Biolabs is offering the most comprehensive services for antibody development projects. With strict regulation and effective execution, we are dedicated to providing the most valuable solutions to complete your projects.
HighlightsWith over a decade of experience in phage display technology, Creative Biolabs can provide a series of antibody or peptide libraries that are available for licensing or direct screening. These ready-to-use libraries are invaluable resources for isolating target-specific binders for various research, diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
HighlightsCreative Biolabs has established a broad range of platforms for developing novel antibodies or equivalents. These cutting-edge technologies enable our scientists to meet your demands from different aspects and tailor the most appropriate solution that contributes to the success of your projects.
HighlightsWith deep understanding in antibody-related realms and extensive project experience, Creative Biolabs offers a variety of references to help you learn more about our capacities and achievements, including infographic, flyer, case study, peer-reviewed publications, and all kinds of knowledge that can assist your projects. You are also welcome to contact us directly for more specific solutions.
HighlightsGet a real taste of Creative Biolabs, one of the most professional custom service providers in the world. We are committed to providing highly customized comprehensive solutions with the best quality to advance your projects.
Highlights"Creative Biolabs is committed to providing highly customized comprehensive solutions with the best quality to advance our global clients’ projects."
The interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) subfamily plays a central role in the regulation of innate inflammatory and immune responses to infections, injury, stress, and allergies. The IL-1R type I family encodes ten members with three domains. The extracellular domain displays homology to immunoglobulin-like (IgG), a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic domain of the IL-1 type I receptor, which is highly homologous with the cytoplasmic domain of all TLRs. The Ig-like domains of the IL-IR family members display an Ig fold, which consists of two b-pleated sheets held together by intradomain disulfide bonds via conserved cysteine residues. Extracellular Ig-like domain is involved in protein-ligand and protein-protein interactions. In humans, the three extracellular Ig domains of the IL-1RI family have six amino acids, Arg431, Lys515, Arg518, Phe513, Trp514, and Tyr519, which are essential to signaling. Among them, Pro521 is required for the maximum signaling capacity, and Phe513 and Trp514 are present in the conserved box 3 of the TIR domain of IL-1RI. IL-1R1, IL-1R2, and IL-1R3 are bona fide receptors for IL-1α and IL-1β. ST2, which is also known as IL-R4, contains ligand IL-33. IL-R5, which is the ligand-binding (α) chain of the IL-18 receptor, is termed as IL-18Rα. IL-1R7, which is also known as IL-18Rβ, is a coreceptor (β) chain involved in IL-18 signal transduction. IL-1 receptor has emerged as an important participant in inflammation and apoptosis.
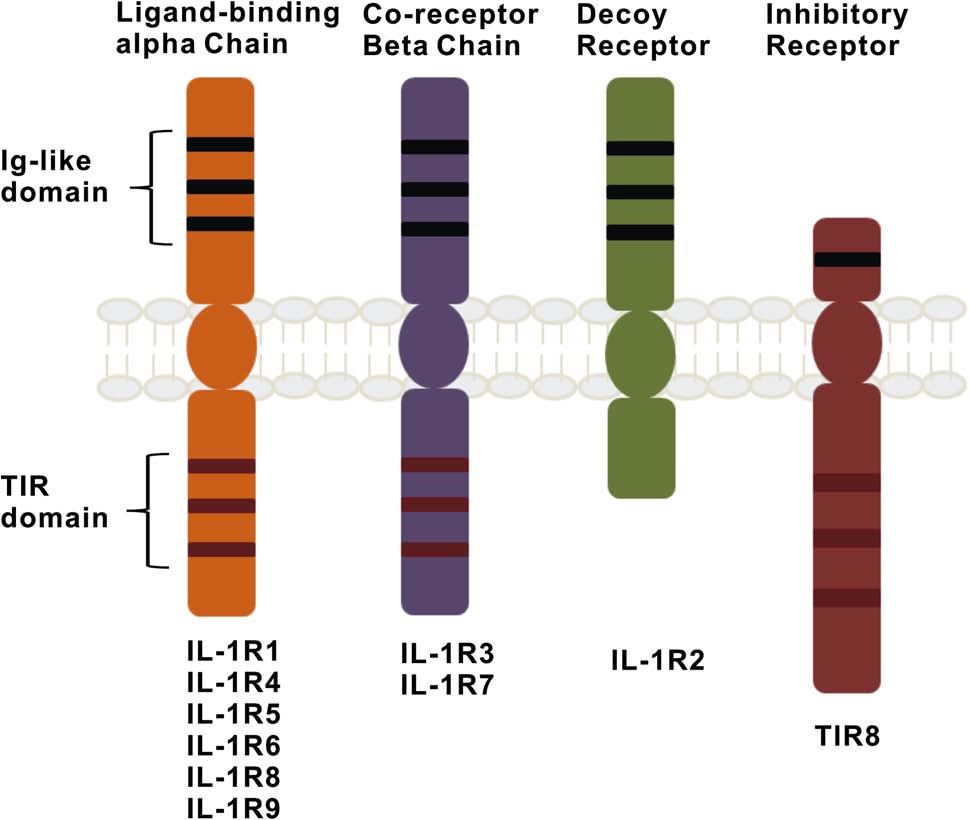 Fig. IL-1 family of receptors.
Fig. IL-1 family of receptors.
The signaling pathways triggered by the activation of the IL-1 receptor and the subsequent protein-protein interactions involve the activation of NF-κB and stress-activated c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) and p38 MAP kinases, resulting in inflammatory responses. IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) is an anti-inflammatory protein used clinically to treat rheumatoid arthritis and is considered a promising candidate therapy for stroke. Studies have shown that treatment with IL-1 RA leads to substantial improvements in outcome in preclinical models of ischaemic stroke, whether measured as reduced infarct volume or improved neurobehavioural outcome.
CD47, also known as integrin-associated proteins, is both a receptor for TSP1 and a ligand for shp-1's inhibitory immunoreceptor signal regulator protein (SIRP alpha), which belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and can transmit foreign signals to cells. CD47 possesses four subtypes formed by different selective splicing, which differ only in the length of the cytoplasmic end, but the CD47 subtype expressed by different cells is very conservative, and it is obvious that the cytoplasmic end is important for its function. Due to the extensive expression of CD47, the signaling pathway may vary depending on the cell type, so its effect on cell proliferation depends largely on the cell type, either activation or loss of CD47 could promote cell proliferation.
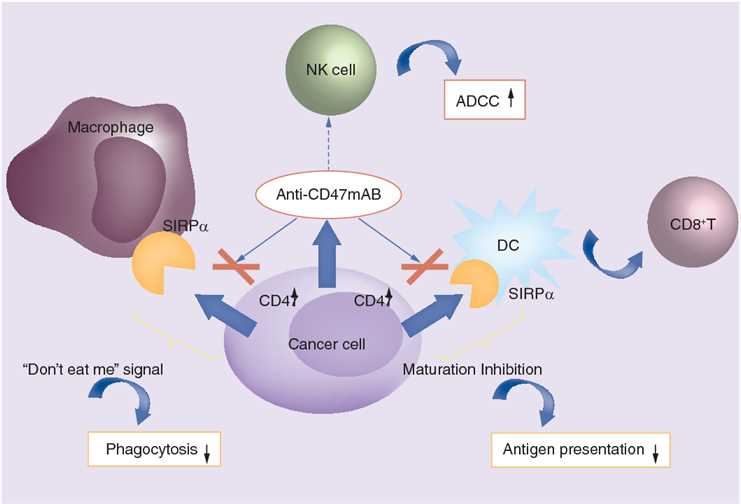 Fig.1 The role of CD47 in cancer and the mechanism of anti-CD47 monoclonal antibodies in cancer treatment. (Tong, 2018)
Fig.1 The role of CD47 in cancer and the mechanism of anti-CD47 monoclonal antibodies in cancer treatment. (Tong, 2018)
Targeting CD47 is in the spotlight of cancer immunotherapy. Blocking this target triggers recognition and clearance of cancer cells by the innate immunity. Among various approaches to immunotherapy, clinical research of anti-CD47 therapy has achieved certain progress. Based on preclinical studies, anti-CD47 has proceeded to clinical trials and at least three CD47 antagonists (including Hu5F9-G4, CC-90002, and TTI-621) are currently in phase I clinical trials, covering hematological neoplasms and tumors. As a leading provider around the world, Creative Biolabs offers customized antibody development services to produce anti-CD47 recombinant human antagonist antibody, which is able to recognize SIRP-α binding region of human CD47 and helps to suppress cancer cell signals.
