Creative Biolabs now provides high-quality membrane protein expression service in yeast cells. With the help of advanced techniques and experienced scientific staff, we have confidence in delivering the most satisfactory results to facilitate diverse research projects.
Recombinant membrane protein production has been a long-term challenge from expression, solubilization, purification to characterization. A variety of heterologous systems have been established, including:
Among them, yeast cells combine the advantages of single cell nature (i.e. fast growth and easy genetic manipulation) and eukaryotic features (compatible with efficient protein folding, processing, and modifications). As microbes, they are quick, easy and inexpensive to culture; as eukaryotes they are able to post-translationally modify eukaryotic membrane proteins. Currently, there are several types of yeast hosts commercial available, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia pastoris, Hansenula polymorpha, Kluyveromyces lactis and Yarrowia lipolytica.
Recent crystal structures of recombinant transmembrane proteins produced in yeast include human aquaporin 2, chicken bestrophin-1, human TRAAK channel, human leukotriene C4 synthase, algal P-glycoprotein homologue and mouse P-glycoprotein using Pichia pastoris; the structures of the Arabidopsis thaliana NRT1.1 nitrate transporter, a fungal plant pathogen TMEM16 lipid scramblase and the yeast mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier were revealed using recombinant membrane protein production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Figure 1).
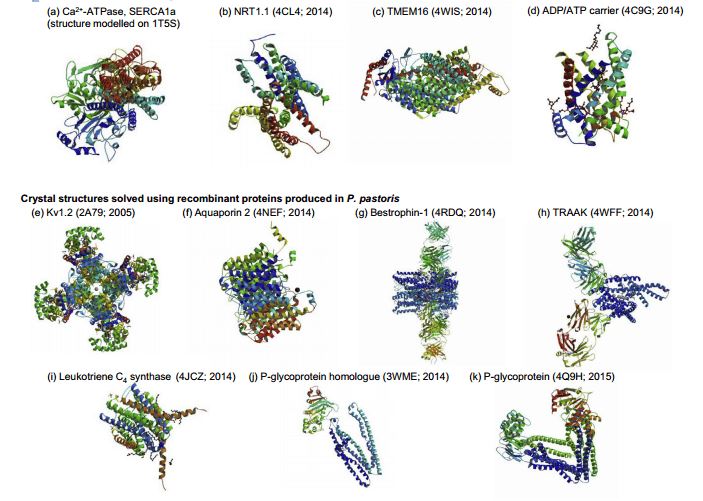 Figure 1. Overview of recombinant transmembrane proteins produced in yeast cells. (Methods, 2016)
Figure 1. Overview of recombinant transmembrane proteins produced in yeast cells. (Methods, 2016)
Creative Biolabs has developed some strategies for improving protein yield of P. pastoris and S. cerevisiae via optimizing the expression plasmid, host cell, culture conditions, as well as the extraction and purification process of functional membrane proteins. The significant advantages of S. cerevisiae are described as below: 1). Its genetics are better understood, and 2). It is supported by a more extensive literature than P. pastoris. While P. pastoris has the advantage of being able to grow to very high cell densities and thus has the potential for large-scale production, particularly for structural analysis. This yeast species also plays an important role in generating high-resolution GPCR crystal structures such as the adenosine A2A and the histamine H1 receptors. Typically, episomal plasmids are used for expression in S. cerevisiae, and the expression cassette is integrated into the genome of P. pastoris. Since the P. pastoris system possesses very strong promoters, only a few gene copies are required to obtain sufficient levels of mRNA. In contrast, in S. cerevisiae, the promoter can be 10- to 100-fold weaker, so the use of episomal plasmids with high copy numbers is required. The strong S. cerevisiae promoter, PGAL1, is induced with galactose while PAOX1 (a very strong P. pastoris promoter) is induced with methanol. However, high mRNA synthesis rates may be countered by high rates of mRNA degradation. Therefore, a suitable balance between mRNA and protein synthesis rates is very critical.
The advantages of our Magic™ protein expression in yeast cells including but not limited to:
Creative Biolabs now offers professional expression and purification service for membrane protein expression in yeast cells. Our scientists will work closely with you to keep you apprised of project progress while taking all your goals into account. We also provide cell-based membrane protein expression service using alternative systems as well as cell-free expression service. Please feel free to inquiry us for a detailed quote.
References
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.