Nuclear receptors (NRs) define a large superfamily of transcription factors that play major functions in eukaryotic cell differentiation, development, reproduction, and metabolic homeostasis. Most of the NRs have been reported to show immunomodulatory properties, making them extremely attractive targets for modifying skin diseases. As a well-recognized supplier in the field of protein engineering, Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive structure-based computational modeling strategies for dermatology research to advance our understanding of NRs and genes they regulate, allowing for the development of high specifically targeted therapeutics.
Skin is known as the largest organ in the body. It is susceptible to environmental stresses, leading to early onset of aging and many other conditions including dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, alopecia, rosacea, and even cancer. Several dermatologic diseases have been characterized by perturbations in the NRs and their natural ligands. For instance, in lesioned psoriatic skin. The NRs in the skin contain the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), Vitamin D receptor (VDR), thyroxin receptor (TR), 9-cis retinoic acid receptors (RXR), retinoic acid receptor (RAR), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR). NR signaling affects keratinocyte proliferation, differentiation, inflammation, and more. These receptors may function either as monomers or dimers.
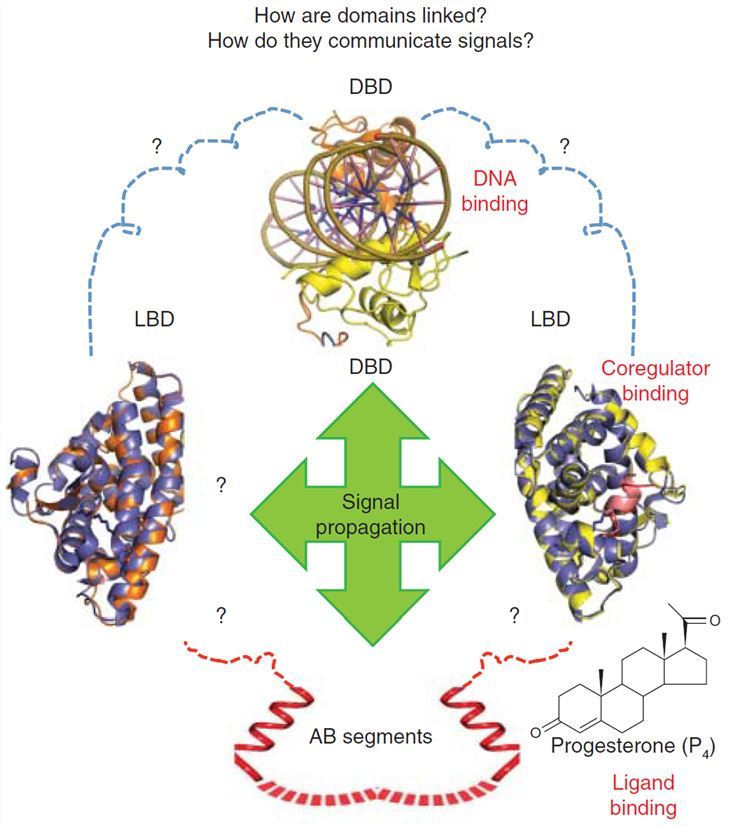 Fig.2 Understanding domain-domain integration in NRs requires structural studies that utilize the complete receptor complexes. (Rastinejad, 2013)
Fig.2 Understanding domain-domain integration in NRs requires structural studies that utilize the complete receptor complexes. (Rastinejad, 2013)
The skin forms a vital barrier between the organism's external environment, offering protection from pathogens as well as various physical and chemical threats. Acute disruption of the skin through physicochemical trauma requires to be repaired timely and efficiently. The NR family of transcriptional regulators has proven to be highly valuable targets for addressing numerous pathologies. Indeed, classic ER group members, such as glucocorticoid, RXR, and VDR, represent mainstay treatments for a number of inflammatory skin disorders. Now, emerging evidence has highlighted critical functional roles for NRs belonging to the adopted and orphan subgroups in skin pathophysiology.
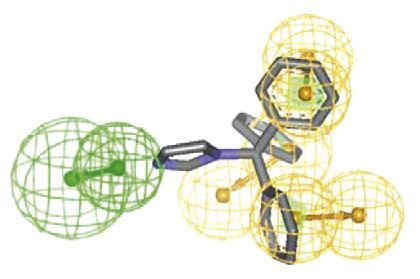
The quality of three-dimensional (3D) models derived from protein sequences gives an independent measure of the suitability of a protein sequence for a certain fold. At Creative Biolabs, our structural biologists could help customers obtain mechanistic insights into how NR proteins are folded and how they recognize their DNA and ligands. The availability of multiple crystal structures is crucial to building useful models in this receptor family. Here, we have used automated structure modeling and model assessment system to identify putative NR-ligand binding domains and listed some common NRs studied in dermatology research.
| GR | VDR | PPARα | PPARγ |
| PPARδ | LXR | NR4A | RXRα |
| RXRβ | RAR | TRα | TRβ |
These proteins are targets for some of the most frequently prescribed medications in dermatology. Advances in this field have updated the knowledge of the mechanisms of NR effects, receptor subtypes, tissue distribution, and interaction with other molecules. We’re focusing on the current understanding of NRs and future directions for NR ligands in dermatology and devote to introducing more powerfully in-silico pharmacology services for the development of therapeutic molecules.
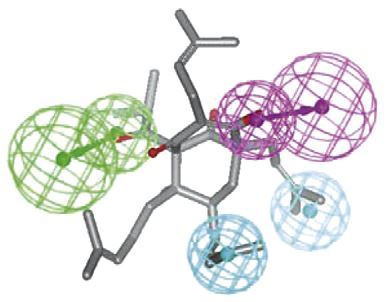
The family of NRs continues to be a rich source of drug discovery targets. Sustained skin pathologies from mild irritations, inflammation through to malignancy considerably impact on morbidity and mortality. As the role of skin in whole-body wellness becomes better described, interest has grown in developing NR target drugs with high safety and efficacy. With expertise in the subject of computational pharmacology, Creative Biolabs has launched structure-based NR modeling strategies using crystal imaging, high-throughput screens, and rational design methods for receptor-ligand design and novel drug discovery. If you’re interested in any service, please don’t hesitate to consult us for more details.
Reference
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.