Reference
Programmed death-1 (PD-1) is a receptor on T cells that has been shown to suppress activating signals from the T cell receptor. When it binds to the ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2, cells expressing PD-1 exhibit functional activities in response to antigen stimulation, including proliferation, secretion of cytokines, and reduction in cytotoxicity. The PD-1 signaling pathway is a key mediator of immune control in the local tumor microenvironment (TME), and its interaction with its ligands downregulates the immune response during infection or tumor development. Scientists hope to design a drug that blocks PD-1/PD-L1 binding to restore the role of autoimmune mechanisms in anti-tumor therapy, and PD-1 has become one of the most interesting antibody design targets.
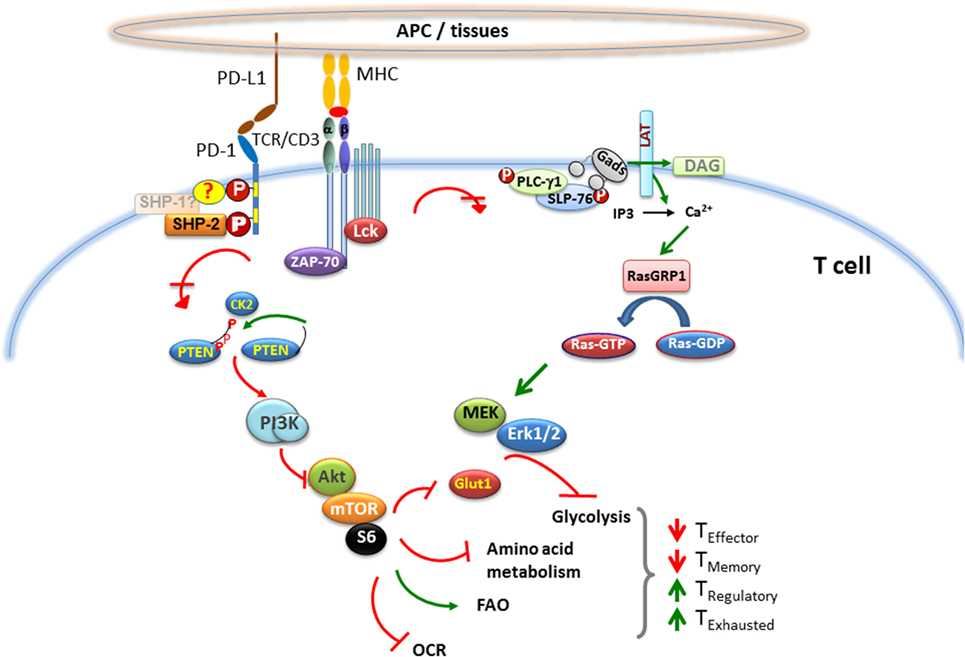 Fig.1 PD-1 pathway.
Fig.1 PD-1 pathway.
At present, PD-1 pathway blocking drugs have shown remarkable efficacy and long-lasting activity in the treatment of many cancer types, and have become a routine medical treatment against tumors. Pembrolizumab and nivolumab, which can be used to treat refractory advanced melanoma, have been approved by regulatory authorities and it is expected that more PD-1 blocking drugs for other cancer types will be put into use in the future. The safety profile of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 drugs is compatible with the development of combination therapies, and the efficacy of PD-1 pathway antagonists can be predicted by preclinical models. By identifying the expression of tumor PD-L1 protein, we can screen out some related factors that block the PD-1 pathway, further reduce the risk of targeted antibody drugs, and increase our understanding of the mechanism basis of this key pathway in tumor biology. Creative Biolabs provides you with antagonist antibody development services, please contact us to inquire about the details of the service.
Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is one of two ligands for PD-1, which is expressed on the surface of macrophages, T cells, B cells, NK cells, DCs and some cancer cells. Binding of PD-1 to PD-L1 inhibits the activation of the t cell, resulting in down-regulation of the immune system. Therefore, PD-L1 is an important immune checkpoint and a common target for many cancer therapeutic antibodies. However, although some antibody drugs have shown significant anticancer activity in clinical trials, only a small percentage of cancer patients can benefit from PD1/PD-L1-targeted mAbs, and there have been reports of related adverse reactions. In view of this, it is highly desirable to continue to develop more secure PD-L1 blocking drugs for different cancer models.
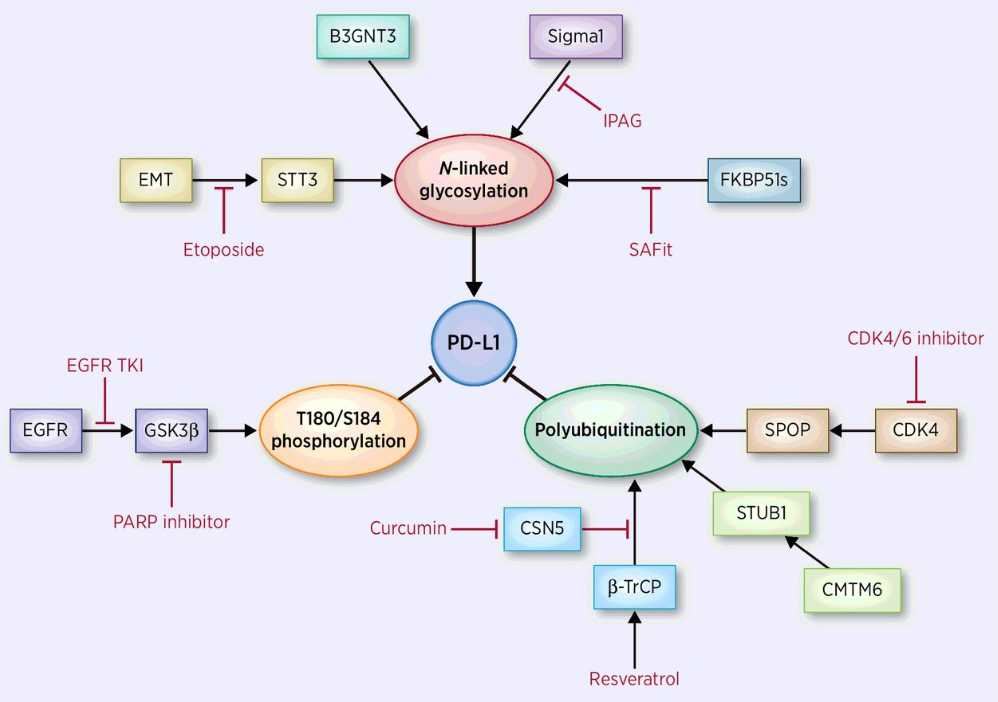 Fig.1 PD-L1 pathway.
Fig.1 PD-L1 pathway.
Immune checkpoints protect tumor cells from being destroyed by the immune system by inhibiting the activity of T cells. The existence of this mechanism provides new ideas and therapeutic targets for tumor treatment. Among them, the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1 has become the focus of our attention due to its involvement in a variety of cancers. At present, some antagonist antibodies that block the interaction of PD-1/PD-L1 have played a significant anti-tumor effect, but their application direction is still combined with other traditional treatment methods. Therefore, there is still a need to work on exploring combination therapies, new molecular targets or targets that have been identified. Creative Biolabs has the world's advanced antibody design level and can provide you with development services for PD-L1 antagonist antibodies, please contact us to inquire about the details of the service.
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen (CTLA-4) is a protein receptor that acts as an immune checkpoint and downregulates the immune response. CTLA-4 induces expression on activated effector T cells and constitutively expresses on regulatory T cell subsets (Treg). The study of the mechanism of CTLA-4 signaling pathway and CTLA-4 blockade-mediated anti-tumor immune activity is the key research field of oncology today. Scientists believe that blocking immune checkpoints such as CTLA-4 can enhance the immune response to tumors. The blocking drug has shown an effect on transplanted human tumors in mice, indicating that it will become one of the main means of resistance to cancer in humans in the future.
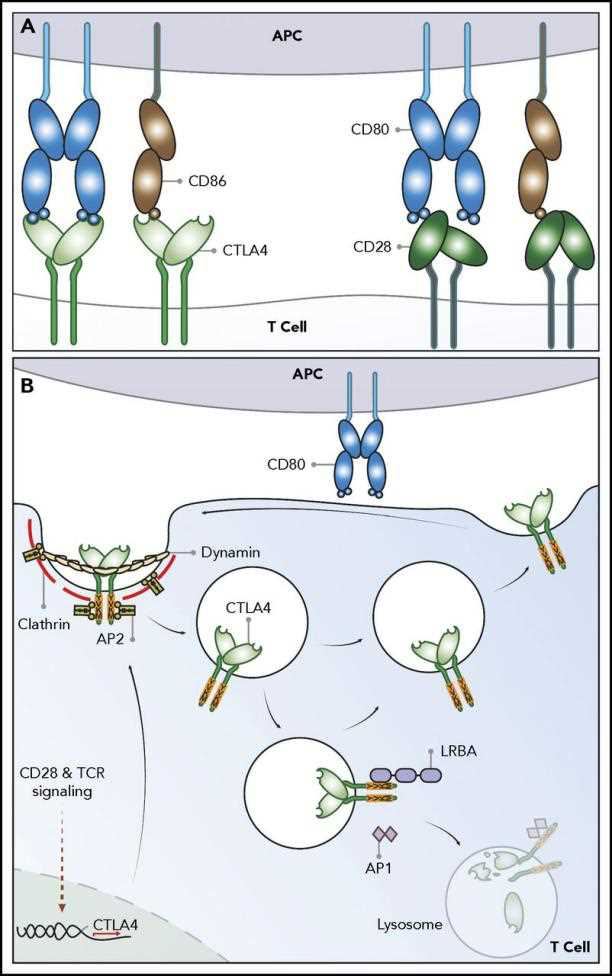 Fig.1 CTLA-4 pathway.
Fig.1 CTLA-4 pathway.
The development of agonist and antagonist antibodies to CTLA-4 permitted the first characterizations of CTLA-4 function in vitro and in vivo. The blockade of CTLA-4 interaction with B7 enhances T cell activation in vitro, whereas antibodies that engage CTLA-4 signaling attenuate T cell activation. Based on studies of anti-tumor immunity in mice, CTLA-4 blocking antibodies, such as ipilimumab and tremelimumab, have been developed in humans, and obtained substantial clinical trial data by using these drugs in cancer patients such as metastatic melanoma. These large numbers of experiments have made us realize that in order to design safer and more efficient immunological checkpoint blocking drugs, we need a more comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the relevant protein interaction mechanisms. Creative Biolabs designs and develops CTLA-4-targeted antagonist antibodies to meet your experimental needs, please contact us to inquire about the details of the service.
Lymphocyte Activation Gene-3 (LAG-3) is a 498-amino acid type I transmembrane protein expressed on activated human NK and T cell lines. The LAG-3 gene is located adjacent to CD4 on chromosome 12 in human. Both LAG-3 and CD4 molecules include four extracellular immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF)-like domains(D1-D4). LAG-3 exhibits rigidity between the D1 and D2 domains and between the D3 and D4 domains due to a long, continuous β-strand that extends between these domains, but with relative flexibility between the D1-D2 and D3-D4 substructures. LAG-3 binds MHC class II primarily through an additional loop consisting of only 30 amino acids in the D1 domain between the C and C′ β strands. The D2 domain has been shown to be essential for LAG-3-MHC class II ligation and is perhaps involved in positioning the D1 domain. While the D3 and D4 domains are dispensable for binding, they may be required to extend the D1 domain within reach of MHC class II.
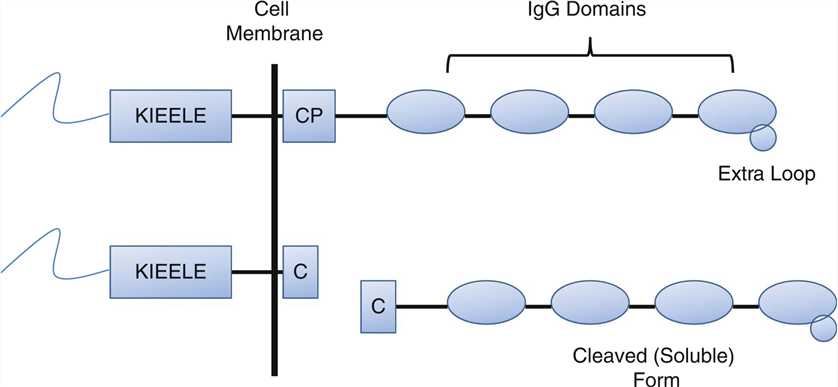 Fig.1 The structure of LAG-3.
Fig.1 The structure of LAG-3.
LAG3 possesses two distinct motifs in the cytoplasmic tail. One is a repetitive “EP” motif consisting of a series of glutamic acid-proline dipeptide repeats. The second is a relatively unique “KIEELE” motif, highlighted by an essential lysine residue. This “KIEELE” motif is required for LAG-3 modulation of T cell function. LAG-3 is a potential cancer immunotherapeutic target due to its negative regulatory role on T cells. There are currently four LAG-3 modulating agents that have entered the clinic as anti-cancer therapeutics, with several more in preclinical development. Initial LAG-3-driven clinical trials focused on a first-in-class agent, IMP321 designed as an APC activator. Three different LAG-3-specific mAbs have been developed for the treatment of cancer: BMS-986016, LAG525 and MK-4280. In addition, the anti-LAG-3 antagonistic mAb (GSK2831781) was designed to deplete LAG3+ expressing cells in patients with autoimmune diseases.
T cell immunoglobulin-3 (TIM-3) was a type I transmembrane protein expressed on activated Th1 and Tc1 cells. Human TIM-3 consists of 302 amino acid residues and belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF), with an extracellular domain consisting of a membrane-distal N-terminal immunoglobulin (IgV) domain, followed by a membrane-proximal mucin domain containing potential sites for O-linked glycosylation. The stalk domain lying between the mucin and transmembrane domain has sites for N-linked sugars, which is followed by a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic tail. The crystal structure of the IgV domain of TIM-3 shows the presence of two anti-parallel β sheets, which are tethered by a disulfide bond. Two additional disulfide bonds formed by four non-canonical cysteines stabilize the IgV domain and reorient a CC′ loop toward a FG loop thereby forming a “cleft” structure that is thought to be involved in ligand binding.
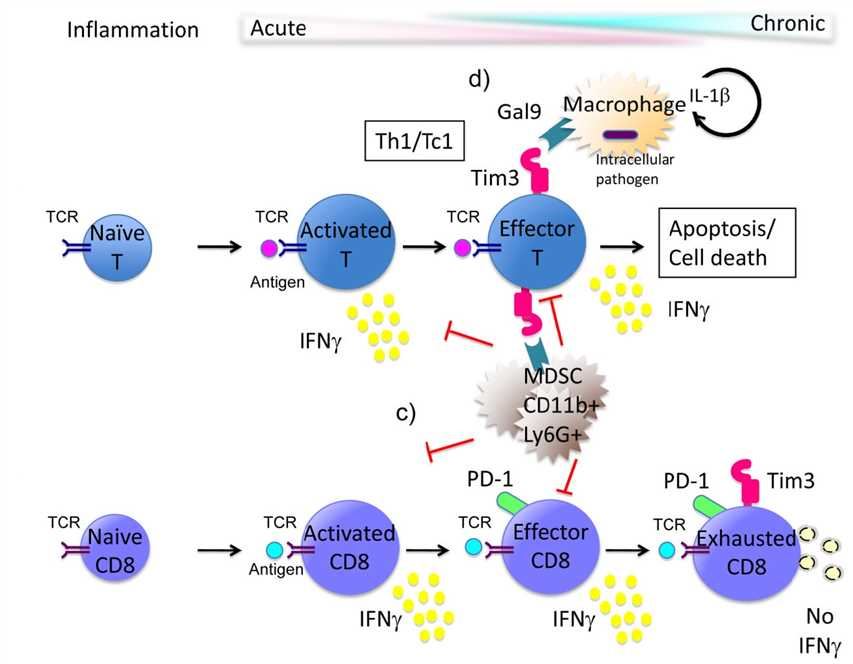 Fig.1 Model of Tim-3 function in the immune response.
Fig.1 Model of Tim-3 function in the immune response.
The S-type lectin galectin-9 (Gal-9) was identified as a TIM-3 ligand. Gal-9 is a soluble molecule that is widely expressed, is upregulated by IFN-γ 2 and binds to oligosaccharides on the TIM-3 IgV domain. Gal-9 triggering of TIM-3 on Th1 cells has been shown to induce cell death or exhaustion. Thus, TIM-3 came to be known as a negative regulatory molecule important for abrogating Th1 and Tc1 driven immune responses. The combined use of antagonistic anti-TIM-3 antibodies with agonistic antibodies to pro-stimulatory molecules on tumor-specific T cells, such as CD137, has demonstrated long-term protection in a murine model of ovarian cancer. This therapeutic regimen of using TIM-3 blockade with activation of a pro-stimulatory molecule on T cells could be exploited in the future to obtain objective anti-tumor responses in patients.
T-cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT) is a member of the poliovirus receptor (PVR)/nectin family, a subset of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It consists of an extracellular immunoglobulin variable-set (IgV) domain, a type 1 transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain possessing a typical immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) and an immunoglobulin tyrosine tail (ITT) motif. The expression of TIGIT is tightly restricted to lymphocytes, with the highest expression being on effector and regulatory CD4+ T cells, follicular helper CD4+ T cells, effector CD8+ T cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. TIGIT binds to two ligands, CD155 (PVR) and CD112 (PVRL2, nectin-2), which are expressed on APCs, T cells, and a variety of non-hematopoietic cell types including tumor cells.
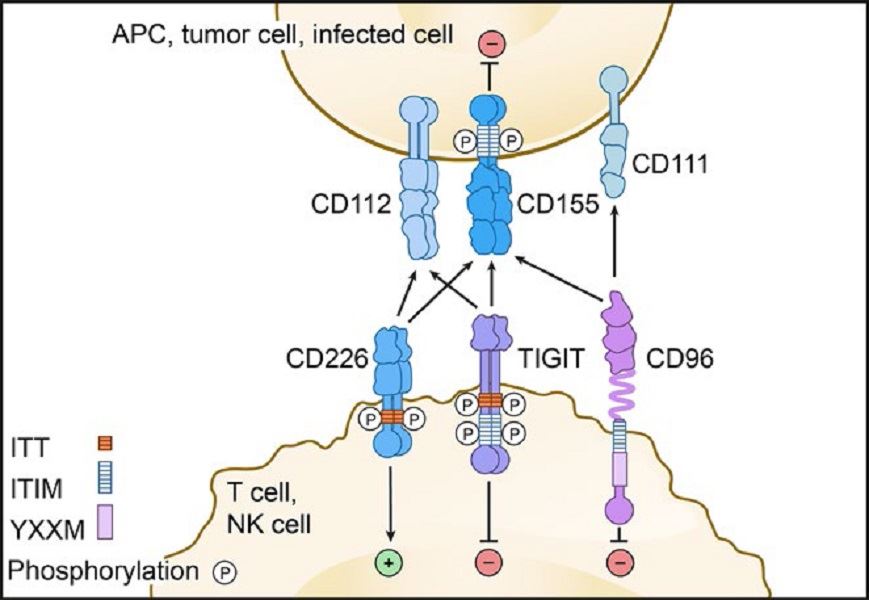 Fig.1 TIGIT pathway.
Fig.1 TIGIT pathway.
The TIGIT IgV domain possesses distinctive (V/I)(S/T)Q, AX6G, and T(F/Y)PX1G submotifs that mediate a ‘lock and key’ trans-interaction with cis-homodimers of PVR. These conserved motifs define a PVR/nectin family comprising TIGIT, CD226, CD96, CD112R, PVR, CD112, and CD113. Nectins and nectin-like proteins are surface receptors that mediate cell-cell adhesion, tissue organization, cell polarization, and signal transduction through homophilic and heterophilic trans-interactions. TIGIT can inhibit lymphocytes through three distinct mechanisms of action. TIGIT can signal through the ITIM and/or ITT motifs on its intracellular tail after binding to PVR. TIGIT can induce PVR signaling in adjacent dendritic cells or tumor cells by binding to PVR. TIGIT can inhibit CD226 signaling by binding to PVR at a higher affinity or disrupting CD226 homodimerization. In preclinical trials, Combination of immunotherapies using different mechanisms of actions are ongoing. Inhibitors used in combination may increase response rates with anti-TIGIT therapies. In harvested human metastatic melanoma tumors, the addition of anti-TIGIT and anti-PD-1 blocking antibodies resulted in increased proliferation of CD8+ TILs with increased degranulation of these cells as compared to those treated with anti-TIGIT or anti-PD1 antibodies alone.
V-domain Ig-containing Suppressor of T cell Activation (VISTA) is a type I transmembrane protein consisting of a single N-terminal immunoglobulin (Ig) V domain, an approximately 30 amino acid (aa) stalk, a transmembrane domain, and a 95 aa cytoplasmic tail. Phylogenetic analysis of the full VISTA molecule shares similarities with PD-1, CD28, and CTLA-4, with the highest identity with PD-1. The analysis of the IgV domain of VISTA shows that this has the greatest homology with programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1). Subsequent sequence prediction and modeling after PD-L1 show that the IgV domain of VISTA possesses the canonical disulfide bond between the putative B and F strands. In addition, VISTA also uniquely has four additional invariant cysteines (three predicted to be within the IgV domain and an additional one in the stalk region). Within the conserved cytoplasmic tail, VISTA resembles CD28 and CTLA-4. VISTA has a conserved Src homology 2 (SH2)-binding (YxxQ, potentially capable of binding STAT proteins) motif in the middle of the cytoplasmic tail and three C-terminal SH3-binding domains (PxxP, two in CD28 and one in CTLA-4). Taken together, these data suggest that VISTA may act as both a ligand and receptor in regulating immune responses.
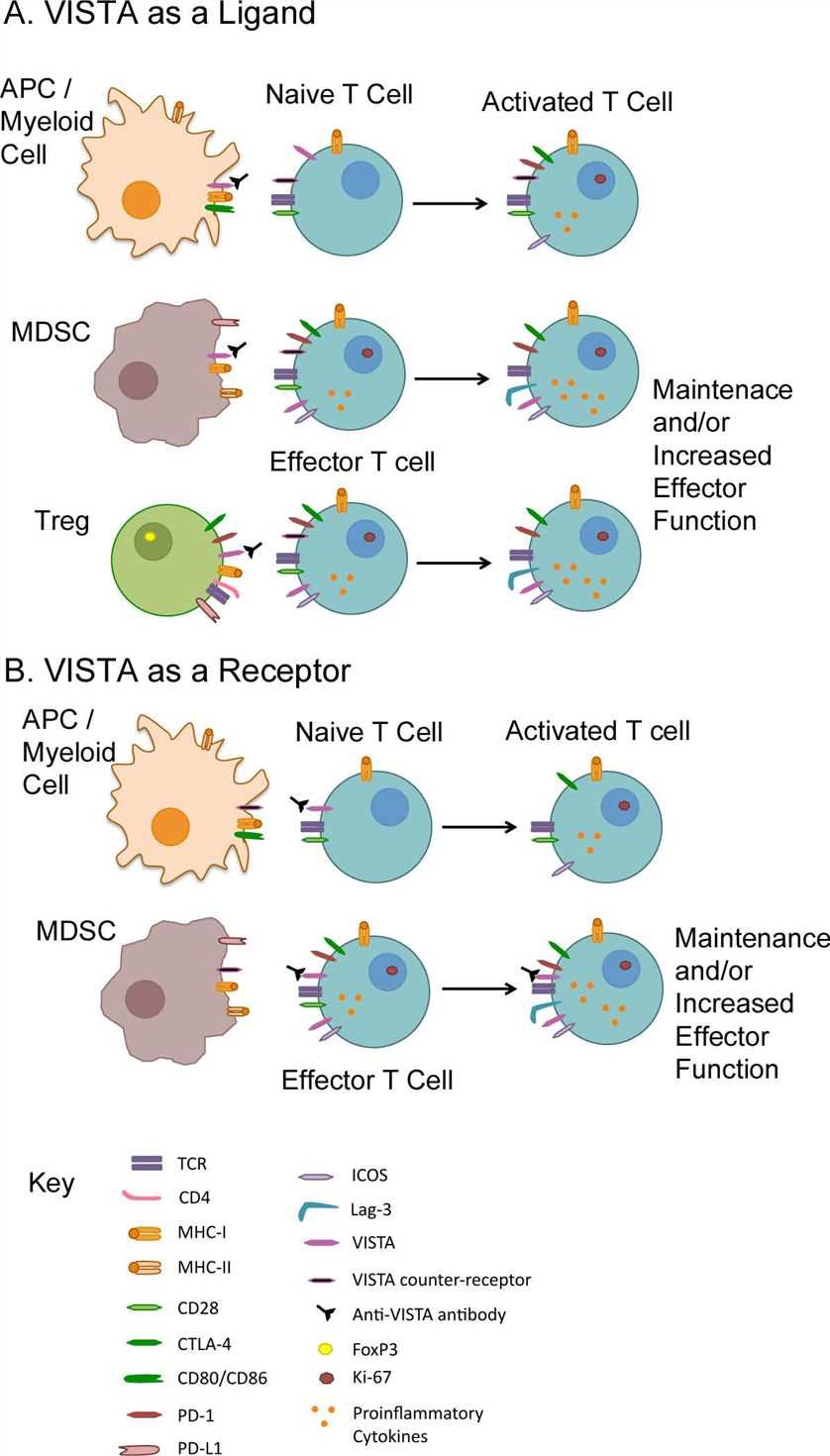 Fig. 1 VISTA function as a ligand and a receptor.
Fig. 1 VISTA function as a ligand and a receptor.
In humans, VISTA is primarily found in hematopoietic tissues. Myeloid cells, including patrolling (CD14dimCD16+) and inflammatory (CD14+CD16+/−) monocytes, and lymphoid and myeloid dendritic cell populations have the highest expression, with intermediate levels on neutrophils. In the context of cancer immunotherapy, one advantage of VISTA blockade as an immunotherapeutic strategy is that tumor cells do not require VISTA expression. Antibodies targeting VISTA for cancer immunotherapy are already under development and VISTA may soon be a part of the immunotherapy revolution.
The serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 1 (SPINK1, also known as pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor) is a 6.2 kDa protein secreted by the pancreatic acinar cells that can potently inhibit trypsin. Mature SPINK1 contains 56 amino acids and three disulfide bonds. SPINK1 has been reported to inhibit human trypsin-1 and -2 (cationic and anionic trypsins), but not trypsin-3 (mesotrypsin). A small amount of trypsinogen is converted to active trypsin and inactivated by SPINK1, thereby preventing damage to pancreatic acinar cells. During the autoactivation of trypsinogen, the newly generated trypsin reacts with SPINK1 and becomes unavailable to catalyze further trypsinogen activation. In time, SPINK1 reserves become depleted and autoactivation can freely proceed. The protective role of SPINK1 is to delay trypsinogen autoactivation. This delay is important as it allows for the digestive proteases to transit from the pancreas to the duodenum in an inactive form. Therefore, a decrease in SPINK1 levels or reduced ductal fluid flow can impair this protective mechanism and increase the risk of premature, intra-pancreatic trypsinogen autoactivation.
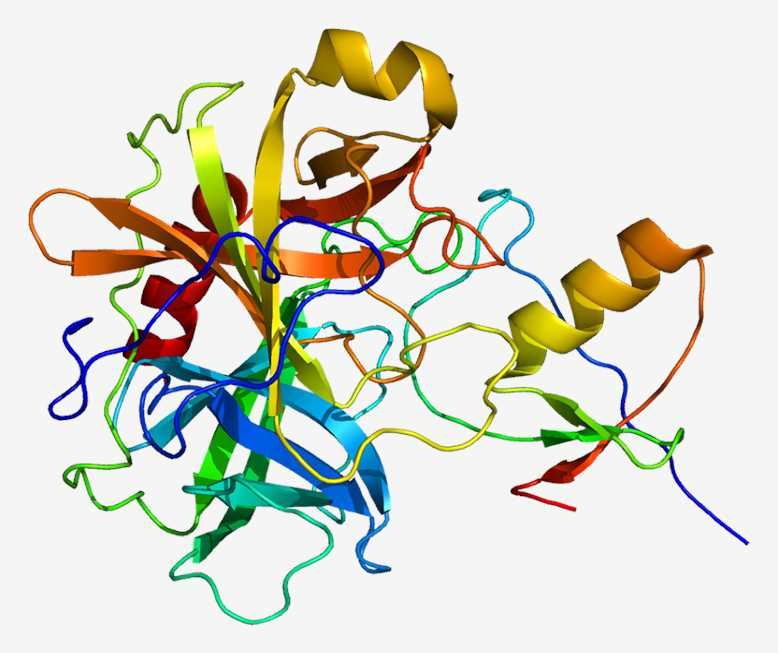 Fig. 1 The structure of SPINK1.
Fig. 1 The structure of SPINK1.
In addition, SPINK1 is able to induce the growth of cultured cells and activate the EGF-receptor. It has been suggested that SPINK1 mediates tumor growth, differentiation, and angiogenesis via stimulation of the EGF-receptor or by suppression of serine-protease- or caspase-dependent apoptosis. There is evidence that SPINK1 plays a role in tissue differentiation and repair, reproduction and regulation of apoptosis. Over-expression of SPINK1 in cancer could block cancer cell apoptosis resulting in suppression of the immune response and escape of cancer cells from immune surveillance. SPINK1 is highly expressed in the pancreas. It has been localized to the zymogen granules of pancreatic acinar cells, where it protects the pancreas from premature activation of trypsinogens. SPINK1 is secreted into the pancreatic fluid along with digestive enzymes.
Factor VIII is a large protein of 2332 amino acids that circulate in complex with von Willebrand factor (VWF). It has a structure consisting of 6 domains, designated A1-A2-B-A3-C1-C2. The 3 A domains are each approximately 330 residues, and approximately 40% identical to each other and to the copper-binding protein ceruloplasmin. The C domains are smaller (approximately 160 residues) and are more distantly related to various members of the discoidin protein fold family, such as galactose oxidase. The B domain has no known structural homologs, is heavily glycosylated, and is relatively dispensable for procoagulant activity. The carboxy-terminal 159 amino acids of factor VIII comprise its C2 domain, which is involved in binding to VWF and primarily responsible for binding to platelet membrane surfaces. Factor VIII is released from VWF and the B-domain is removed upon its activation to factor VIIIa, the cofactor that facilitates the junction of activated factor IX (factor IXa) and factor X on the phospholipid membrane to produce activated factor X (FXa).
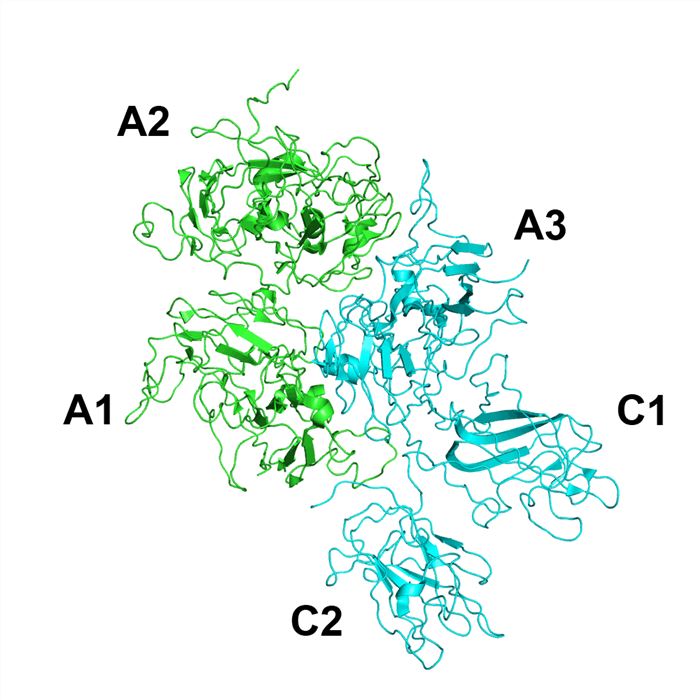 Fig.1 The structure of Factor VIII.
Fig.1 The structure of Factor VIII.
Factor IX is a vitamin K-dependent protease with a mature protein length of 415 amino acids, organized into a gamma-glutamic acid (GLA) domain (residues 1-40), a short hydrophobic stack (residues 41-46), two epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) domains (EGF1: residues 47-83, and EGF2: residues 88-127, which are connected by linker residues 84-87), an activation peptide (residues 146-180), and a serine protease or catalytic domain (residues 181-415). The GLA domain possesses several intermediate- and low-affinity Ca²⁺ binding sites, and the EGF1 and protease domain each possess a single high-affinity Ca²⁺ binding site. Ca²⁺ binding to each domain imparts structural properties to Factor IX that confer biologic function. It is activated to factor IXa when cleaved by activated factor XI or tissue factor-factor VIIa.
Factor VIII inhibitors in hemophilia A (HA) and factor IX inhibitors in hemophilia B (HB) are significant clinically when they require a change in a patient’s treatment regimen. Factor VIII inhibitors are directed at limited epitopes of the large factor VIII molecule, most often against the A2, C1, and C2 domains. Factor IX inhibitors are most often directed against the GLA or protease domains. Conventional treatment products for HA have included recombinant full-length factor VIII, recombinant factor VIII with the B-domain deleted, plasma-derived purified factor VIII and plasma-derived factor VIII with VWF. Conventional treatment products for HB include recombinant full-length factor IX and plasma-derived factor IX. Modified longer half-life products include Fc-fusion and albumin-fusion factor IX.
Lymphatic Vessel Endothelial Receptor-1 (LYVE-1), a member of the Link superfamily closely related to the leucocyte HA receptor CD44, is the major HA receptor in the endothelia of afferent lymphatic vessels and lymph node sinuses. LYVE-1 is a 340 residue integral membrane receptor containing an extended form of the conserved HA-binding Link module at the end of a 211-212 residue extracellular domain, a 21 residue transmembrane anchor and a 63 residue cytoplasmic tail. Like CD44, the consensus Link module in LYVE-1 is predicted to comprise a sandwich of two beta sheets made up of six beta strands (β1-β6) stabilized by a pair of conserved disulfide bonds. This, in turn, is bracketed by two additional beta strands (β0 and β7) linked by a third conserved disulfide bond.
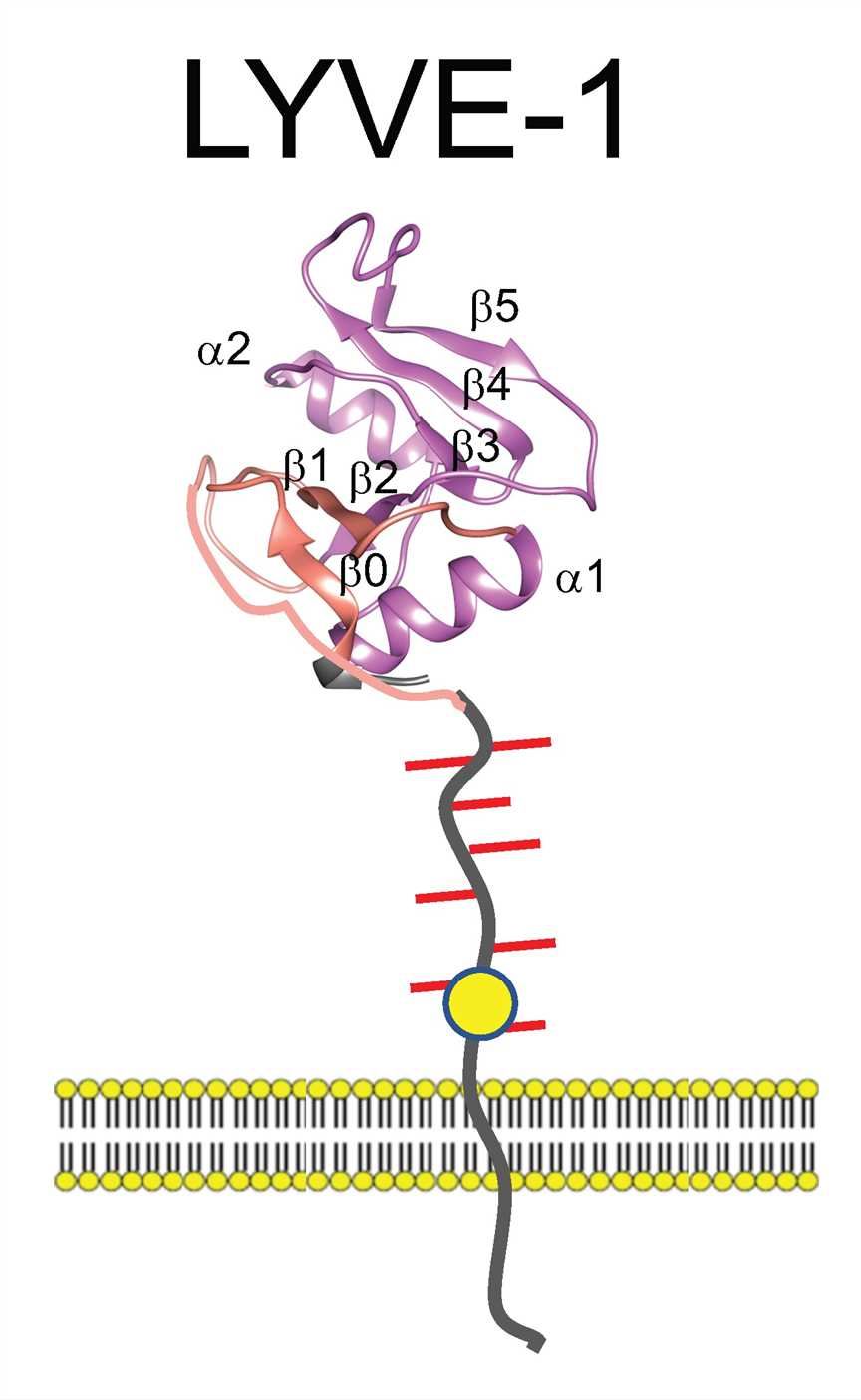 Fig. 1 The structure of LYVE-1.
Fig. 1 The structure of LYVE-1.
LYVE-1 is largely confined to lymphatic endothelial where it displays a punctate pattern of distribution on the luminal and basolateral plasma membrane surfaces as well as variable retention in a perinuclear, ER-derived intracellular compartment. The receptor is also expressed in liver and spleen sinus vascular endothelia, in pulmonary endothelial, and in a rare macrophage sub-population resembling so-called immune-regulatory M2-like cells with endothelial progenitor potential that are occasionally present in inflamed and tumor tissue. LYVE-1 has been identified as that of a lymphatic docking receptor for dendritic cells, selectively engaging with their surface HA glycocalyx to regulate entry to peripheral lymphatics and migration to downstream lymph nodes for immune activation. Furthermore, LYVE-1 mediates the trafficking of macrophages and is also exploited by HA-encapsulated Group A streptococci for lymphatic invasion and host dissemination. Consistent with a role in lymphatic trafficking, the interaction of LYVE-1 with HA and its degradation products can also activate intracellular signaling pathways for the endothelial junctional retraction and lymphatic endothelial proliferation. LYVE-1 has potential as a new target for therapeutic intervention. This targeting feature could in principle be used to block unwanted immune or associated inflammatory responses in any appropriate disease context.
C1 inhibitor is a member of the serpin family of protease inhibitors. Its structure and mechanism of protease inactivation are similar to other members of the family. Protease inactivation by serpins depends on a trapping mechanism that is activated following recognition, by protease, of the reactive center loop, which is displayed above the surface of the molecule. Cleavage of the peptide bond (P1-P1’) at the reactive center triggers a molecular rearrangement and results in covalent bond formation between the P1 residue of the inhibitor and the active site serine of the protease. C1 inhibitor inactivates a variety of proteases including complement system proteases (C1r, C1s, MASP2), contact system proteases (factor XII, plasma kallikrein), an intrinsic coagulation protease (factor XI) and the fibrinolytic proteases (plasmin, tissue plasminogen activator). C1 inhibitor contains a long amino-terminal domain of approximately 100 amino acid residues that are heavily glycosylated with both N- and O-linked sugars.
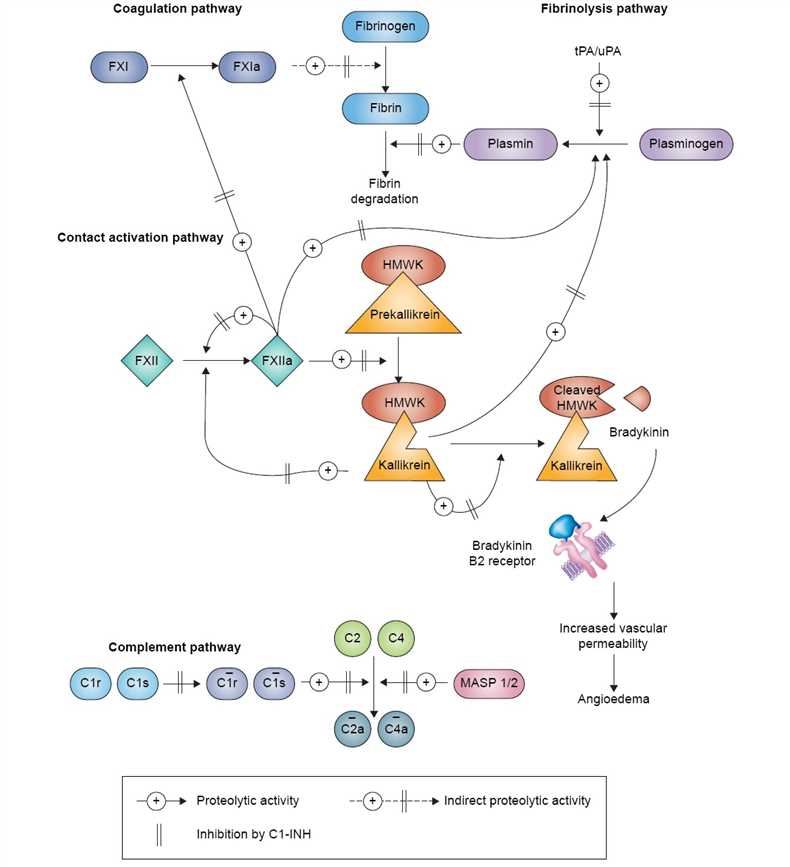 Fig.1 Pathways inhibited by C1 hibitor.
Fig.1 Pathways inhibited by C1 hibitor.
C1 inhibitor plays important roles in the regulation of vascular permeability and in the suppression of inflammation. Vascular permeability control is exerted largely through inhibition of two of the proteases involved in the generation of bradykinin, factor XIIa and plasma kallikrein (the plasma kallikrein-kinin system). Anti-inflammatory functions are exerted via several activities including inhibition of complement system proteases (C1r, C1s, MASP2) and the plasma kallikrein-kinin system proteases, in addition to interactions with a number of different proteins, cells, and infectious agents. C1 inhibitor has been used for the treatment of attacks of angioedema for many years. For this disease, it is quite effective and well-tolerated with few side effects. Over the past few years, it has been considered for use in a variety of inflammatory diseases including IR injury, hyper-acute transplant rejection, gram-negative sepsis, particularly endotoxin shock, in addition to a number of other conditions.
KIR (Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor) is a family of cell surface proteins found on critical cells of the immune system termed natural killer (NK) cells. The stimulation or tolerance of NK cells is achieved by a cross-talk of signals from cell surface receptors. KIR is a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I inhibitory receptor who regulates the killing function of NK cells by interacting with MHC molecules. This interaction allows them to detect virally infected cells or tumor cells, and prevent damage to healthy cells. KIR serves as a key regulator of NK cell function in humans, and inhibitory KIR can efficiently block the killing effect of NK cells on neoplasms.
Immune checkpoint blockade stands for a valuable cancer therapy that aims to restore an effective antitumoral response mediated by endogenous immune cells. As highly polymorphic activating, inhibitory receptors, distinct structural domains in various KIR family members determine the function by offering docking sites for ligands or signaling proteins. And most molecules are inhibitory, indicating that their recognition of MHC restrains the cytotoxic activity of their NK cells. As a corollary to targeting negative regulators of T cells, KIR family of NK cell negative regulators would become a novel and active kind of immunotherapy. As an expert in the antibody market, Creative Biolabs is specialized in new antagonistic antibody design, characterization, and development, and provides custom antagonistic antibody services for KIR target and other immune checkpoints for associated disease blockage.
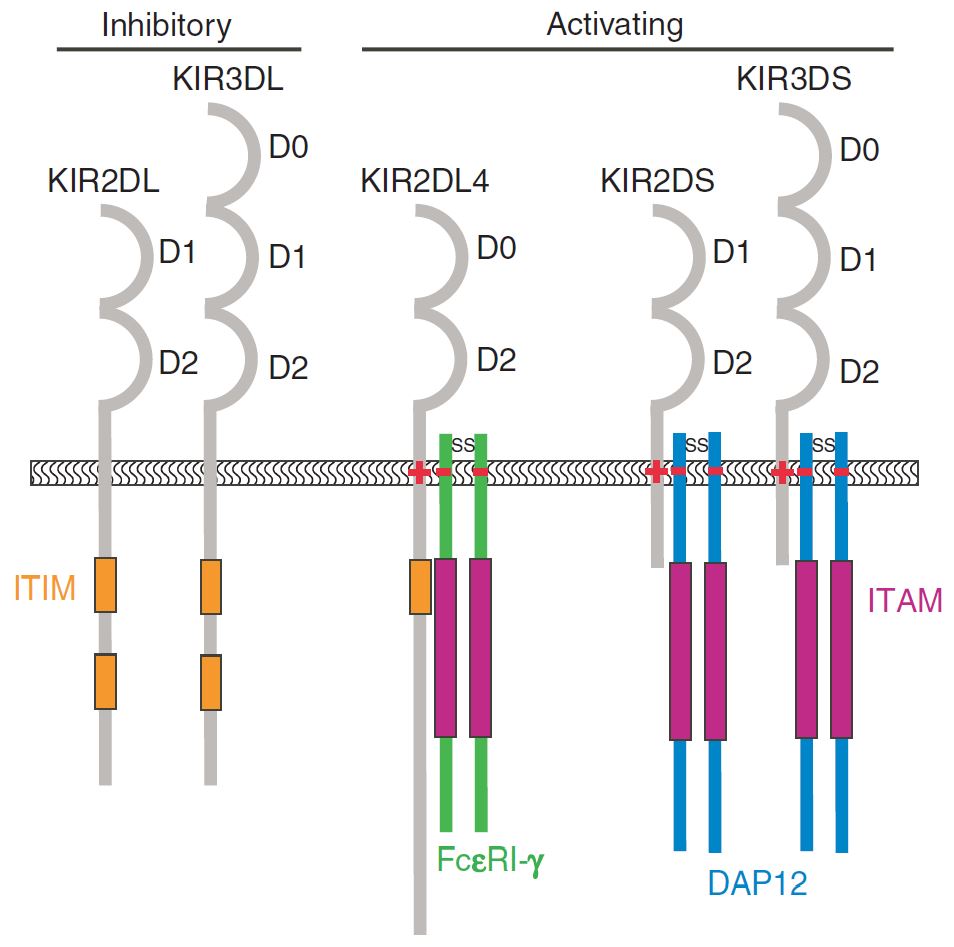 Fig.1 The major structural differences between different KIR family members. (Campbell, 2011)
Fig.1 The major structural differences between different KIR family members. (Campbell, 2011)
Reference
TGF-β (Transforming growth factor-beta) is a ubiquitous cytokine that plays an important role in many cellular processes, including tumor invasion and metastasis. Almost every cell type has the ability to release TGF-β, and to respond to TGF-β signal through its receptors on the cell surface. Therefore, gain or loss of function of the TGF-β pathway and its components are known to induce a variety of diseases, even cancers. In epithelial cells, TGF-β works as a tumor suppressor, where it inhibits proliferation, mediates differentiation, and initiates apoptosis. Conversely, in other situations, TGF-β accelerates tumor progression by promoting cell invasion and metastasis. Consequently, TGF-β has a dual role in tumorigenesis and development, both as a tumor suppressor and tumor promoter. These effects are not limited to the tumor cell itself, but can also be modulated by the stroma and the immune system. The dichotomous parts of TGF-β in cancer gives a better guide for the patient selection of the use of anti-TGF-β therapies in current clinical trials.
The misregulation of TGF-β signaling is involved in the pathogenesis of various diseases, thus its inhibitors are potential to be novel drugs for the treatment of cancer, osteoporosis, fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, obesity, and bone, tooth remodeling. Monoclonal antibodies against TGF-β (type 1 and 2), named lerdelimumab and metelimumab respectively, have been developed and now are in phase II/III studies in fibrosis, nephropathy, glioblastoma, colorectal cancer, and non-small cell lung carcinoma. At Creative Biolabs, we offer comprehensive checkpoint antagonistic antibody development services to assist clients in producing therapeutic antibodies, which have the opportunity to become promising lead compounds in drug development for varying pathological contexts.
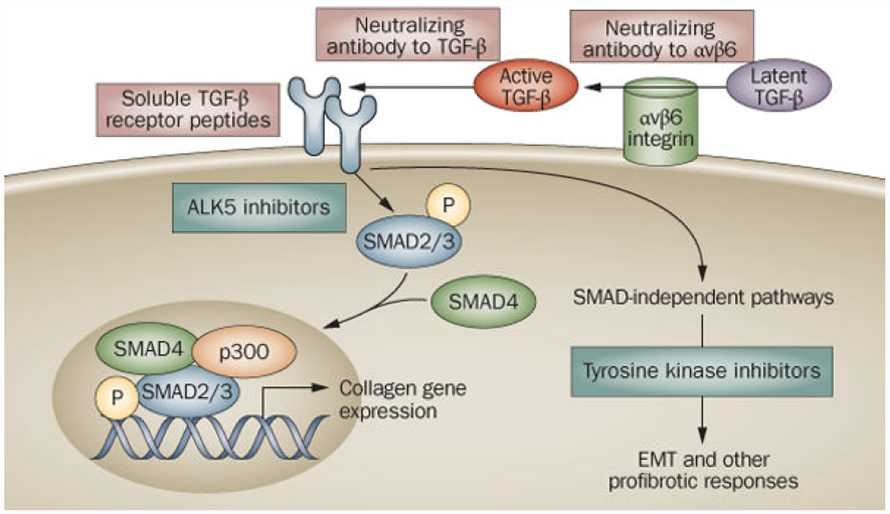 Fig.1 Antagonism of TGF-β signaling: targeting the extracellular pathway. (Varga, 2008)
Fig.1 Antagonism of TGF-β signaling: targeting the extracellular pathway. (Varga, 2008)
Reference
IL-10 (Interleukin-10), initially known as cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is shown to be produced primarily by mouse T helper cell type 2 (TH2) cells, where it inhibits the production and activation of cytokines by T helper cell type 1 (TH1) cells. It has been characterized as an anti-inflammatory cytokine secreted by T helper cells, B cells, macrophages, and a variety of other immune cells. These cells also serve as its targets, meaning that IL-10 presence and action is highly controlled and perhaps compartmentalized. IL-10 can enhance humoral immune responses, increasing class II expression on B cells and inducing immunoglobulin production. This cytokine has been mapped to human chromosome 1q23.3 and expresses its regulatory functions by binding to a specific cell surface receptor (IL-10R) that consists of two chains (IL-10R1 and IL-10R2).
IL-10 regulates immune-mediated inflammation and modulates the function of cells, including lymphocytes, monocytes, dendritic cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. As a potent immunosuppressive molecule, it blocks immune responses at diverse levels by directly and indirectly acting on both the innate and adaptive arms of the body’s immune system. IL-10 is able to inhibit the production of proinflammatory cytokines, antigen presentation, and cell proliferation. Accordingly, it is a pleiotropic cytokine with multiple immunostimulatory and immunosuppressive effects on a wide range of cell types. At Creative Biolabs, our experts offer cost-effective service packages of customized anti-IL-10 antagonistic antibody development for global customers to promote their projects on academic studies or clinical applications.
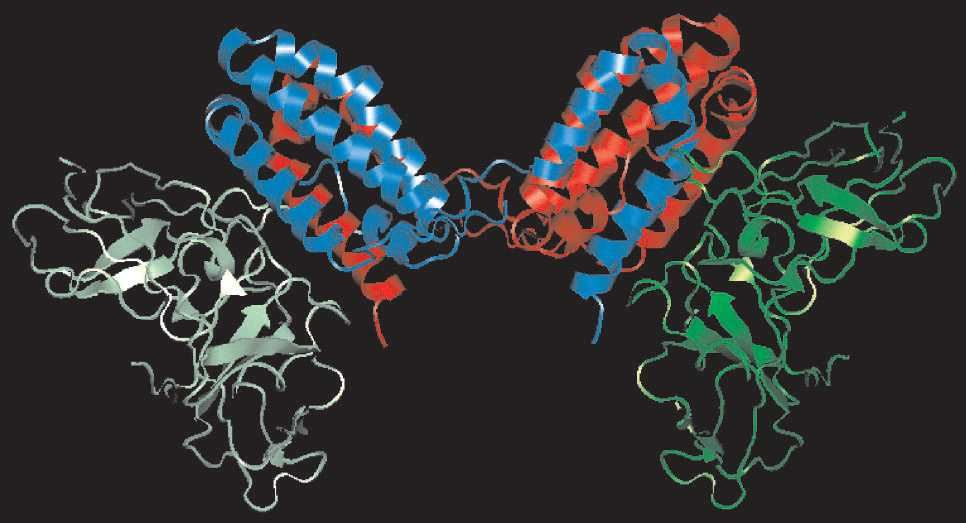 Fig.1 Three-dimensional structure of IL-10. (Asadullah, 2003)
Fig.1 Three-dimensional structure of IL-10. (Asadullah, 2003)
Reference
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
